Category: Biology
-

Amphibolic Pathway: Definition and Example I Research...
Continue ReadingWhat is Amphibolic Pathway?
Survival of the organism depends on the nutrient uptake from the environment and complete utilization of nutrients.
This process is vital and forms a dynamic nature of the cell. The conversion of external nutrient to an internal biomolecule is a main function of any biosystem present and is achieved through the process of metabolism.
Metabolism is the process by which nutrient are converted to desirable products for synthesis and breakdown of biochemical components
"A pathway which participates in Catabolism and anabolism is termed as amphibolic pathway"
Metabolism is otherwise termed as Catabolism + Anabolism. Catabolism is a process of breaking down of Complex food molecules to simpler compounds.
Anabolism is mainly concerned with the biosynthesis of Chemical compounds which are essential for storage and other functions from smaller molecules.
Synthesis (Anabolism) and degradation (Catabolism) of any biomolecule takes place in a series of process which are distinct in its own mechanism and have specific pathway.
But there are certain pathways which can act both catabolic an anabolic under appropriate circumstances.
A pathway which participates in Catabolism and anabolism is termed as amphibolic pathway.
Amphibolic Pathway involves many intermediates which forms new compounds (biosynthesis) such as amino acid, fats, glucose etc., or they get oxidized to produce energy.
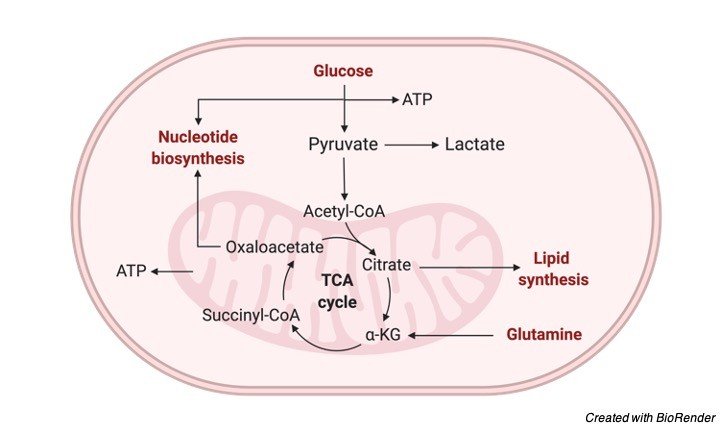
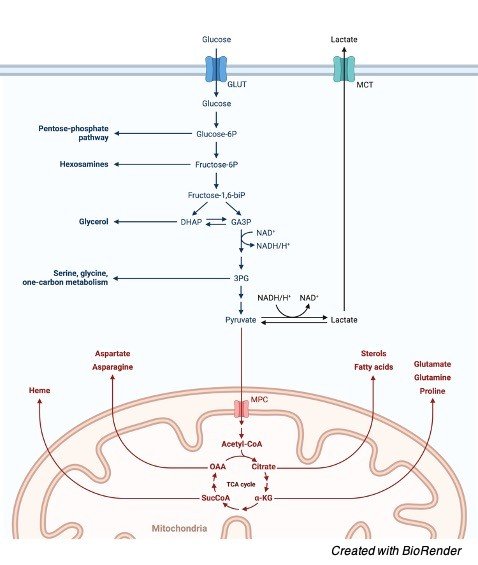
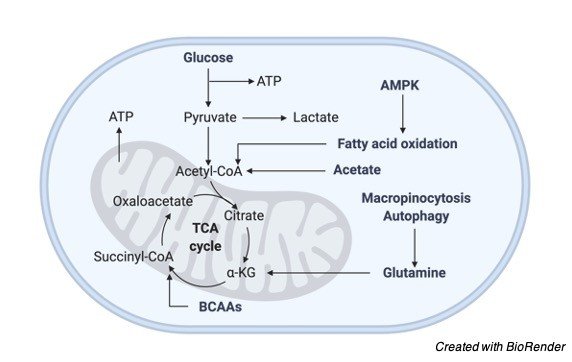
An ideal example for Amphibolic Pathway is the CITRIC ACID CYCLE. The citric acid cycle is Amphibolic because it oxidizes Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins to yield energy and it is the common oxidative pathway for any biochemical compound.
Any biochemical degradation either directly yields acetyl Co – A or through pyruvate and other components of citric acid cycle.
Similarly, the intermediates from the citric acid cycle becomes precursor for the synthesis of Glucose, fats, Amino Acid etc.,
The catabolism and anabolism of the intermediates present in the citric cycle depends upon the internal cues of the body.
Internal cues can be the requirement of synthesis or breakdown of a compound and is dependent on many other factors.
Amphibolic Pathway Characteristics
The main characteristics of amphibolic pathway is the involvement of both catabolic and anabolic pathway and Citric Acid Cycle becomes an ideal cycle to understand the Amphibolic Pathway

Catabolic Nature of Citric Acid Cycle
In cellular respiration, citric acid cycle is the common oxidative pathway where the Acetyl Co – A breakdown yielding NADH, FADH and ATP in plants GTP in Animals.
The basic biological compound namely Proteins, Fats and Glucose oxidizes to form Acetyl Co – A directly or through Pyruvate enters the common pathway of oxidation.
From the basic cellular respiration, we know that the substrates of Citric Acid Cycle are not completely derived from glycolysis but the amino acids and lipids also contribute to the substrate.
Catabolic activities of citric acid cycle are,
1. Oxidation of Glucose
2. Transamination of Amino Acids
3. Oxidation of Fatty acids
Glucose is broken down to pyruvate by Glycolysis.
Fatty Acids on Beta – Oxidation provides Acetyl Co – A directly
Amino Acid Catabolism
Essential and non – essential amino acids are present in body for the proper functioning of the living system.
Among all of them each amino acids do not form acetyl Co – A directly.
Few forms other intermediates of the Citric Acid Cycle by the process of Transamination or Aminotransferase. The Aminotransferase reaction involves the transfer of alpha – amino group from the carbon skeleton and transforming the skeleton to Amphibolic intermediate to produce energy.
Few amino acids oxidize to become pyruvate and Acetyl Co -A also.
For example:
I. Glutamine is transformed to Glutamate with enzyme involving Glutaminase. Glutamate then by transamination becomes alpha – ketoglutarate.
II. Similarly, Asparagine becomes Aspartate on transamination’s yields oxaloacetate and Certain Amino acids like alanine, Serine etc., directly oxidizes to produce pyruvate
Anabolic Nature of Citric Acid Cycle
Biosynthesis of glucose, fatty Acids, Amino Acids, Nucleic Acids are produced from the intermediates of the Krebs cycle.
The intermediates form many precursors corresponding to their respective substrates from which the biosynthesis takes place.
Anabolic activities are;
I. Citrate from mitochondria enters cytosol to oxidize to form Acetyl Co – A, this initiates the Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids.
II. α-ketoglutarate is the precursor for Amino Acid Glutamate which on Transamination provides Glutamine, Arginine and Proline and provides Purines.
III. Succinyl Co – A becomes a precursor for Porphyrin and Heme forming oxygen carriers in Blood.
IV. Oxaloacetate is the precursor for Aspartate and they form Asparagine to produce pyrimidines and other Amino acids that acts as an intermediate for Gluconeogenesis
Amphibolic Pathway Citations
Share
Similar Post:
-
What is Lactic Acid? Where Does it...
Continue ReadingWhat is Lactic acid?
Do you know what type of acid is present in all the milk products including cheese, milk, curd and butter.
Yeah, absolutely it’s a Lactic acid.
Lactic acid is generally considered as an organic acid and it is produced by a fermentation process which occurs in milk sugar.
