Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
The Epstein Barr Virus (EBV), additionally called Human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4), is a virus of the herpes family (which incorporates Herpes simplex virus and Cytomegalovirus) and is perhaps the most widely recognized viruses in people.
The vast majority become tainted with EBV, which is regularly asymptomatic however ordinarily causes irresistible mononucleosis.
EBV is named after Michael Epstein and Yvonne Barr, who along with Bert Achong, found the virus in 1964.
Structure of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
Like other herpesviruses, Epstein Barr virus (EBV) has a toroid-formed protein center that is wrapped with DNA, a nucleocapsid with 162 capsomers, a protein covering between the nucleocapsid and the envelope and an external envelope with outer glycoprotein spikes.
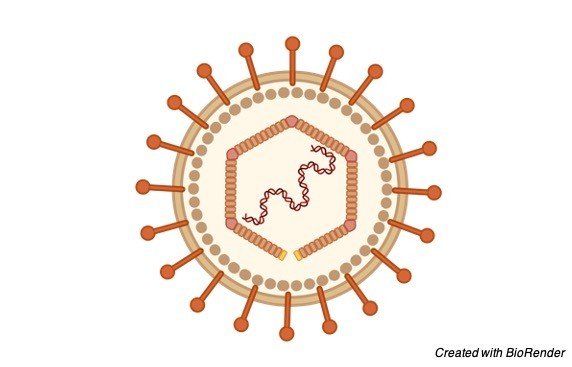
The significant EBV capsid proteins are 160, 47 and 28 kDa, comparable in size to the significant capsid proteins of herpes simplex virus. The most plentiful EBV envelope and covering proteins are 350/220 and 152 kDa, separately.
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) Infection
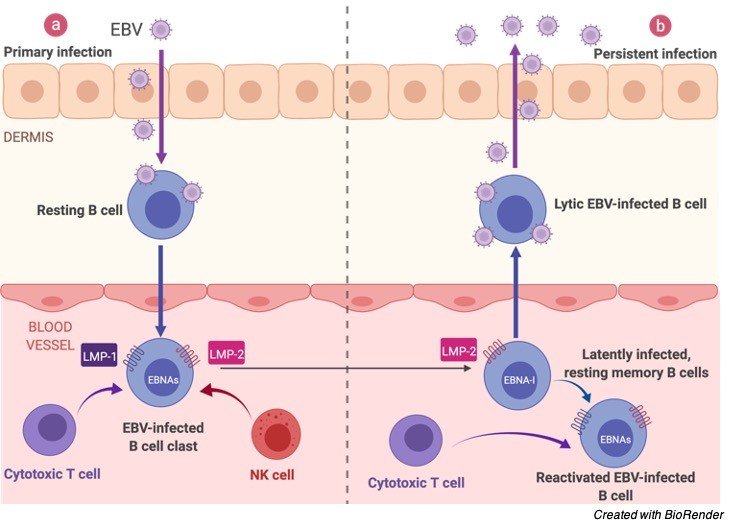
On contaminating the B-lymphocyte, the straight virus genome circularizes, and the virus therefore perseveres inside the cell as an episome.
The virus can execute numerous unmistakable projects of gene articulation which can be comprehensively classified as being lytic cycle or idle cycle.
The lytic cycle or useful disease brings about arranged articulation of a large group of viral proteins with a definitive goal of creating irresistible virions. Officially, this period of disease doesn’t unavoidably prompt lysis of the host cell as EBV virions are created by growing from the tainted cell.
The inactive cycle (lysogenic) programs are those that don’t bring about creation of virions. An exceptionally restricted, unmistakable arrangement of viral proteins are delivered during inactive cycle contamination.
These incorporate Epstein-Barr atomic antigen (EBNA)- 1, EBNA-2, EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, EBNA-3C, EBNA-pioneer protein (EBNA-LP) and dormant layer proteins (LMP)- 1, LMP-2A and LMP-2B and the Epstein-Barr encoded RNAs (EBERs).
Also, EBV codes for no less than twenty microRNAs which are communicated in inactively contaminated cells.
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) Gene Structure
From investigations of EBV gene articulation in refined Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines, no less than three projects exist:
EBNA1 just (bunch I)
EBNA1 + EBNA2 (bunch II)
Dormant cycle proteins (bunch III).
It is additionally hypothesized that a program in which all popular protein articulation is stopped exists. At the point when EBV contaminates B-lymphocytes in vitro, lymphoblastoid cell lines in the long run arise that are equipped for endless development.
The development change of these cell lines is the outcome of viral protein articulation. EBNA-2, EBNA-3C and LMP-1 are fundamental for ‘change’ while EBNA-LP and the EBERs are not.
The EBNA-1 protein is fundamental for support of the virus genome. It is proposed that after normal contamination with EBV, the virus executes a few or the entirety of its collection of gene articulation projects to build up a diligent disease.
Given the underlying shortfall of host invulnerability, the lytic cycle creates a lot of viruses to contaminate other (probably) B-lymphocytes inside the host.
The dormant projects reinvent, and sabotage tainted B-lymphocytes to multiply and carry contaminated cells to the destinations at which the virus apparently endures.
Ultimately, when have resistance creates, the virus continues by winding down most (or conceivably the entirety) of its genes, just sometimes reactivating to deliver new virions.
An equilibrium is ultimately struck between intermittent viral reactivation and host insusceptible observation eliminating cells that actuate viral gene articulation.
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) Infection Cycle
The site of industriousness of EBV might be bone marrow. EBV-positive patients who have had their own bone marrow supplanted with bone marrow from an EBV-negative giver are discovered to be EBV-negative after transplantation.
