Frameshift Mutations: Definition, Mechanism, and Examples
Frameshift Mutation Definition
Frameshift mutations occur when nucleotides in the coding region are inserted or deleted, resulting in an altered amino acid sequence during codon translation. A phenotypic alteration, such as the synthesis of an altered protein, may occur from this sort of mutation.
What is Frameshift Mutation?
Frameshift mutation is a form of gene mutation in which the addition or deletion of one or more nucleotides produces a shift in the reading frame of the codons in the mRNA, which can result in an amino acid sequence change during protein translation.
Frame shift mutation is a variant. Reading frame mutation, reading frame shift or framing mistakes are all synonyms for frameshift mutation.
Causes of Frameshift Mutation
The nucleotides of a nucleic acid (such as DNA) can be “read” in groups of non-overlapping, consecutive triplets known as a reading frame. Triplets (or codons) in a reading frame are translated into particular amino acids during translation (or a codon signal).
As a result, if a mutation occurs, such as an insertion or deletion of a nucleotide, the reading frame may be altered. The amino acid sequence is entirely altered. Such changes are known as frameshift mutations (also called reading frame mutation, reading frame shift, or framing error).
The deletion of two nucleotides, which in the above diagram are the nucleotides containing bases, cytosine (C) and guanine (G), has resulted in an erroneous amino acid (G). Glutamate has taken the role of arginine (arg) (glu).
The reading frame is unaffected by the insertion or deletion of nucleotides in multiples of three. As a result, the protein in these situations is likely to have an additional or missing amino acid.
Frameshift mutations are most commonly generated by a mutational mistake during DNA replication or repair. Exposure to acridine dyes, which are capable of causing frameshift mutations, can also cause them. The reading frame of the nucleotide sequence changes due to insertion or deletion (also known as indels) of the nucleotide.
However, the consequences of these mutations vary depending on where they occur. At the interstitial or intercalary location, a nucleotide can be added or deleted.
In certain cases, the insertion and deletion of nucleotides happen at the same time (known as double frameshift), restoring the reading frame to its original state.
A frameshift mutation can cause the whole structure and function of a protein to be lost, resulting in a non-functional polypeptide. However, the phenotypic impact of the mutation will be decided by the resultant codons, post-mutation, and mutation location.
There are three sorts of codons that occur from frameshift mutations;
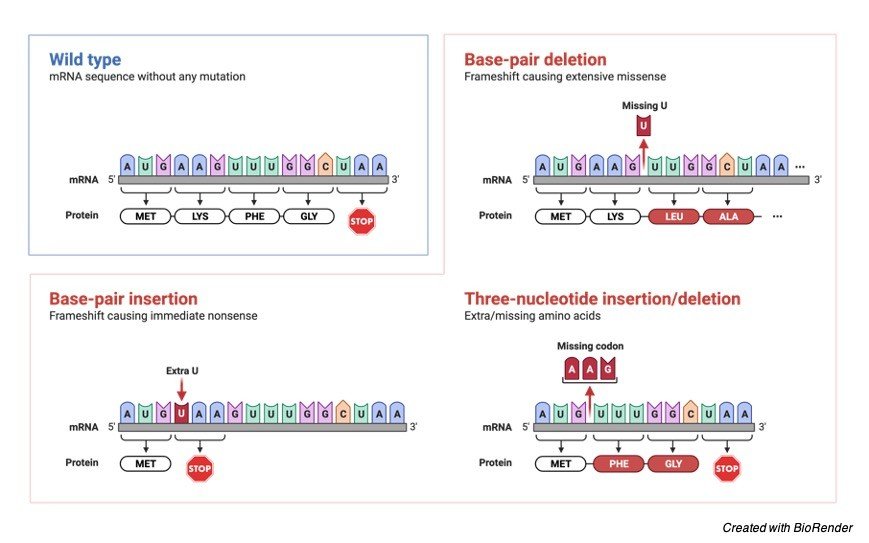
1. Sense Codons: are codons that are read in the same way they were before frameshift mutation.
2. Missense Codons: these are codons that result in the production of an erroneous or different amino acid.
3. Non-sense Codons: these are codons for which no matching tRNA exists, causing the translation process to be truncated.
As a result, frameshift mutations produce an aberrant or faulty protein product with an incorrect amino acid sequence. Such proteins may be entirely new or unusable, depending on where the mutation occurs. A stop codon can also occur from a frameshift mutation. The premature stop codon on mRNA will interrupt the translation process, resulting in a short polypeptide.
The protein may be shorter or longer than the normal protein, depending on the degree and type of the frameshift mutation. Such mutations might arise naturally or as a result of external stressors.
Frameshift mutations are more common in Adenine-Thymine (AT)-rich areas of the nucleic acid, which is an intriguing finding.
Types of Frameshift Mutations
Frameshift mutations can arise when a nucleotide in the nucleic acid is deleted or inserted. A Deletion frameshift mutation occurs when one or more nucleotides in a nucleic acid are deleted, causing a shift in the nucleic acid’s reading frame, or reading frameshift.