It was first identified by Carl Wilhelm in 1780 in milk. It is a colorless water-soluble substance which has been widely used in food and pharmaceuticals and it has also been synthesized by our body in many metabolic conditions.
The First Demonstration of Lactic Acid
Lactic acid was first identified by Scheele in sour milk in the year 1780. Further when Pasteur was undergoing research on pasteurization, he found the microorganism which is necessary for lactic acid production.
Lactic acid is also being commercially sold for many purposes.
How Lactic Acid is Utilized by Human Body?
Lactic acid is used for the process of conversion of glucose into energy when our body has very low oxygen content.
We often release a painful sensation when we exercise or do heavy activities suddenly or after a long interval, it is due to the accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles which results in muscle cramps at a certain area in our body.
It does not cause any serious issues as liver has the capability to breakdown the extra lactate.
How Lactic Acid Build up in Our Body?
In some cases, our muscles do not have enough oxygen to breakdown glycogen into glucose for the synthesis of energy molecules which is known as ATP, at this time lactic acid gets accumulated in a certain area where enough oxygen is not available which is often referred to as anaerobic metabolic process.
When lactate gets accumulated it leaves to formation of lactic acidosis.
It may also upgrade at the times of heart attack, sudden shock, and at the cases of lung diseases.
Lactic acid forms in many varieties at each area according to their nature.
When they are being accumulated at muscles and blood tissues they are known as dextrorotary form.
The lactate which is obtained as a result of sucrose formation is known as levorotary form, when the same lactate if produced by bacteria during fermentation they are known as racemic form.
Thus, each of its form has its origin from the process of their accumulation or synthesis.
To explain in detail about how our body produces lactic acid, as said earlier lactic acid gets accumulate in our body when we perform heavy works or exercises during a sudden period of time.
This because when we perform powerful activities, we take a long and faster breathes which leads to the usage of more oxygen by the muscles, which tend to perform that action, which results in synthesizing energy anaerobically.
We generally get energy by the process of glycolysis, where glucose is reduced to pyruvic acid and release of ATP molecules occurs through further process which is important for the energy source.
This is a general process, but when our muscles are in a state with absence or lack of oxygen the pyruvate which is produced through a process of glycolysis convert itself into a substance namely lactate and supplies energy in the anaerobic form which leads to the accumulation of lactate at higher levels.
But this is performed by our body, for a longer time it leads to side effects by the accumulation of lactate at higher levels in the tissues which also disrupts the other metabolic activities of the muscle and creates an acidic environment around the muscle cells.
So, it results in degrading a working capability of the muscle and cannot perform any heavy or powerful activities further.
But on considering an immune response of our body, natural immune barriers prevent the muscle tissues from permanent damage and initiates the cells to work normally by upcoming the situation and by performing regular muscle contraction improves the lactic acid accumulation.
This is because our body gets slow during these conditions and allows the reverse mechanism of conversion of lactate into pyruvate and normal aerobic respiration is followed by the tissues.
Fermentation of Lactic Acid
Lactic acids are also synthesized in industries for various purposes through fermentation.
Several microorganisms are involved in the production of lactic acid, each of it has the mechanism of producing either D (-) lactic acid or L (+) lactic acid depending on their nature.
The racemic form is formed due to the presence or production of an enzyme known as racemase, the lactic acid usually be in an active form unless it is deactivated by any other enzymes.
The two most important steps involved in the production of lactic acid are as follows,
1. Homo-fermentative Process
This type of process involves the utilization of certain bacteria such as Lactobacillus delbruckii, L.casei, L.leichmanii, streptococcus lactis etc. which utilizes its EMP pathway to synthesis pyruvic acid which helps in the production of lactic acid by reducing lactate dehydrogenase.
Though these microbes can serve under anaerobic conditions they are known an anaerobic microbe.
2. Heterofermentative Process
This process involves the synthesis of lactic acid, ethanol, acetic acid, carbon dioxide and water with the help of Leuconostoc mesenteroids.
Manufacturing of Lactic Acid
The medium should be prepared such that it contains masses of molasses, maltose, lactose, sucrose, calcium carbonate, hydrogen and phosphate which are kept at a pH of 5.5 to 6.5.
As lactic acid is soft and delicate in nature the mixture of metals is avoided in the culture medium and fermenters are nature based and mostly wood fermenters are used.
The use of Thermophilic clostridia in the culture results in the formation of major and important constituents of lactic acid namely butanol and butyric acid.
Uses of Lactic Acid
Considering lactic acid as a commercial one it can also be used in polymer production since it has a property of weak acid.
It is also being used in food and other industries such as production of beverages in preservation as it has an acidic property which is due to the anaerobic property of that which prevents the food from spoilage.
It is also being used in leather industries for de-lining and also in laundry and textiles for the treatment of fabric.
Calcium lactate is being used as a source of calcium in pharmaceuticals and also in baking units.
Lactic Acid Citations
- Lactic acid and exercise performance : culprit or friend? Sports Med . 2006;36(4):279-91.
- Lactic acid fermentation of human excreta for agricultural application. J Environ Manage . 2018 Jan 15;206:890-900.
- Biosynthesis of D-lactic acid from lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol Lett . 2018 Aug;40(8):1167-1179.
Share
Similar Research Position:
-
What is Sex Determination System? Definition and...
Continue ReadingSex Determination Overview
By nature, we all look every living organism in this environment as male or female, considering from a plant, pets and we the humans; because these characters are externally shown and they can be easily differentiated into separate individuals.
We will be discussing here about how each sexes are determined, either through gene or through other external features.
Usually, all organisms in this living environment are classified as two sexes namely male and females depending upon their gametes and sexual characters and differentiation among them.
Accordingly, the Latin term sex means separation or section. Some organisms of lowest forms contain more than two sexes, where the species of protozoa which is known as Paramecium bursaria has eight sexes.
The organisms which usually posses two sex organs in a same individual are referred as hermaphrodite individuals.
Earthworms are hermaphrodites: each carries male and female sex organs.
Where as in flowers the staminate or anther is seen in males and pistillate is being seen in females but they are present in the same plant hence the term monoecious is used here.
But most of the flowers has both male and female organs in a same plant and it is called as the original or a perfect flower.
As such for animals the organisms which produce male and female gametes individually are referred by the term dioecious.
However, these sex cells and reproductive organs and their respective hormones play an important role in determining their primary and secondary sexual characters.
Mechanism of Sex Determination
Mostly our sexes are determined in a genetical manner and they are classified into four categories as follows,
1. Heterogamesis or sex chromosome mechanism
2. Genic balance mechanism
3. Male haploidy or haplodiploidy mechanism
4. Single gene effects.
1. Heterogamesis
Generally, in dioecious organisms two types of chromosomes are present such as autosomes and sex chromosomes.
The sex chromosomes form two types of sex determination depending on two systems namely heterogametic females and heterogametic males.
In heterogametic sex, females have two x chromosomes where as the males have one x and one y chromosomes with 50 percent of the gametes.
The heterogametic male contains XX-XO type in plants and XX-XY type in mammals.
Where as the heterogametic female contains ZZ-ZO types in moths and ZW-ZZ type in fishes and certain insects
2. Genic Balance
This mechanism explains that some genes are being carried by sex chromosome which is responsible for the determination of sex in individuals.
There will be mostly an inherited mechanism of sexes in both individuals considering from masculine features in male to feminine characters in female.
This was discovered by Wilson, Bridges and Goldschmidt in different organisms.
If an individual is found intermediate between both sexes they are referred to as intersexes.
