What is Endospore Formation?
o An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by Gram-positive bacteria which forms when a bacterium produces a thick internal wall that encloses its DNA and part of its cytoplasm.
o Remember that Gram + bacteria produce endospores.
o The primary function of most endospores is to ensure the survival of a bacterium through periods of environmental stress.
o They are therefore resistant to ultraviolet and gamma radiation, desiccation, lysozyme, temperature, starvation, and chemical disinfectants.
Endospore Formation
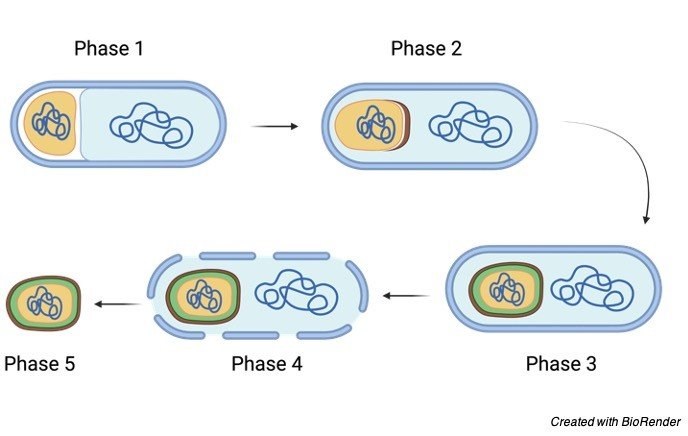
Endospore Formation Steps
o In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall.
o One side then engulfs the other side.
o The chemistry of the cell wall of the engulfed bacterium changes slightly to form the cortex of the endospore.
o Several protein layers lie over the cortex to form the resistant structure called the spore coat.
o A delicate covering called the exosporium, sometimes surrounds the spore coat.
oThe outer cell then lyses, releasing the dormant endospore.
o The endospore must be activated before it can be germinated and grow.
o Activation usually involves heat.
o Germination is triggered by nutrients.
Endospore Formation Citations
Share