Deletion is a more typical method for causing a frameshift mutation, which causes an altered reading frame. (+) 1 frameshift mutation is another name for this mutation.
Insertion frameshift mutation occurs when one or more nucleotides are added to the nucleic acid’s base sequence, causing a shift in the reading frame. The number of nucleotides and the position of nucleotide insertion determine the severity of this sort of frameshift mutation.
The (-) 1 frameshift mutation is another name for this mutation. Understanding frameshift mutations that arise when a nucleotide is inserted or deleted from the usual nucleotide sequence.
Effects of Frameshift Mutations
Frameshift mutations can lead to the following outcomes:
1. A protein with a changed coding sequence may be unusable or a totally different protein. As a result, a variety of metabolic processes may be disrupted.
2. An abrupt halt to the translation process results in non-usable protein, which has ramifications for the physiological systems involved.
3. A frameshift mutation can also lead to cellular translational process abnormalities. The cellular machinery may correct the mistake by upregulating the expression of the mutant gene if no functional protein is produced owing to frameshift mutation. This can cause the cell’s translation machinery to malfunction. As a result, a high number of misfolded proteins may develop, which might be fatal to a cell.
4. However, as seen in HIV patients with frameshift mutations in the chemokine receptor gene, the altered protein might be advantageous and give protection (CCR5).
5. Frameshift mutations cause Crohn’s illness, cystic fibrosis, and some kinds of cancer.
The Genetic Code
The nucleotides encode all of the genetic information in RNA and DNA. A three-nucleotide sequence contains genetic information. Each nucleotide triplet is eventually translated into particular proteins that are necessary for diverse biological activities. There are two crucial stages in the translation of genetic information into protein.
1. Transcription: The genetic information encoded on DNA is “rewritten” on RNA in this process.
2. Translation: In this case, the transcribed RNA is “translated” into a particular amino acid sequence, which finally forms a polypeptide or protein chain.
Discovery of the Genetic Code
The transmission of genetic characteristics in Gregor Mendel’s early genetic studies suggested that genetic information is passed down from generation to generation as a discrete physical and chemical entity. Amino acids were later considered to be genetic information carriers.
The codons or triplets on the DNA sequence were found by scientists including Francis Crick, Sydney Brenner, Leslie Barnett, and Richard Watts-Tobin. Marshall Nirenberg, Heinrich J. Matthaei, and Har Gobind Khorana (1961-1964) discovered and deciphered the nature of a codon.
Reading Frames and Triplet Codon
The whole genome is split into three three-nucleotide segments that do not overlap. The reading frame is defined by the triplet codon that starts the translation process. A particular amino acid or a stop signal known as a codon is encoded by each triplet of the nucleotide. Twenty amino acids are encoded by 64 codon combinations.
However, three of these 64 codons are stop codons, resulting in 61 codons coding for amino acids and three codons coding for the end of the translation process (i.e., 61 codons for amino acids + 3 stop codons = 64 codons).
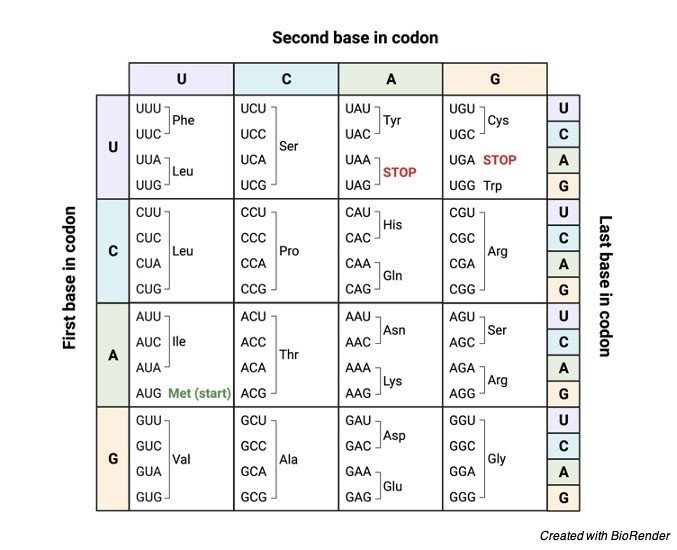
The following are some of the characteristics of a codon:
1. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid during translation. The beginning of amino acid synthesis, as well as methionine synthesis, is encoded by the AUG codon.
2. The three “stop” codons are UAG, UGA, and UAA, which signal the end of amino acid synthesis.
3. Codons are a universal language.
4. The translation process begins with a start codon and continues until the stop codon occurs on mRNA.
From the N-terminus (methionine) to the C-terminus, mRNA is encoded from 5′ to 3′, and it translates into an amino acid in a protein.
Ribosome Translocation
Each codon is converted into an amino acid by mRNA. The ribosomes then link these amino acids together in a process known as ribosome translocation. Protein synthesis is a cyclic process in which the ribosome advances three bases after adding one amino acid to the expanding chain of the polypeptide (i.e., one codon). The function of proteins and polypeptides is disproportionately affected by ribosome mobility.