Sex Determination in Drosophila
The Y chromosomes present in a drosophila are very much important for maintaining the fertility in male flies but they do not have much importance in determining the sex.
The sex of the flies are determined polygenically, where the genes are situated in a distributive manner such that autosomes determine the male character and where as in female it is determined by X chromosome.
Bridges crossed the polyploid flies of experimentally produced female drosophila which has triploid set of chromosomes (3AA:3XX) to that of the diploid male chromosomes.
Which resulted in the formation of intersexes, superfemales and super males and also a normal diploid male along with the triploid females.
From this experiment he concluded that autosomes also carry the genes which are responsible for sex determination.
The intersexes obtained were sterile with both male and female phenotypic characters. This proves the genic balance mechanism.
Sex Determination in Human
Like Drosophila, sex determination can also be seen in humans, where male has XX-XY pair of chromosomes, here Y trait has a potential to bring all male determining characters, where as X chromosome is considered as a feminine character determiner.
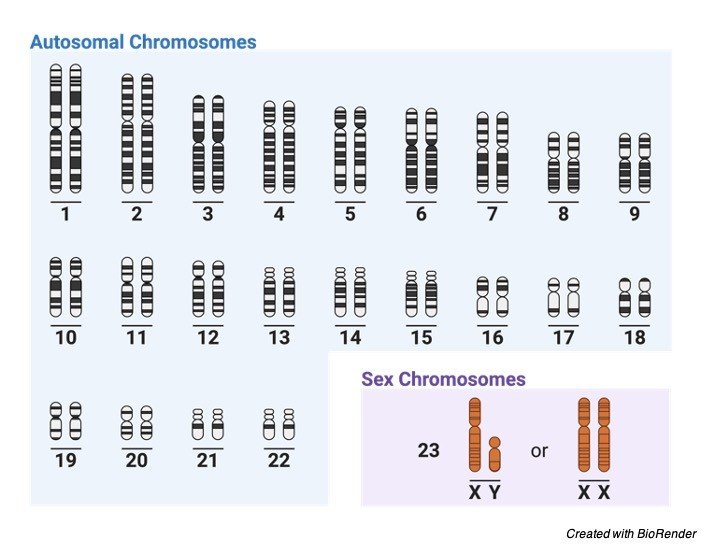
Whereas the male having one X and one Y chromosomes can be a normal male by overcoming the feminine characters of X chromosome until there is no chances of chromosomal abnormalities or abbretions, which results in syndromes such as Turner and Klinefelter’s which causes feminine characters in male; like inhibiting sperm production, lack of masculine features; such as bread growth and body hairs, etc. which leads to many physical and mental abnormalities.
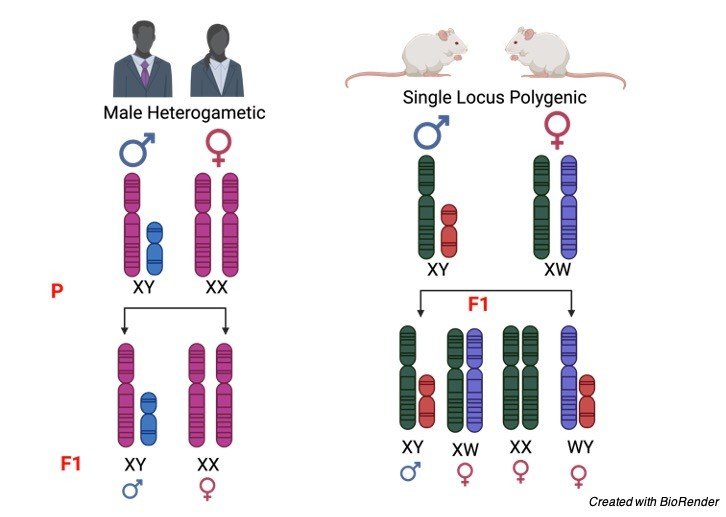
Where in Turners syndrome the lack of female characters tends to occur, such as shield chest, short stature, congenital malformations and webbing of neck etc,.
The individual who has addition of both type of chromosomes that is extra X and Y chromosomes, shows true hermaphroditism which have both ovarian and testicular tissues and genitalia appears to be intersexual.
3. Male Haploidy or Haplodiploidy
This is considered as one of the types of parthenogenesis mechanism which is commonly seen in hymenopterous insects.
These types of insects include ants, bees, wasps and sawflies.
Where fertilise eggs develop into diploid females and also as unfertilised eggs are developed into haploid males.
So, this is also considered as a form of sex determination. Considering an example of honey bee, where they can lay two varieties of eggs.
Such that it produces a fertilised egg by controlling a splinter of her sperm receptacle and an unfertilized one. Here the fertilised egg has diploid zygote and develops into a female and an unfertilised egg has only 16 zygotes and develops into a male.
Later the females are grown up as a honey bee or worker bee depending upon the food they consume or diet they undertake and the one which is developed from unfertilised eggs are males.
Single Gene Control of Sex
In certain organisms like Neurospora, Chlamydomonas, asparagus, yeast, maize etc, the single gene plays a very important role in determination of sexes and also in expressing the genes hence it is known as single gene control of sex.
Sex Determination System Citations
- Putting the heat on sex determination. Genetica . 1992;87(1):1-6.
- Prenatal sex determination and selection. Hum Reprod . 1993 Oct;8(10):1545-9.
- Genetic sex determination of mice by simplex PCR. Biol Sex Differ . 2017 Oct 17;8(1):31.
- Sonographic fetal sex determination. Obstet Gynecol Surv . 2009 Jan;64(1):50-7.
- Polygenic sex determination. Experientia . 1964 Apr 15;20(4):190-9.
- Sex Determination and Sex Chromosomes in Amphibia. Sex Dev . 2017;11(5-6):298-306.
Share
Similar Post:
-
Cytoplasm: Definition, Function, and Example
Continue ReadingWhat is Cytoplasm?
We all know that cells are the basic, structural and functional units of all living organisms.
Cells are made up of many organelles and they are bound embedded in the cytoplasm.
It plays a very important role in functioning of the cell and also contains the genetic information of the cell, as it contains chromosomes in it.
The term cytoplasm was first coined by Rudolf Von Kolliker, a Swiss biologist.

"Cytoplasm is contained within cells in the space between the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane"
Cytoplasm is considered as the fluid compartment of the cell, which contains cytosolic filaments, ion substances, proteins and other macromolecular substances. Along which the other cell organelles are found suspended.
The Eukaryotic cytoplasm contains all the cell organelles found embedded in it except the nucleus.
The prokaryotic cytoplasm is found throughout the cell carrying its genetic material as the prokaryotic organism does not have its well- defined nucleus.
Does Cytoplasm Have Any Structure?
Cytoplasm doesn’t have a specific structure its just a jelly or glassy liquid like substance which fills up the space in each cells volume and make the other cell organelles being embedded in it and provides a better environment for the organelles and genetic materials to carry out their function.
Cytoplasm Vs Cytosol
In biology, Cytoplasm is often confused with cytosol due to their similarity in understanding of these words.
Cytoplasm is the liquid part of the cell which is found outside or around the nucleus.
Where as Cytosol is denoted as the substances or proteins which are found in the cytoplasm apart from other cell organelles.
Protoplasm Vs Cytoplasm
The protoplasm is jelly like substance, which is composed of macromolecules and water.
It is actually a colorless living part of the cell. It can be generally known as the organic or inorganic substance which is made up of cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria and plastids of a cell, which play a major role in functioning of the cell.
Thus, cytoplasm is a part of a protoplasm which is placed in between the nucleus and the cell membrane in all eukaryotic cells. Where the organelles are embedded in it.
