What is Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)?
Inside the cytoplasm of most creature cells is a broad organization (reticulum) of film restricted channels, aggregately called the endoplasmic reticulum (or ER).
The endoplasmic reticulum is a name gotten from the way that in the light magnifying lens it’s anything but a “net in the cytoplasm.”
The endoplasmic reticulum is just present in the eukaryotic cells. In any case, the event of the endoplasmic reticulum differs from one cell to another.
For instance, the erythrocytes (RBC), egg and undeveloped cells need the endoplasmic reticulum.
Some bit of ER layers stays nonstop with the plasma film and the atomic envelope.
Features of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The membrane of the ER is 50 to 60 Aº thickness and liquid mosaic like the unit layer of the plasma film.
They are found to contain numerous sorts of compounds that are required for different significant manufactured exercises.

The main catalysts are the stearases, NADH-cytochrome C reductase, NADH diaphorase, glucose-6-phosphatase, and Mg++ enacted ATPase.
The layer of endoplasmic reticulum stays persistent with the films of the plasma layer, membrane, and Golgi apparatus.
The hole of the ER is all around created and goes about as a section for the secretory items.
Structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum
The ER may happen in the accompanying three structures: Lamellar structure or cisternae, Vesicular structure or vesicle and cylindrical structure or tubules.
I. The Cisternae
RER normally exists as cisternae that happen in those cells which have engineered jobs as the cells of the pancreas, notochord, and cerebrum.
The cisternae are for some time, smoothed, sac-like, unbranched tubules having a breadth of 40 to 50 μm.
They stay orchestrated parallelly in packs or stakes.
II. The Vesicles
The vesicles are oval; layer bound vacuolar structures having a distance across of 25 to 500 μm.
They frequently stay secluded in the cytoplasm and happen in many cells yet particularly bountiful in the SER.
III. The Tubules
The tubules are fanned designs shaping the reticular framework alongside the cisternae and vesicles.
They normally have a measurement from 50 to 190 μm and happen practically in every one of the cells.
Cylindrical type of ER is frequently found in SER and is dynamic in nature, i.e., it is related with film developments, splitting and combination between layers of cytocavity organization.
It might be unpleasant or smooth. The external surface of harsh ER has appended ribosomes, while smooth ER doesn’t have connected ribosomes.
The ER goes about as secretory, stockpiling, circulatory and sensory system for the cell. It is likewise the site of the biogenesis of cellular films.
Types of Endoplasmic Reticulum
I. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
They are likewise called as the agranular endoplasmic reticulum. This kind of endoplasmic reticulum has smooth surfaces in light of the fact that the ribosomes are not joined to its layers.
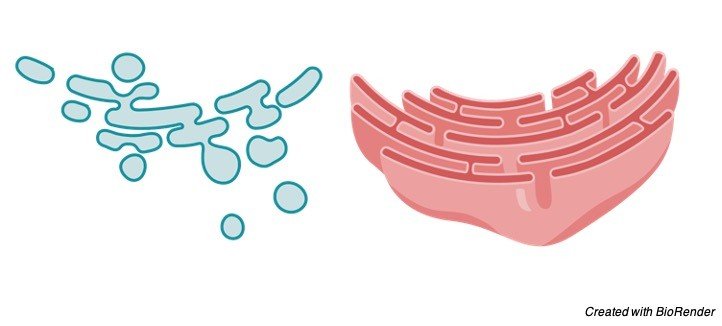
The smooth kind of endoplasmic reticulum happens generally in those cells, which are associated with the digestion of lipids (counting steroids) and glycogen.
Eg. fat cells, interstitial cells, glycogen putting away cells of the liver, conduction filaments of heart, spermatocytes, and leucocytes.
II. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
It has harsh walls on the grounds that the ribosomes stay connected to its layers. On their films, RER contains certain ribosome explicit, transmembrane glycoproteins, called ribophorins I and II, to which are joined the ribosomes while occupied with polypeptide union.