Frameshift Mutation Examples
Let’s look at a base sequence in RNA that codes as follows to better understand frameshift mutations:
AUG-AAT-AAC-GCU = start-leucine-asparagine-alanine
If an A nucleotide is added or inserted after the start codon AUG as a result of a mutation in the aforementioned sequence, This will alter the reading frame fully:
AUG-AAA-TAA-CGC = start-lysine-isoleusine-alanine
As can be seen, adding only one nucleotide to the RNA sequence entirely changed the base sequence, resulting in the production of completely new amino acids during translation.
Other Examples
The coding sequence for a particular polypeptide is read continuously from the start codon AUG to one of the three stop codons in the reading frame of any mRNA.
The ribosome interprets whichever codons follow the start codon as it travels along the mRNA three bases at a time during translation. The usual reading frame can be disrupted by adding or removing one or two bases (or any other number that is not a multiple of three), resulting in the creation of a fully non-functional protein.
A premature stop codon can also be introduced by frame changes.
Original coding sequence: atggtgcatctgactcctgaggagaagtct
Amino acid translation is M V H L T P E K S
Frameshift: atggtgcctgactccTGAggagaagtct
Amino acid translation is M V P D S * G E V X
Frameshift Mutation Diseases
Mutations are a source of diversity; yet, some mutations are harmful and result in illness. Frameshift mutations have been linked to the following diseases:
1. Tay-Sachs Disease: Tay-Sachs disease is caused by a frameshift mutation in the Hex-A gene. In the absence of Hex-A, aberrant lipid build-up in the brain occurs. The lipids build up in the neurons and finally kill them. This is a deadly illness.
2. Cystic Fibrosis: Cystic fibrosis is caused by two frameshift mutations in the CFTR genes (one involves the insertion of two nucleotides and the other involves the deletion of one nucleotide). The CFTR gene controls the correct passage of ions across cell membranes in the lungs and other organs, such as chloride and sodium. In cystic fibrosis, frameshift mutations cause organ dysfunction, recurrent lung infections, and pancreatic damage.
3. Leigh Disease: The NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 4 (NDUFS4) gene has a frameshift mutation that makes Leigh illness. Leigh illness. Leigh disease is a mitochondrial mutational illness that manifests as a progressive neurodegenerative condition that begins in childhood. The patient had feeding problems, hypotonia, seizures, central respiratory impairment, and failure to thrive in this case.
4. Type A Niemann-Pick Disease: Type A Niemann-Pick disease has been linked to a frameshift mutation in the acid sphingomyelinase gene (fsP330).
5. Crohn’s Disease: A frameshift mutation in the NOD2 gene causes Crohn’s disease susceptibility. The truncated protein NOD2 is produced by cytosine insertion (3020insC), which has been linked to Crohn’s disease.
6. Specific Diseases: frameshift mutations can cause malignancies including lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and hereditary breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancer.
7. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: One of the main causes of sudden death in young adults is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a cardiac myocyte genetic disease. A frameshift mutation in Troponin C induces hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (c.363dupG or p.Gln122AlafsX30).
8. Smith–Magenis Syndrome: caused by an interstitial deletion in the retinoic acid-induced 1 (RAI1) gene. This is an uncommon multiple congenital abnormality or mental retardation condition. Mental retardation, craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities, speech and developmental delays, unique behavioural characteristics, and sleep disruption are all common in these people.
9. Hereditary Polyneuropathy: a dominant-negative frameshift mutation in the LRSAM1 gene causes hereditary polyneuropathy.
Effects of Frameshift Mutations
Frameshift mutations can be advantageous, harmful, or fatal. Induction of frameshift mutation, for example, has been utilised to produce bacteria capable of generating nylonase, a degrading enzyme. Some incidences of albinism have been linked to the premature termination of any of the enzymes required for melanin synthesis.
Various mutations, including frameshift mutations, in the HEXA gene, which codes for the alpha subunit of the lysosomal enzyme beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase A, cause Tay Sachs illness.
Point Mutations vs Frameshift Mutations
Let’s compare and contrast point mutation and frameshift mutation to see how they vary. In point mutation, one base in the nucleotide sequence is replaced by another base. As a result, the nucleotide sequence or nucleic acid reading frame stays unaltered.
Point mutation is also known as single base substitution because of this. Point mutations are divided into two categories: transition and transversion.
Purines and pyrimidines make up DNA. When a purine base is substituted for another purine base, transition point mutation occurs, whereas transversion happens when a pyrimidine or vice versa is exchanged for a purine base.
The insertion or deletion of a base in a frameshift mutation leads to a change in the nucleotide’s reading frame in a nucleic acid.
Frameshift Mutation Citations
- Frameshift mutation, microsatellites and mismatch repair. Mutat Res . 1999 Nov;437(3):195-203.
- Frameshift mutation: determinants of specificity. Annu Rev Genet . 1990;24:189-213.
- Frameshift mutation of UVRAG: Switching a tumor suppressor to an oncogene in colorectal cancer. Autophagy . 2015;11(10):1939-40.
Share