Function of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm provides a suitable environment for all other cell organelles to maintain their turgidity which helps them to maintain their shape.
The fluid form of the cytoplasm is made up of salts and water which form a jelly like structure and helps the other cell organelles to embed themselves in that space.
The Cytoplasm also acts as a center for other cell organelles to perform their function, as it contains many enzymes and molecules which helps them to perform their metabolic reactions.
As cytoplasm helps the cell organelles to fit it into, so that they cannot move here and there and fix themselves in their origins, if not there is a high chance of mixing up of molecules of one organelle into the other which results in change in body functioning.
The fluid matrix of the cytoplasm which is known as cytosol has no organelle, so it fills up the space which is left out by the organelles.
Cytoplasm also paves the role for many cellular functions to occur in it where the ribosomes synthesize their proteins and the process of cellular respiration takes by initiating glycolysis and reproduction of cell phases like mitosis and meiosis occurs.
Cytoplasmic Streaming
Cytoplasmic streaming is often referred to as cyclosis by which the molecules or substances present in the cell are circulating within the cell.
Cyclosis mostly occur in all types of cells such as Plant cells, in bacteria and fungi.
But these movements change accordingly with the type of chemicals and hormones present in it and also according to the temperature and humidity of the cell.
Plants perform cyclosis to settle the chloroplast in the area, where we can get suitable sunlight.
Whereas chloroplast is a very important and essential component in performing the photosynthesis which help the plant to stay alive.
Whereas in protists such as slime molds and amoeba the cyclosis movement is used for the locomotion.
These temporary movement of cells is termed as pseudopodia which helps the cell in capturing the food.
Cyclosis also helps the cell in cell division processes where the daughter cells are divided by the process of mitosis and meiosis.
Other Features of Cytoplasm
As discussed above cytoplasm is a glassy liquid substance which contains all the cell organelles and other substances except the nucleus.
The eukaryotic cytoplasm is present between the cell membrane and the nucleus of the cell, where as in prokaryotes cytoplasm just acts as a covering to all the substances in a cell membrane.
However, in both the cases the role of cytoplasm is to carry all the metabolism and growth and functions of all other organelles present in a cell.
The organelles present in the cytoplasm perform various functions, where as the nucleus contains the genetic information and helps in caring our hereditary characters throughout the generations.
Mitochondria which is found embedded in the cytoplasm acts as a powerhouse of the cell producing Adenosine tri phosphate.
The chloroplast present in plants cell helps in performing photosynthesis.
Likewise, each cell organelles perform various functions, but without the help of cytoplasm which provides them a good outer condition by providing proper humidity and other conditions, these cells cannot undergo their functions.
The cytosol which acts as a fluid part of the cell, consisting of 70% of water and other molecules including ion particles such as chloride, potassium, bicarbonate magnesium and calcium serves as a site for many chemical reactions.
Cytosol also plays an important role in cell signaling and osmoregulation by inducing action potentials such that of nerve and muscle cells.
Cytoplasmic Biochemical Reactions
Basically, cytoplasm acts as a center for many biochemical reactions, the biochemical reactions are thereby classified as anabolic and catabolic reactions, where catabolism refer to a breakdown of complex molecules and anabolism refers to a synthesis of biomolecular substances with the help of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) to form a complex substance.
Biological Functions of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm acts as a center for both growth and metabolism, as said earlier it helps in both generation and degradation processes.
Whereas glycolysis, which is the first process in the cellular respiration occurs at a cytosol, the fluid component of the cell and this process for further followed by oxidative decarboxylation reaction and Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle and followed by electron transport chain.
Citations
Share
Similar Post:
-

Transfer RNA (tRNA): Definition, Structure, and, Function
Continue ReadingThe role of RNA in protein synthesis
1. mRNA: This is a messenger RNA, transfer the genetic detail duplicated from DNA in fashion of a sequence of 3-base code ‘term’, every term states a certain amino acid.
2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): It links with a batch of proteins to configure ribosomes. It is the complicated form, moves physically along with a mRNA molecule, facilitates the fabrication of various amino acids into protein chains. They also link tRNAs and different supplementary molecules necessary for protein synthesis. Ribosomes are made up of a large and small subunit, each of which having their unique rRNA molecule or molecules.
3. Transfer RNA (tRNA): It is pivotal in decrypting the key codons in mRNA. Every amino acid possesses their individual kind of tRNA, which attach it and transfer it to the expanding end of a polypeptide chain when the subsequent codon on mRNA needs it. The correct tRNA with its attached amino acid is selected at each step because each specific tRNA molecule contains a 3-base sequence that can pair with base of its reciprocal codon in the mRNA.

About tRNA
Every tRNA carry a set of 3 nucleotides known an anticodon. The anticodon of a said tRNA can attach to one or more particular mRNA codons.
The codons are predetermined for the tRNA thus, transferring the amino acid to that specific location.
Variety of tRNA are streaming within a cell, possessing their own anticodon along with complimentary amino acid and they attach to codons inside of the ribosome, where they remit amino acids for incorporation into the protein chain.
Thus, proteins are constructed from miniature units known as amino acids, which are described by 3-nucleotide mRNA sequences called codons.
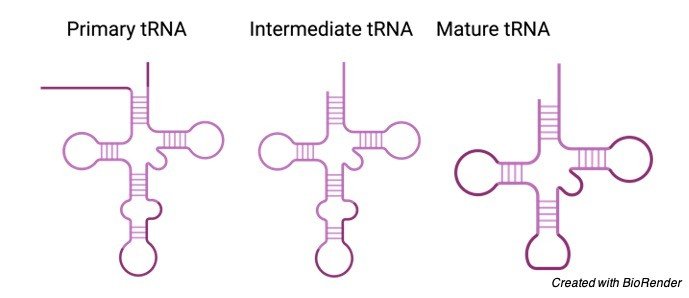
The 3D Structure of tRNA
A tRNA is formed from a single strand of RNA in a similar fashion mRNA is formed.
However, the strand takes on a complex three dimensional structure since base pairs form between nucleotides in different parts of the molecule.
This creates double-stranded regions and loops, overlapping the tRNA into an L shape.
The tRNA molecule has a noticeable folded structure with 3 hairpin loops that form the structure of a 3-leafed clover.
One of these hairpin loops contains a sequence known as the anticodon, which can admit and decode an mRNA codon.
Every tRNA have their correlated amino acid attached to its end.
When a tRNA identifies and attaches to its corresponding codon in the ribosome, the tRNA shifts the suitable amino acid to the tip of the lengthening amino acid chain.
Then the tRNAs and ribosome carry on to decipher the mRNA molecule until the entire series is translated into a protein.
tRNA and its Decoding Role
The genetic information passed from DNA to protein via mRNA in which the nucleotide sequence of mRNA is converted into chain of the amino acid to form protein.
However, this deciphering procedure is carried out with the help of two kinds of adapter molecules: tRNAs and an enzymes known as aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
There are 2 functions which are performed by all tRNAs:
1. To get chemically connected to a specific amino acid and to base-pair with a codon in mRNA so as to put in the amino acid in the lengthening peptide chain.
Every tRNA molecule is exquisitely identified by the 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
In a similar fashion, every enzyme molecules inimitably attaches the 20 amino acids to a specific tRNA, forming an aminoacyl-tRNA.
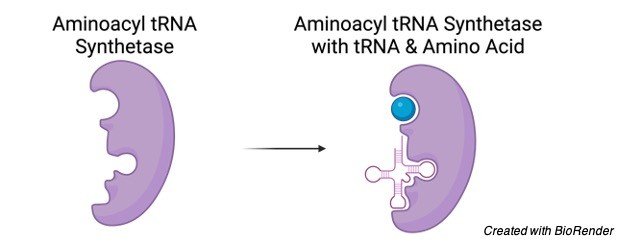
2. When the accurate amino acid is linked, then a tRNA identifies a codon in mRNA, thereby bringing its amino acid to the expanding polypeptide.
