About PhD In Psychology
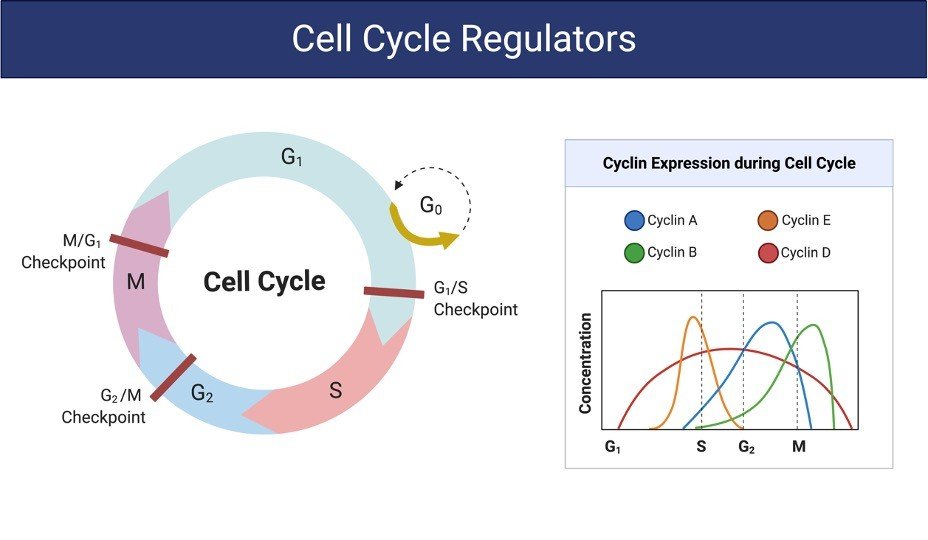
Cell cycle analysis by quantitation of DNA content was one of the fantastic applications of flow cytometry.
The mammalian DNA, yeast, DNA, plant DNA or bacterial DNA can be easily stained by a variety of DNA binding dyes such as propidium iodide.
The premise of these DNA binding dyes is that they are stoichiometric, i.e. they bind in proportion to the DNA amount present in the cell.
In this way if cells are in S phase will have more DNA than cells in G1 phase.
They will take up proportionally more dye and will fluoresce more brightly until they have doubled their DNA content.
The cells in G2 phase will be approximately twice as bright as cells in G1. DNA-binding dyes include propidium iodide (PI), Hoechst 33342, 33258 and S769121, 7-aminoactinomycin-D (7-AAD), DRAQ5™ and DRAQ7™, TO-PRO-3, 4’6’-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI).
In general, cells must be fixed and permeabilized to allow entry of the DNA binding dye which is otherwise actively pumped out by living cells.
Alcohol or aldehyde are commonly used to fix the cells.
Alcohol is a dehydrating fixative which also permeabilizes cells of interest. This will allow easy access of the dye to the DNA and gives good profiles (low coefficient of variation, CV).
The disadvantage of alcohol fixation is that it is often incompatible with fluorescent proteins and some surface markers.
For simultaneously proteins or surface markers examination, use of an aldehyde (cross-linking) fixative, such as paraformaldehyde is more efficient and appropriate.
Aldehyde fixation in cell cycle analysis may lead to poorer quality profiles (higher CVs) but will allow simultaneous detection of other fluorochromes and membrane-bound surface proteins.
Another disadvantage of paraformaldehyde fixation is, generally paraformaldehyde does not permeabilize the cell membrane, and so further sample processing is required.
With fixed cells, samples may be processed, stained and analyzed at the conclusion of an experiment.
Alcohol-fixed cells are stable for several weeks at 4°C and several weeks in -20 °C.
Aldehyde fixed cells are stable for 2 to 3 days. An alternative method to allow the DNA dye into the cells is to permeabilize them with a detergent such as Triton X-100 (0.1%) or NP40 (0.1%).
Usually, it is also necessary to combine a fixation (paraformaldehyde) and permeabilization (Triton X-100) for the intracellular staining.
On the other hand, methods are available, e.g. use of citrate buffers (in combination with detergent), although these are not so widely used.
There are also some dyes that will enter live cells and quantitatively bind to DNA, these include Hoechst 33342, DRAQ5™ (ab108410) and the DyeCycle dyes
Adopted from BioRender
Cell Cycle Assay Reagents
70% Ethanol
Propidium iodide (stock solution 50 µg/ml)
Ribonuclease I (stock 100 µg/ml)
Cell Cycle Assay Procedure
1. Seed appropriate number of cells (e.g. 1.5×105 MDA-MB-231, 1X105 MCF-7, and 1X105 SK-BR-3) in 6 well plates in 2 ml complete media.
Seed less number of cells in control wells if your cells are fast growing like MDA-MB-231 so that they will not die due to over confluence.
Incubate in 5% CO2 incubator for 18-24 hours.
2. When the cells are at 40-50% confluence, discard the media and add 1 ml of serum deprived media (containing 0.5% FBS) to synchronize the cells.
Incubate in 5% CO2 incubator for 6 hours.
3. After this period discard the media and add 1 ml complete media.
Then, treat the cells in same media at different doses of your test compound in triplicates. Make a negative control with no treatment.
Incubate in 5% CO2 incubator for 18-24 hours.
4. Harvest the cells (both dead and live cells) after the incubation period by trypsinizing them (add 500 μL Trypsin per well).
Pool triplicate wells into single 15 ml tube.
Centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes to pellet down.
5. Wash the pelleted cells with 2-3 ml of PBS.
Re-centrifuge the cells at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes.
6. Give second washing with 2-3 ml PBS if necessary.
Again centrifuge cells at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes.
7. Discard the PBS. Gently mix the pelleted cells in the remaining PBS and fix each cell suspension in 1-3 ml of 70% ethanol (depending on the number of cells in the suspension).
8. Keep them at -200C for a minimum of 1 day (although they can stay for up to 2-3 days).
9. Spin down the cells at 1800 rpm for 5 minutes.
Discard the supernatant.
Wash the pellet in 2-3 ml PBS.
Again spin down at 1800 rpm for 5 minutes.
10. Give a second wash with PBS if necessary.
Spin down the cells at 1800 rpm for 5 minutes to remove the traces of ethanol.
Mix the cell pellet in remaining PBS.
11. Make PI-RNase master mix by taking 5μl of PI (2mg/ml stock) and 2μl of RNase (10mg/ml stock) in 300 μl PBS per sample.
12. Add 300 μl of master mix per sample. Mix well.
13. Incubate for 30 minutes in dark at RT.
Transfer to FACS flow tubes. Keep the tubes on ice.
14. Analyse the samples via FACS as soon as possible and interpret using software
Cell Cycle Assay Citations:
Share