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) Inactive Antigens
All EBV proteins are created by elective joining of a record beginning at either the Cp or Wp advertisers at the left finish of the genome (in the regular terminology).
The genes are requested EBNA-LP/EBNA-2/EBNA-3A/EBNA-3B/EBNA-3C/EBNA-1 inside the genome.
The inception codon of the EBNA-LP coding area is made by a substitute join of the atomic protein record. Without this commencement codon, EBNA-2/EBNA-3A/EBNA-3B/EBNA-3C/EBNA-1 will be communicated relying upon which of these genes is on the other hand grafted into the record.
EBNA-1
EBNA-1 protein ties to a replication beginning (oriP) inside the viral genome and intercedes replication and parceling of the episome during division of the host cell.
It is the solitary viral protein communicated during bunch I idleness. EBNA-1 has a glycine-alanine rehash that hinders antigen handling and MHC class I-confined antigen show in this manner restraining the CD8-limited cytotoxic T-cell reaction against virus tainted cells.
EBNA-1 was at first recognized as the objective antigen of sera from rheumatoid joint inflammation patients (rheumatoid joint pain related atomic antigen; RANA).
EBNA-2
EBNA-2 is the fundamental viral transactivator, changing record from the Wp advertisers utilized during at first after contamination to the Cp advertiser.
Along with EBNA-3C, it likewise initiates the LMP-1 advertiser. It is known to tie the host RBP-Jκ protein that is a central member in the Notch pathway. EBNA-2 is fundamental for EBV-intervened development change.
EBNA-3A/EBNA-3B/EBNA-3C
These genes additionally tie the host RBP-Jκ protein.
EBNA-3C
EBNA-3C is additionally a ubiquitin-ligase and has been displayed to target cell cycle controllers like pRb.
LMP-1
LMP-1 is a six-length transmembrane protein that is additionally fundamental for EBV-intervened development change. LMP-1 intervenes motioning through the Tumor rot factor-alpha/CD40 pathway.
LMP-2A/LMP-2B
LMP-2A/LMP-2B are transmembrane proteins that demonstration to obstruct tyrosine kinase flagging. It is accepted that they act to repress enactment of the viral lytic cycle.
It’s obscure whether LMP-2B is needed for EBV-intervened development change, while various gatherings have detailed that LMP-2A then again is, or alternately isn’t required for change.
EBER-1/EBER-2
EBER-1/EBER-2 are little RNAs of an obscure job. They are not needed for EBV-intervened development change.
miRNAs
EBV microRNAs are encoded by two records, one set in the BART gene and one set close to the BHRF1 bunch. The three BHRF1 miRNAS are communicated during type III dormancy while the enormous group of BART miRNAs (up to 20 miRNAs) are communicated during type II inertness. The elements of these miRNAs are at present obscure.
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) Surface Receptors
The Epstein-Barr Virus surface glycoprotein H (gH) is fundamental for infiltration of B cells yet in addition assumes a part in connection of virus to epithelial cells.
In lab and creature preliminaries in 2000, it was shown that both opposition of RA-intervened development restraint and advancement of LCL expansion were productively switched by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) bad guy RU486.
Sicknesses Related With Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
• Irresistible states
• Irresistible mononucleosis
• Stevens-Johnson condition
• Hepatitis
• Herpes
• Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (otherwise called Kikuchi’s infection)
Diseases Caused by Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
• Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, including essential cerebral lymphoma
• Hodgkin’s infection • hairy leukoplakia
• Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
• Smooth muscle tumors
• Immunocompromised/stifled states: Normal variable immunodeficiency
Summary Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
Much of the time of irresistible mononucleosis, the clinical conclusion can be produced using the trademark group of three of fever, pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy going on for 1 to about a month.
Serologic test outcomes incorporate an ordinary to reasonably raised white platelet tally, an expanded complete number of lymphocytes, more prominent than 10% abnormal lymphocytes, and a positive response to a “mono spot” test.
In patients with manifestations viable with irresistible mononucleosis, a positive Paul-Bunnell heterophile immunizer test result is demonstrative, and no further testing is essential.
Moderate-to-undeniable degrees of heterophile antibodies are seen during the principal month of ailment and decline quickly after week.
Bogus positive outcomes might be found in few patients, and bogus adverse outcomes might be acquired in 10% to 15% of patients, fundamentally in youngsters more youthful than 10 years old.
Genuine episodes of irresistible mononucleosis are amazingly uncommon. At the point when “mono spot” or heterophile test results are negative, extra research center testing might be expected to separate EBV contaminations from a mononucleosis-like sickness prompted by cytomegalovirus, adenovirus, or Toxoplasma gondii.
Direct recognition of EBV in blood or lymphoid tissues is an examination instrument and is not accessible for routine determination.
All things considered; serologic testing is the technique for decision for diagnosing disease.
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) Citations
- Epstein Barr virus strains and variations: Geographic or disease-specific variants? J Med Virol . 2017 Mar;89(3):373-387.
- Epstein Barr virus (EBV) status in colorectal cancer: a mini review. Hum Vaccin Immunother . 2019;15(3):603-610.
- Epstein Barr virus strain variation and cancer. Cancer Sci . 2019 Apr;110(4):1132-1139.
- Epstein Barr Virus. Microbiol Spectr . 2016 Jun;4(3).
- Epstein Barr virus (EBV) reactivation and therapeutic inhibitors. J Clin Pathol . 2019 Oct;72(10):651-658.
Share