How Synthetases Recognize tRNAs.
After further studies on tRNA, 30 – 40 variety of tRNAs were recognized in bacterial cells while about 50 – 100 in animal and plant cells.
Therefore, the count of tRNAs in almost all cells is exceeding the number of amino acids observed in proteins.
Moreover, they differ from the number of codons in the genetic code.
Accordingly, several amino acids possess more than one tRNA to which they can link.
Furthermore, several tRNAs can attach to more than one codon. Aforementioned, the majority of amino acids are encoded by more than one codon, needing some tRNAs to identify more than one codon.
Function of tRNA Molecules
The function of 70 – 80 nucleotides long tRNA is based on their accurate 3D structures.
In solution, all tRNA molecules overlap into a same stem-loop setting that mimic a cloverleaf which when drawn in two dimensions.
The 4 stems are small double helices fixed by Watson-Crick base pairing; 3 out of 4 stems have loops containing 7 or 8 bases at their tail end, whereas the rest, unloop stem embody the free 3′ and 5′ ends of the chain.
3 nucleotides entitled the anticodon, located at the middle of one loop, can form base pairs with the 3 corresponding nucleotides forming a codon in mRNA.
As delineated earlier, determined aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases identifies the surface structure of every tRNA for a particular amino acid and covalently bind the specific amino acid to the unloop amino acid acceptor stem.
The 3′ terminal end of each tRNAs has the sequence CCA, which in most instance adjoins when synthesis and processing of the tRNA are finish.
Observed in 3 dimensions, the overlapped tRNA molecule has an L shape with the anticodon loop and acceptor stem forming the ends of the two arms.
Loading tRNA With an Amino Acid
Enzymes known as aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases have this pivotal role.
There is an individual synthetase enzyme for each amino acid, wherein an enzyme recognizes only particular amino acid with its respective tRNAs.
Whenever the amino acid and its tRNA binds its respective enzyme, the enzyme blends them together.
The above reaction has been powered by the “energy currency” molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Sometimes, an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase miscalculate, wherein it attaches to the incorrect amino acid.
For instance, the threonine synthetase occasionally seize serine by coincidence and binds it to the threonine tRNA.
Fortunately, the threonine synthetase has a proofreading site, which dislodges the amino acid from the tRNA.
tRNA Summary
Genetic information is transmitted into mRNA in the form of a triplet code.
Every amino acid is encoded by surplus of 3 – base sequences, or codons, in mRNA.
Each codon identifies one amino acid, however, majority of amino acids are encoded by multiple codons.
All tRNAs have a same 3 – D structure that comprises an acceptor arm that binds a particular amino acid and a stem-loop with a 3- base anticodon sequence at its ends.
The anticodon can base-pair with its complimentary codon or codons in mRNA.
Since it is a nonstandard interplay, a tRNA may base-pair with more than one mRNA codon, and in contrast, a specific codon may base-pair with several tRNAs.
Each of the 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases identifies a single amino acid and covalently links it to an associated tRNA, producing an aminoacyl-tRNA.
This reaction triggers the amino acid, so it can involve in peptide-bond development.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) Citations
- tRNA Modifications: Impact on Structure and Thermal Adaptation. Biomolecules . 2017 Apr 4;7(2):35.
- tRNA biology charges to the front. Genes Dev . 2010 Sep 1;24(17):1832-60.
- Transfer RNA: From pioneering crystallographic studies to contemporary tRNA biology. Arch Biochem Biophys . 2016 Jul 15;602:95-105.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Green Revolution: Definition, Advantages, Importance, & Facts
Continue ReadingWhat is Green Revolution?
Green Revolution is really the way toward expanding agrarian creation by utilizing present day machines and procedures.
It was a logical exploration-based innovation drive performed among 1950 and the last part of the 1960s, that expanded horticultural creation around the world, especially in the creating scene, starting most uniquely in the last part of the 1960s.
It utilized HYV seeds, expanded utilization of manure and more specialized techniques for water system to build the creation of food grains.
Green Revolution in India
In India Green Revolution started in the mid 1960s that prompted an expansion in food grain creation, particularly in Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh.
Significant achievements in this endeavor were the advancement of high-yielding assortments of wheat.
The Green revolution is revolutionary in character because of the presentation of new innovation, groundbreaking thoughts, the new use of data sources like HYV seeds, composts, water system water, pesticides, and so on.
As every one of these were brought out of nowhere and spread rapidly to accomplish sensational outcomes subsequently it is named as a revolution in green agribusiness.
Reason Behind Green Revolution
The world’s most exceedingly awful recorded food debacle occurred in 1943 in British governed India known as the Bengal Famine.
An expected 4,000,000 individuals died of yearning that year alone in Eastern India (that incorporated the present Bangladesh).
The underlying hypothesis set forward to clarify that disaster was that there was an intense shortage in food creation nearby.
Notwithstanding, Indian financial analyst Amartya Sen (beneficiary of the Nobel Prize for Economics, 1998) has set up that while food lack was a supporter of the issue, a more strong factor was the aftereffect of madness identified with World War II which focused on food supply for the British rulers.
The insanity was additionally misused by Indian merchants who accumulated food to sell at more exorbitant costs.
By and by when the British left India four years after the fact in 1947, India kept on being spooky by recollections of the Bengal Famine.
It was in this way normal that food security was a vital thing on free India’s plan. This mindfulness drove, on one hand to the Green Revolution in India and on the other, administrative measures to guarantee that financial specialists could always again be unable to store nourishment for reasons of benefit.
Notwithstanding, the expression “Green Revolution” is applied to the period from 1967 to 1978. Somewhere in the range of 1947 and 1967, endeavors at accomplishing food independence’s were not totally fruitful.
Endeavors until 1967 to a great extent focused on growing the cultivating regions. Be that as it may, starvation passings were all the while being accounted for in the papers.
In an ideal instance of Malthusian financial matters, populace was developing at a lot quicker rate than food creation. This called for extreme activity to expand yield. The activity came as Green Revolution.
The expression “Green Revolution” is an overall one that is applied to fruitful rural analyses in numerous Third world nations. It’s anything but explicit to India. However, It was best in India.
Factual Results of Green Revolution
A record grain yield in 1978-79 around 131 million tons happened because of the Green Revolution. Consequently, it made India as one of the world’s greatest agrarian maker.
In India Green Revolution recorded a significant degree of accomplishment. India likewise turned into an exporter of food grains around that time.
Monetary Results of Green Revolution
Yield regions under this venture required more water, more composts, more pesticides, and certain different synthetic substances.
This expanded the development of the nearby assembling area. Expanded modern development made new positions and added to the nation’s GDP.
The expansion in water system made the requirement for new dams to saddle storm water. The put away water was utilized to make hydro-electric force.
The entirety of this brought about modern development, made positions and worked on the personal satisfaction of individuals in towns.
Sociological Results of Green Revolution
This new innovation utilized regular use of water, composts, bug sprays, bigger volumes of transportation, power, and so on The agrarian specialists as well as modern laborers landed a lot of positions on account of the production of offices like processing plants, hydro-electric force stations, and so on to back up the revolution.
Political Results of Green Revolution
Quite possibly the main factors that made Mrs. Indira Gandhi (1917-1984) and her gathering the Indian National Congress, an extremely incredible political power in India is this Green Revolution. India changed itself from a destitute country to an exporter of food.