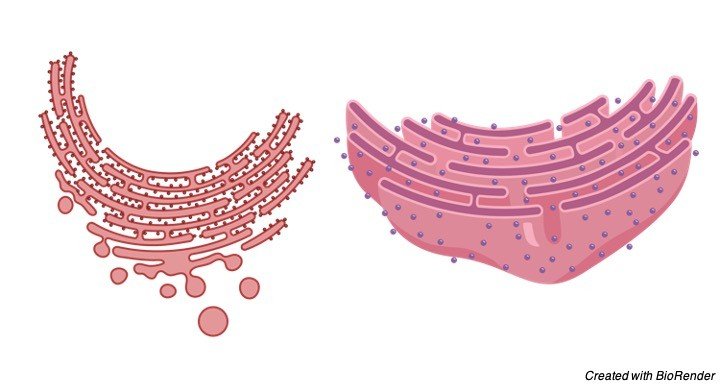
The unpleasant sort of ER is discovered plentifully in those cells which are dynamic in protein combinations like pancreatic cells, plasma cells, cup cells, and liver cells.
Function of Endoplasmic Reticulum
Elements of smooth ER incorporate lipid digestion (both catabolism and anabolism; they blend an assortment of phospholipids, cholesterol, and steroids).
Glycogenolysis (corruption of glycogen; glycogen being polymerized in the cytosol).
Medication detoxification (by the assistance of the cytochrome P-450). The endoplasmic reticulum gives a ultrastructural skeletal structure to the cell and gives mechanical help to the colloidal cytoplasmic network.
The trading of molecules by the cycle of assimilation, dispersion and dynamic vehicle happens through the layers of the endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum is the primary part of the endomembrane framework, additionally called the cytoplasmic vacuolar framework or cytocavity organization.
The endoplasmic layers contain numerous catalysts that perform different engineered and metabolic exercises.
Further, the endoplasmic reticulum gives an expanded surface to different enzymatic responses.
The endoplasmic reticulum goes about as an intracellular circulatory or shipping framework.
As a developing secretory polypeptide rises out of the ribosome, it goes through the RER film and gets aggregated in the lumen of RER.
Here, the polypeptide chains go through fitting, development, and sub-atomic collapsing to frame practical auxiliary or tertiary protein molecules.
RER squeezes off certain little protein-filled vesicles which at last get melded to cis Golgi.
The ER layers are found to lead intra-cellular driving forces. For instance, the sarcoplasmic reticulum communicates driving forces from the surface layer into the profound district of the muscle filaments.
The ER layers structure the new atomic envelope after each atomic division.
The SER contains a few key catalysts that catalyse the union of cholesterol which is likewise a forerunner substance for the biosynthesis of two sorts of mixtures—the steroid chemicals and bile acids.
RER additionally blend layer proteins and glycoproteins which are co-translationally embedded into the unpleasant ER layers.
In this manner, the endoplasmic reticulum is the site of the biogenesis of cellular layers.
Significance of Endoplasmic Reticulum
i. Transport of Materials: The ER works with transport of materials starting with one piece of the cell then onto the next accordingly framing the cell’s circulatory framework.
ii. Arrangement of Desmotubule: Tubular augmentation, called desmotubule, reaches out through plasmodesmata to make ER persistent in the two contiguous plant cells. Backing The ER goes about as an intracellular supporting system, the cytoskeleton that likewise keeps up with the type of the cell.
iii. Confinement of Organelles: It keeps the cell organelles appropriately positioned and dispersed according to one another.
iv. Surface for Synthesis: The ER offers broad surface for the blend of an assortment of materials.
v. Capacity of Materials: The ER gives space to impermanent capacity of manufactured items like proteins and glycogen. The ER helps in the trading of materials between the cytoplasm and the core.
vi. Area of Enzymes: An assortment of catalysts is situated in the ER to catalyse the biochemical responses.
Endoplasmic Reticulum Citations
- The endoplasmic reticulum: structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci . 2016 Jan;73(1):79-94.
- Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling – from basic mechanisms to clinical applications. FEBS J . 2019 Jan;286(2):241-278.
- Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2007 Jul;8(7):519-29.
- Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature . 2016 Jan 21;529(7586):326-35.
Share