What is Haemophilia?
Haemophilia is one kind of inherited genetic disorder. This is the condition where body does not have the capability to clot the blood cells during a case of an injury or any other accidents.
This leads to the higher risk in people due to its blood accumulation in the joints or at the central nervous system.
The individuals who are not suffering so much and has only mild symptoms after an injury or an accident does not cause any serious issues.
Where as bleeding in joints results in permanent damage to the bone cells or cartilage, and bleeding in brain can cause severe headache, seizures, unconsciousness and some times it may also lead to mortality of an individual.
Types of Haemophilia
Haemophilia is generally classified into two types based on the clotting factors such as follows;
Haemophilia A occurs due to a condition where there is a production or synthesis of low amount of clotting factor VIII.
Haemophilia B is caused due to the low production of clotting factor IX.
This is considered as an inherited disorder because they are passed down from their parents where the parent carrying X chromosome with defects passes the defected X chromosome to an offspring.
It is rare that the person is affected by his self without carrying inherited gene due to the result of mutation or any other defects in the chromosome or this may also happen when the self-antibodies are reacting against the body’s own clotting factors.
The other type which is said to be haemophilia C is due to the lower levels of clotting factor X and the other type known as Para haemophilia, which is due to the minimal amounts of clotting factor V.
The haemophilia which are due to acquired conditions causes cancers, autoimmune disorders etc.
To find the ability of blood to clot is the only source of diagnosis for this disorder.
Characteristics of Haemophilia
Most of the sex-linked genes are present on the X chromosome because for a simple reason that X chromosomes are larger than Y chromosomes.
Haemophilia is also an X-linked disorder, it is a type of bleeding disease which is due to the absence of clotting factors in the blood.
People who are affected with this condition have a long day bleeding or oozing of blood from the place of injury or surgery or even when the tooth is picked off.
When haemophilia undergoes a serious condition, it leads to continuous bleeding even when we met with small minor injuries, these may also result in the bleeding of joints and muscles, brain or other internal organs.
This above condition happens often in haemophilia A which is also known as classic haemophilia or factor VIII deficiency and haemophilia B condition is referred to as factor IX deficiency or Christmas disease.
These two types are almost similar in showing their symptoms and both are inherited through X- linked inherited recessive pattern.
The genes responsible for this condition are located on the X chromosome which is one of the types of allosome.
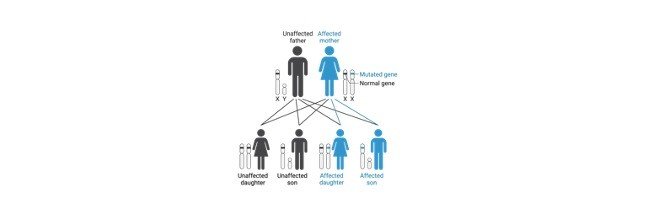
As males have only one X chromosome passing of one defective allele or mutation in one of the alleles in X chromosome can cause this condition easily, where as the females have two X chromosomes in their allosomes; So it is necessary for a female individual that both the chromosomes to get mutated or inherited to get this condition.
If only one of the chromosomes has got mutated then the respective female is considered as carrier female.
This is the reason why males are affected more than the females. It is also because the fathers do not pass the X-linked traits to their son is also to be considered.
The below graph shows how the haemophilia is being inherited.

How to Prevent Haemophilia?
We know that since it is an inherited disorder there is no chances of preventing this condition, but it can be diagnosed before the child has been given birth by the process of amniocentesis.
Where the parents are led to under a counselling to understand the risks of having a baby with this disorder and it is left to their decision whether to brought up a child carefully or terminate it.
It is the better option to consult a physician if the parents are grandparents have the condition of haemophilia. So they can come to know the results earlier.
According to research it is said that if 50 percentage if chance where the son will have haemophilia and the other 50 percentage chance is that his daughter will be carrier.
Symptoms of Haemophilia
Usually, the symptoms are based on levels of clotting factors that is present in our blood, which are responsible for clotting the blood after bleeding due to an injury or an accident.
These factors are identified during any surgical operations or while overcoming an injury with bleeding.
Symptoms of spontaneous bleeding include large and deep bruises joint pain along with swelling, unexplained bleeding and bruises, sometimes there may also a blood in urine or stools.
Nose bleeds often without having an appropriate reason, excessive bleeding and pain in the gums of the teeth and bleeding may occurs often after vaccinations.
Haemophilia Citations
Share