This gave India adoration and appreciation from everywhere the world, particularly from the Third world country.
Disservices of the Green Revolution
The negative social impact of the Revolution was additionally soon noticeable. Differences in pay have been augmented by these advancements in horticulture.
Rich landowners have power over the horticultural info and worked on synthetic composts.
The most noticeably terrible part is that the helpless ranchers wound up impeded by little homesteads of land and insufficient water supply. With complete horticultural methods and data sources, the Green revaluation would in general have its most focused application on enormous homesteads.
As a convergence of the new innovation to enormous homesteads, the Inequalities have additionally Increased.
The helpless ranchers have been unfavorably influenced by a developing propensity among the rich ranchers to recover land recently rented out under tenure understanding, which has been made beneficial by better yields from new innovation.
Poor people and in reverse class of ranchers has been progressively driven into the position of the landless worker.
An intense expansion in a more elevated level of lease with land esteem taking off.
Likewise in light of unnecessary utilization of manures soil began to become soluble or acidic relying on the idea of the compost utilized.
Conclusion
India has made a colossal accomplishment in term of the Green Revolution, as it’s anything but an extraordinary degree of food security.
It’s anything but countless needy individuals out of destitution and aided numerous non-needy individuals keep away from the neediness and yearning they would have encountered had it not occurred.
This revolution has saved over a billion group everywhere on the world from starvation.
Green Revolution Citations
- The green revolution. Nutr Rev . 1969 May;27(5):133-6.
- From green to gold: agricultural revolution for food security. J Exp Bot . 2020 Apr 6;71(7):2211-2215.
- A Strigolactone Biosynthesis Gene Contributed to the Green Revolution in Rice. Mol Plant . 2020 Jun 1;13(6):923-932.
- Toward a “Green Revolution” for Soybean. Mol Plant . 2020 May 4;13(5):688-697.
- Green revolution: impacts, limits, and the path ahead. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2012 Jul 31;109(31):12302-8.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Cytoplasm: Definition, Function, and Examples
Continue ReadingWhat is Cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is the liquid matrix of the cell in which the membrane bound organelles such as Mitochondria, Golgi Apparatus ribosome, nucleus and other chemical components proteins, Glucose, Lipids.
The cytoplasm was first discovered by Anton Von Leuwenhoek and termed by Kolliker in 19th century.
Though cytoplasm is a liquid component the diverse make of the components provides a structural organization and the components are sequentially arranged and are well synchronized.
The cytoplasm is an indicator to the outside environment and changes the activity of the cell frequently to maintain HOMEOSTASIS.
Characteristic of Cytoplasm
1. Cytoplasm is a well – organized liquid matrix:
Earlier it was considered as a part of protoplasm but invention of Electron Microscopes provided a depth of knowledge regarding the organization of cytoplasm inside the cell.
2. The movement of matrix is well programmed:
Based on the cell’s necessity, transportation of enzymes, proteins and other substances which are required at different part of the cell.
3. Cytoplasm is the internal milieu of the cell:
They act as regulators maintaining a cell’s vital survival function even the external factors disrupt the homeostatic function and maintain the internal environment.
4. Maintains the integrity of the cell:
The cell shape, movement, protein synthesis and other metabolic activities are governed by the cytoplasm.
5. High viscosity matrix and colloid:
The thickness of the matrix is usually higher than that of water. Higher the viscosity easier the organelles can suspend. Because of the suspension of the organelles the matrix is colloid.
Components of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm has both solid and liquid components of Cytoplasm.
Solid Components are
1. Organelles bound by two membrane
a. Plastids – special feature present only in plant cell has a variety of types and function. The 2 types are Leucoplasts and Chromoplasts.
i. Leucoplasts are colorless components which have their role in storage and metabolism of starch.
ii. Chromoplasts are colored compound mainly green in plants forming the chloroplasts which are essential in photosynthesis.
b. Mitochondria – Power house of the cell provides energy in ATP from the cellular respiration.
2. Organelles Bound by one membrane
a. Peroxisomes – Peroxisomes are protective in function producing peroxides
b. Vacuoles – Specialized feature present in plants where the food molecules are stored for metabolism when needed.
3. Ribosomes – Ribosomes are molecular compounds which is involved in formation of protein for cell structural function.
4. Endomembrane system – consists Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus and Nuclear Envelope
5. The endomembrane system constitutes the internal membrane providing organelle free matrix for cell survival.
The endoplasmic reticulum arises from the nucleus extends throughout the length and reaches plasma membrane forming the endomembrane.
I. Nuclear envelope: Nuclear Envelope is made up of flattened cisternae like discs. Many discs come together forming a small pore which allows a contact between cytoplasm and nucleus.
The outer membrane contacts endoplasmic reticulum and the inner membrane has had thread of chromatin molecule.
II. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is the major constituent of the endomembrane system. They are tubule and flattened that carries out the function of storage.
The ER is of 2 types:
a. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
b. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum protein synthesized are stored at RER but transported through SER.
Their main function remains secretion.
III. Golgi Complex flattened stack of disc from dictyosomes forms the determined structure.
Golgi Bodies are concerned with packaging and storing of the secretory molecule and then vesicles are pinched off from Golgi complex through exocytosis.
6. Cytoskeleton
I. Micro tubules – Microtubules are thin and rigid structures made up of 13 filaments. Protein component is the main structural source for the tubule structure is contributed by Tubulin.
They are easily depolymerized and can shape and function of any cell by contributing to Cell division providing spindle fibers, Asters, Locomotion etc.,
II. Centrioles – cylindrical structure and paired. They migrate to animal pole during cell division
III. Basal Bodies – a structure similar to centrioles are present at the bases of cilia or flagella. Cilia and Flagella both has a common arrangement of microtubule (9 + 2). These are used in order for locomotion purposes.
IV. Microfilaments – are smallest structure made up of actin associated with myosin and other aiding proteins which help in contraction thereby causing motility of the organism.
V. Intermediate Filaments – they are mechanical in function
Liquid components are:
1. Cytosol – A liquid component comprises the structural organelles of cell. They are present inside the cell. Responsible for movement and integrity.
2. Hyaloplasm – is the ground cytoplasm which does not have any structural component. They are present outside the endomembrane system.
Their main role is to regulate the internal milieu. This is also called as Ground cytoplasm / Cytoplasmic matrix proper.
Other components Excretory products, Metabolic storage, Secretory materials
Cytoplasm: Plant vs Animal Cells
The difference between plant and animal cell cytoplasm is negligible as the cytoplasm has common role in both cell types.
The main difference will be the presence and absence of organelles present in them such as vacuoles, chloroplasts etc.,
Significance of Cytoplasm
1. Microtubules specifically locate and guide the enzymes. Precise positioning information is provided for the enzymes to catalyst the biosynthesis.
2. The ER is related to the formation of glyoxysomes and vacuoles
3. Golgi Complex is distributed in the cytoplasm in the form of dictyosomes.
4. Cytoplasmic Streaming – Also known as CYCLOSIS, is a process where the cell components are circulated inside the matrix for maintain the process of homeostasis.
The streaming is influenced by the pH, temperature and various other factors which modify the body’s homeostatic condition.
For Example: Sunlight falls on a particular spot of the plant. The other regions lack sunlight here the cytoplasmic streaming with the help of microtubules and filaments the chloroplast is moved to sun receiving regions.
5. The structural integrity, motility, shape are all maintained by the Cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm Citations
- Consequences of phase separation in cytoplasm. Int Rev Cytol . 2000;192:331-43.
