Table of Contents
Cellular Respiration Definition
For the production of ATP, molecules like glucose are oxidized, this is called as Respiration. It involves 3 stages and occurs at various positions within the cell. In aerobic as well as anaerobic condition, respiration can take place.
Cellular Respiration Steps
i. Glycolysis
In Glycolysis, a 6C hexose undergoes few steps and gets disintegrated into a 3C compound called the pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm and requires 2 ATP for this process and obtains 2 ATP out of the process. The hydrogen atoms from the glucose are taken by the cytochrome system.
Glucose molecule transforms into pyruvic acid is the last step in anaerobic respiration, however in aerobic condition it is further degraded into Krebs cycle compound. However, when not present it can be transformed to lactic acid.
ii. Krebs Cycle
From a single glucose molecule, more ATP can be created, in aerobic conditions. The pyruvic acid from the cytosol in glycolysis is moved to mitochondria, an organelle which has large area and is somewhat sausage shape and respiration will take place over here.
Pyruvic acid in aerobic condition it is further degraded into Kreb cycle 2C compound. Now the 2C compound will further attach to a 4C compound which is a part of the cycle.
In aerobic respiration, oxygen binds with carbon compound and CO2 is liberated. Thus, this is why animals liberate out CO2. Carbon compounds are oxidized by the enzymes and the hydrogen atom are given to the cytochrome system.
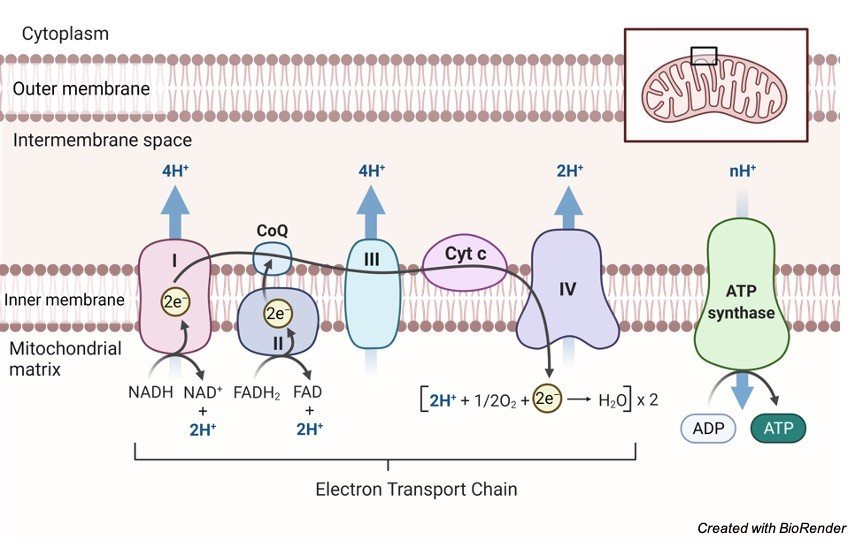
iii. Cytochrome System
The hydrogen carrier system, another name for cytochrome system, is the place where the hydrogen atoms are dispatched from kreb cycle and glycolysis. In the mitochondria is the cristae, where extremely small particles are present in the outer layer. The atoms are collected by the hydrogen acceptors.
The working of cytochrome system is as follows: where the previous coenzymes are consigned to the other coenzymes, which gets oxidized and liberates energy and hydrogen, these hydrogen will attach with the oxygen atoms of the aerobic respiration and will result in the formation of water molecule.
From one single molecule of glucose, 38ATP is gained in aerobic respiration. Glucose is also obtained from the food we consume, which can be utilized during respiration, however the mechanism differs. Through respiration plants also obtain energy.
Cellular Respiration Citations
Share