Krebs Cycle or TCA Cycle
Krebs Cycle or TCA Cycle is an aerobic process, occurs in the cytoplasm for prokaryotes, mitochondrial matrix for eukaryotes.
The process of ATP production in the Krebs cycle is called Substrate-level phosphorylation
Krebs Cycle or TCA Cycle
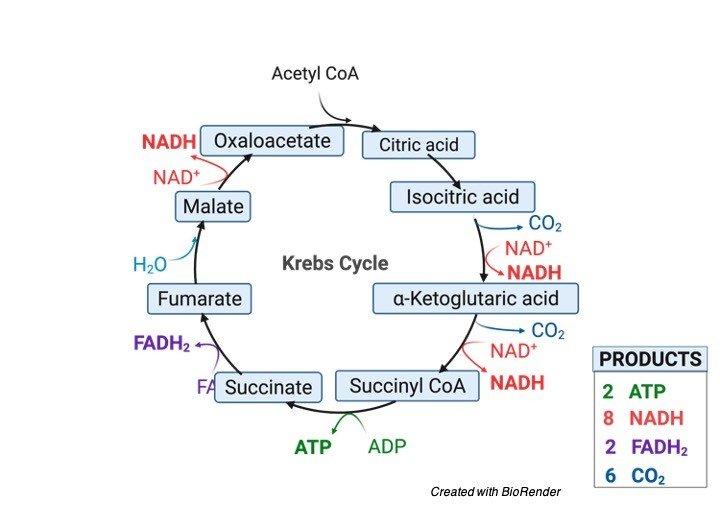
Total:
⊛ 4 CO2 produced
⊛ 2 GTP/ATP produced
⊛ 6 NADH produced (making 18 ATP in ETC)
⊛ 2 FADH2 produced (making 4 ATP in ETC)
"Each turn in the Krebs Cycle produces (1 glucose provides two turns)"
⊛ 2 CO2 produced
⊛ 1 GTP/ATP produced
⊛ 3 NADH produced (making 9 ATP in ETC)
⊛ 1 FADH2 produced (making 2 ATP in ETC)
Krebs Cycle or TCA Cycle Regulation
⊛ The cycle is regulated at the three steps that are highly exergonic: those catalyzed by citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and a- ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
⊛ NADH and ATP are both negative regulators; ADP and Ca2+are positive regulators (activators).
⊛ Triglycerides can also be catabolized for ATP. Fatty acids are converted to acyl CoA along the outer membrane of the mitochondrion and endoplasmic reticulum at the expense of 1 ATP. Then 2 carbons are cleaved to make acetyl CoA in the matrix. This reaction also produces FADH2 and NADH for every two carbons taken from the original fatty acid. Acetyl CoA then enters into the Krebs cycle as usual. This is called beta oxidation.
⊛ The fatty acids are linked to Coenzyme A and carried into the mitochondrial matrix by the g-amino acid L-carnitine. They are then are oxidized TWO carbons at a time in the KREB cycle, yielding an NADH, FADH2, and acetyl CoA.
⊛ Amino acids are deaminated in the liver. The deaminated product is either chemically converted to pyruvic acid or acetyl CoA, or it may enter the Kreb cycle at various stages depending upon which amino acid was deaminated.
Krebs Cycle or TCA Cycle Citations
Share