- The periplastidal compartment: a naturally minimized eukaryotic cytoplasm. Curr Opin Microbiol . 2014 Dec;22:88-93.
- How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell . 1982 Sep;30(2):345-7.
- Molecular pathways involved in the transport of nuclear receptors from the nucleus to cytoplasm. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol . 2018 Apr;178:36-44.
- Cytoplasm’s Got Moves. Dev Cell . 2021 Jan 25;56(2):213-226.
Share
Similar Post:
-
Glucose Oxidation Respiratory Balance Sheet
Continue ReadingAbout Glucose Oxidation Respiratory Balance Sheet
Respiratory balance sheet is a mathematical calculation of net ATP produced by cellular respiration during glucose oxidation which includes Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation under aerobic condition utilizing one glucose molecule.
Features of Glucose Oxidation Respiratory Balance Sheet
Certain assumptions were considered while forming the balance sheet:
1. For an oxidizing Glucose molecule, it must follow the cellular respiration process in a sequence such that glucose must follow every step of glycolysis to form 2 molecules of pyruvate.
Pyruvate must enter Krebs Cycle to produce reducing equivalents.
The reducing equivalents from Glycolysis and Krebs cycle must enter Electron Transport Chain where they get converted into ATP.
2. Reducing equivalents such as the NADH must carried to Electron Transport Chain in mitochondria
3. The intermediates formed during the oxidization of glucose should not participate in any biosynthesis process to form other products such as Amino acids, Purines pyrimidines or porphyrins.
4. The cellular respiratory substrate must only be GLUCOSE other substrates must not be considered.
Considering the dynamic nature of our cell and living system the above assumptions do not apply practically for a working cell. The balance sheet assumptions are theoretically accepted and followed.
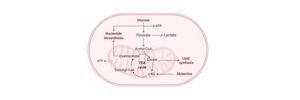
Glucose Oxidation Respiratory Balance Sheet
When NADH produces 3 ATP and FADH2 produces 2 ATP
Respiration Process Direct Synthesis In ETC ATP Consumed Net Gain NADH+FADH2 Glycolysis 4 6+Nil 2 8 Krebs Cycle 3 18+4 Nil 24 Acetyl CoA Formation Nil 6+Nil Nil 6 Total Gain 6 30+4 -2 38 When NADH produces 2.5 ATP and FADH2 produces 1.5 ATP
Respiration Process Direct Synthesis In ETC ATP Consumed Net Gain NADH+FADH2 Glycolysis 4 5+Nil 2 7 Krebs Cycle 2 15+3 Nil 20 Acetyl CoA Formation Nil 5+Nil Nil 5 Total Gain 6 25+3 -2 32 Under Anaerobic respiration, the pyruvic acid converts to lactic acid producing only 6 ATP.
The list of reactions which produced direct ATP synthesis and reduced equivalents are given below:
Glucose Oxidation: Glycolysis
1. Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate + NAD → 1,3 – diphosphoglycerate + NADH
Enzyme: Glyceraldehyde – 3 phosphate dehydrogenases
2. 1,3 diphosphoglycerate +ADP + Pi → 3 – phosphoglycerate + ATP
Enzyme: Phosphoglycerate Kinase
3. Phosphoenol pyruvate + ADP + Pi → Pyruvate + ATP
Enzyme: Pyruvate Kinase
These 3 reactions take place twice therefore they produce 4 ATP + 2 NADPH = 4 + 2 (3) = 10
Two other reaction consumes ATP
1. Glucose + ATP → Glucose 6 phosphate + ADP + Pi
Enzyme: Hexokinase
2. Fructose 6 Phosphate + ATP → Fructose1,6 diphosphate + ADP + Pi
Enzyme: Phosphofructokinase
ATP consumed is 2. Therefore, Glycolysis as a whole provides 8 ATP.
Under Anaerobic condition:
2Pyruvate + 2NAD → 2Lactate/ethanol + 2NADH → 6 ATP
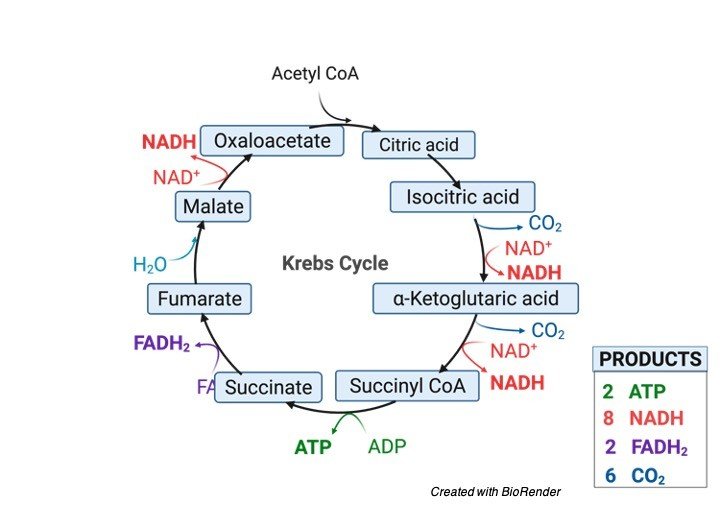
Glucose Oxidation: Citric Acid Cycle
1. 2 Pyruvate + 2 NAD → 2 Acetyl Co – A + 2 NADH
Enzyme: Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
2. 2 Isocitrate + 2 NAD → 2 Oxalosuccinate + 2 NADH
Enzyme: Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
3. 2 α – ketoglutarate + 2 NAD → 2 Succinyl Co – A + 2 NADH
Enzyme: α – ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase
4. 2 Succinyl Co – A + 2GDP + 2Pi → 2 Succinate + 2GTP
Enzyme: Succinate Thiokinase
5. 2 Succinate + 2FAD → 2Fumarate + 2FADH2
Enzyme: Succinate Dehydrogenase
6. 2 Malate + 2 NAD → 2 oxaloacetate + 2 NADH
Enzyme: Malate Dehydrogenase
2 pyruvate molecules undergo complete oxidation and provide 30 ATP molecules.
Glucose Oxidation Citations
- Respiratory metabolism: glycolysis, the TCA cycle and mitochondrial electron transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol . 2004 Jun;7(3):254-61.
- The effect of selenium-deficiency on rat fat-cell glucose oxidation. Biochem J . 1983 Aug 15;214(2):471-7.
- Ascorbic acid and glucose oxidation by ultraviolet A-generated oxygen free radicals. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci . 1996 Jul;37(8):1549-56.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Citric Acid Cycle: an Overview, Mechanism, and,...
Continue ReadingWhat is Citric Acid Cycle?
Citric Acid Cycle is an essential catabolic cycle of cellular respiration involves pyruvate as an end product from glycolysis to form energy in terms of ATP, NADH and FADH2. Which in further processes to provide ATP.
The Citric Acid Cycle takes place in Mitochondria and are coupled with Electron Transport Chain to produce ATP.
Hence Mitochondria is the power house of the cell. The Citric Acid Cycle was discovered by Hans Kreb in 1937 from animal enzymes.
Therefore, it can be named as the Krebs’s Cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Contains 3 carboxyl group in the component).
Citric Acid Cycle Feature
1. Takes place during aerobic respiration:
Pyruvate under aerobic condition produces energy and under anaerobic condition they undergo a process of fermentation forming lactic acid or alcohol
2. TCA Cycle is irreversible at 3 steps: producing high amount of negative energy.
The 3 steps involve the enzymes: citrate synthase, α – ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and isocitrate dehydrogenase.
3. Pyruvate; an end product of glucose metabolism; is transported from cytosol to mitochondria to become Acetyl Co – A.
Pyruvate is transported to mitochondria through Voltage gated channel crossing outer mitochondrial membrane. Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier then takes pyruvate through Inner Mitochondrial Membrane.
