What is Gel Electrophoresis?
Before knowing about Gel electrophoresis, let us know few basics of what electrophoresis is?
Electrophoresis is a process used for the separation of macro and micro molecules in an electric field by applying charges at both the extents.
The mixture of substances is spread in the supporting film. The supporting films are placed in a salt solution filled in a container, where one container holds a cathode and the other carries an anode.
When the electric current is allowed to pass through this field, negatively charged molecules move towards the anode and positively charged molecules move towards the cathode.
Depending on the type of supporting films, they are classified as different types of electrophoresis. The supporting films may be of paper, agar, gel or starch.

Horizontal Gel electrophoresis
Depending on the type of substances to be separated the type of electrophoresis varies.
Moving boundary electrophoresis and Gel electrophoresis is used for the separation of proteins.
Discontinuous electrophoresis is used for the separation of proteins from plasma membrane.
SDS-PAGA (Sodium dodecyl Sulphate – Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is used for the separation of macro molecules according to their size like membrane proteins and protein element of cytoskeleton.
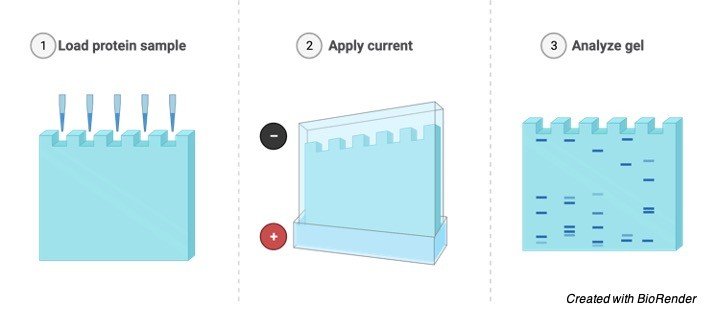
Vertical Gel electrophoresis
The rate of Migration of molecules in an electric field can be calculated according to the size and number of groups of charged particles in one molecule, Electrophoresis is used for the separation of proteins, amino acids and nucleic acids.
Application of Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is used for the separation of proteins such as DNA, RNA and other macromolecules depending on their size and charge of the particles.
As mentioned above it is technique where the gel containing the molecules is allowed to run on the electric field where current is passed through and the molecules will be separated depending on the size and charge by passing at different directions with different speed which helps them to separate accordingly.
Considering all the molecules have the same amount of charge so it can be separated by gel electrophoresis by considering their size.
Now let us know how the DNA fragments are separated even though they have the same size relatively depending upon their fragments.
We can measure the absolute size of the DNA by comparing it with the standard yard stick which is being made up of known sizes of DNA fragments,
Principle of Gel Electrophoresis
This technique is generally known as gel electrophoresis because the supporting film is made up of jelly like substance which is made up of Polysaccharide named agarose.
It is usually in a powdered dry form as flakes and it can be converted into a gel form by heating in a buffer solution containing water and some kind of salts and further it is allowed to cool so that it forms like a solid slimy gel.
When considering the gel at molecular level it is seen that the agarose molecules present in it are held together by hydrogen bonds with minute pores in it.
At the end of the supporting film two well like depressions are seen where the samples are kept to undergo the test.
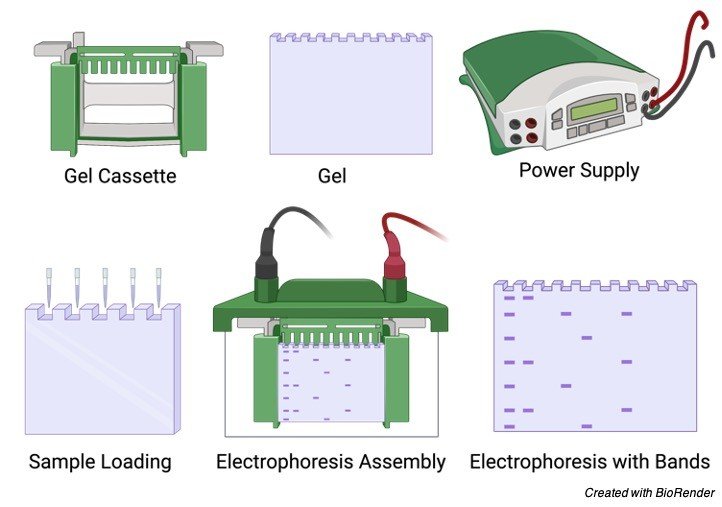
The prepared gel is then placed in a gel box and the samples are added or kept in the well and the positive electrodes are placed at one end of the gel box and the negative electrode in the opposite direction.
Then the salt solution which helps in conducting the current is poured on the gel which is being placed in a gel box.
This forms a glassy layer over the gel. The end of the box where wells are present is marked as negative electrode and the other side without wells is considered as positive electrode.
Gel Electrophoresis Samples
Once the gel is placed in the gel box, the samples are being loaded in the wells, one well is kept consigned for DNA ladder, which is the known length of DNA fragments, these ladders can be purchased commercials according to our size and needs.
Considering an example of PCR reaction here, after loading the DNA ladder, in one well, the samples needed for the pcr reaction is loaded in the remaining wells and the gel box is switched on and the current is allowed to flow through the gel box.
As the DNA molecules contain a sugar phosphate group, they carry a negative charge and started moving towards the positive charge.
Maximum of 80 to 120 V is used to run the gel, more than this high voltage is not recommended as it allows the gel to melt even though it coordinates in faster moving.
Once the gel is allowed to run the smaller DNA fragments flows faster while the larger ones does not move and stays near the wells.
Visualization
Sample (DNA, RNA or Proteins) fragments are thus separated by size of the particles accordingly.
Small particles are found at the end of the gel and larger particles near the wells.
To examine the size of the bands that are found on it, this process is being carried out by staining the gel with staining dye for e.g. DNA-Staining dye and by placing it under the uv light.
The bands start glowing and thus allowing us to see the location of the DNA throughout the gel.
Band mentioned here is nothing but a well-defined line that runs along the DNA, where each band contains large number of fragments of DNA with same sizes.
A band is necessary for the visualization of DNA because they are not visibly seen as such lying on the gel.
Thus, the band helps us to determine the size of their fragments depending upon their location on the band.
Gel Electrophoresis Citations
- Understanding gel electrophoresis. Nature . 1990 May 31;345(6274):381.
- Introduction to Protein Electrophoresis. Methods Mol Biol . 2019;1855:23-29.
- High Sensitivity Protein Gel Electrophoresis Label Compatible with Mass-Spectrometry. Biosensors (Basel) . 2020 Oct 31;10(11):160.
- Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Curr Protoc Immunol . 2005 Nov;Chapter 8:Unit 8.5.
- Ultrarapid Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Mini-Gel Electrophoresis. Methods Mol Biol . 2019;1855:491-494.
Share