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex; an enzyme oxidizes Pyruvate to form Acetyl Co – A.
4. Cycle involves C6 to C4 in a series of steps:
Tricarboxylic Acid (C6 – 6 carbon compound) is formed by the combination of Acetyl Co – A (C2) and Oxaloacetate (C4).
Condensation process takes place between Oxaloacetate and Acetyl Co – A to form C6 compound.
Further the C6 compound catabolize to produce reduced equivalents (NADH, FADH2).
Oxaloacetate + Acetyl Co – A à Citrate (C6)
5. Eight enzymes are involved in 4 oxidations:
On each oxidation, number of carbo atoms present reduces gradually leaving out C4 compound. C4 the condense to form C6 and he cycle continues.
6. Two sources for Acetyl Co – A:
Acetyl Co – A is not only derived from Glycolysis. Fatty Acid oxidation also provides Acetyl Co – A as its direct end product which can be utilized by the Citric Acid Cycle.
7. A cycle with various intermediate forms:
Citric acid cycle forms various intermediates which provides substrates for different biosynthetic process in plants.
For Example: α – keto glutarate forms glutamate which is essential in Nucleic Acid formation
8. Citric Acid Cycle coupled with Electron Transport Chain:
The reduced equivalents from the cycle is directly transported to complexes present in the inner cell membrane of mitochondria to yield ATP.
Mechanism of Citric Acid Cycle
The Citric Acid Cycle has two steps:
1. Pyruvate Decarboxylation
2. Citric Acid Formation
3. TCA Cycle
Step: 1 Pyruvate Decarboxylation
Enzyme Complex involved – Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (combination of enzymes, coenzymes and cofactors)
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC) consists of 3 enzymes and 3 cofactors.
They are:
a. Pyruvate decarboxylase(E) + Thiamine pyrophosphate (CoF) – Complex 1
b. Dihydrolipopyl Transacetylase (E) + Lipoic Acid (CoF) – Complex 2
c. Dihydrolipopyl Dehydrogenase (E) + Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (CoF) – Complex 3
The enzyme complex catalyses the oxidation reaction of Pyruvate to Acetyl Co – A inside the mitochondria with the release of CO2 and reduction of NAD → NADH2
Step: 2 Citric Acid Formation
Enzyme: Citrate Synthase This step is the 1st step of the Citric Acid cycle
I – Citric Acid, a six-carbon compound is formed by condensation and hydrolysis. Acetyl Co – A and Oxaloacetic Acid combines along CH3 and COO- group of acetyl Co – A and Oxaloacetic Acid respectively. On hydrolysis, Coenzyme A is released and Citric Acid is formed.
Step: 3 TCA Cycle
Citrate is the tricarboxylic compound from which the cycle proceeds.
II – Formation of Isocitrate
Enzyme: Aconitase
Enzyme aconitase mediates dehydration and rehydration of citrate molecule forming an isomer of citrate which is isocitrate.
III – α – Ketoglutarate Formation
Enzyme: Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
Dehydrogenase is associated with oxidation of the isocitrate to form α – ketoglutarate with a release of CO2 and formation of carboxyl group. This oxidation involves a reduction of NAD → NADH2. The six – carbon compound now becomes five carbon compound (C5).
IV – Succinyl Co – A synthesis
Enzyme: α – Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex
The enzyme functions similarly to that of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase accounts for the oxidation of α – Ketoglutarate to Succinyl Co – A. CO2 is released and NAD → NADH2. In this step 4 the five – carbon compound reduces to four – carbon compound (C4).
V – Succinate
Enzyme: Succinyl Co – A synthase
The mitochondrial matrix provides a phosphate group to be attached to the Co – A releasing Coenzyme from the compound. On hydration (i.e. addition of water) succinate is formed. ADP → ATP
VI – Fumarate
Enzyme: Succinate Dehydrogenase
The enzyme catalysis the formation of Fumarate by reducing FAD → FADH2. A double bond is formed between 2nd and 3rd carbon.
VII – Malate
Enzyme: Fumarase
Adding Fumarase and hydrating Fumarate results in the formation of Malate.
VIII – Oxaloacetate formation
Enzyme: Malate dehydrogenase
As dehydrogenase is coupled with formation of reduced equivalents, oxaloacetate is formed by reducing NAD → NADH2. This is the last and the fourth oxidation step in the TCA cycle.
Significance of Citric Acid Cycle
1. Citric Acid Cycle mainly provides ATP as energy. This is the important function of the citric acid cycle.
Acetyl Co – A + FAD + 3 NAD + ADP + H2O →
→ CO2 + ATP + 3 NADH + FADH + Co – A
One NADH = 3 ATP
One FADH2 = 2 ATP
ATP = 1
Total = 3(3) + 2 + 1 = 9+2+1 = 12
Citric Acid Cycle provides 12 ATP but glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate molecule the above calculation accounts only for one cycle of pyruvate.
Two cycle of Citric Acid then provides 2(12) = 24 ATP molecules
2. Citric Acid cycle is Amphibolic. Amphibolic means a process or a reaction which can be both Catabolic and Anabolic.
Catabolic nature is the breakdown of pyruvate for energy.
Anabolic nature is that the intermediates of Citric Acid Cycle can be used for the synthesis of amin acids, purine, porphyrin and pyrimidines
3. As Citric Acid cycle provides intermediates for synthesis of amino acid, purines etc., the cycle cannot run in a proper way.
To make the cycle to run in a proper way, many replenishing reactions are taking place to fill the missing intermediates. This process is called the anaplerosis.
4. Citric Acid cycle is the final common oxidative for energy production of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
Citric Acid Cycle: Animal vs Plant Cells
The main difference is the enzyme Succinyl Co – A in animals involves the formation “GTP” whereas plants involves in the formation of “ATP”.
Citric Acid Cycle Citations
- Citric acid cycle and role of its intermediates in metabolism. Cell Biochem Biophys . 2014 Apr;68(3):475-8.
- Impaired Citric Acid Cycle in Nondiabetic Chronic Kidney Disease. EBioMedicine . 2017 Dec;26:6-7.
- Citric acid cycle redux. Trends Biochem Sci . 1990 Nov;15(11):411-2.
- Citric acid cycle intermediates in cardioprotection. Circ Cardiovasc Genet . 2014 Oct;7(5):711-9.
- The key role of anaplerosis and cataplerosis for citric acid cycle function. J Biol Chem . 2002 Aug 23;277(34):30409-12.
- Regulation of leukocyte function by citric acid cycle intermediates. J Leukoc Biol . 2019 Jul;106(1):105-117.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Growth Factors: Definition, Types, and Examples
Continue ReadingWhat are Growth Factors?
An irreversible, progressive change in a living being for a particular time according to the availabilities of the essential internal and external factors is growth.
In plant’s life term the growth is unlimited and continuous when optimal conditions are present.
Plant growth consists of development of the zygote to seed, on appropriate condition seed germinate to form root and shoot.
Proceeding from then seeds differentiates into different system of a plant bearing different functions.
Development and growth of a plant depend completely upon seed health and the external, internal factors aiding its growth.
Growth factors influence each stage of development by determining the availability of essential nutrients, climate etc., which are external and hormonal synthesis, physiological maintenance, availability of enzymes and substrate for metabolic process etc., are internal.
Growth efficiency is high when internal and external factors are available in essential level and are synchronous with each other enhancing the growth of an organism.
Type of Growth Factors
Growth factors are common for all plant species but the optimal requirement for each species differ making each species unique and distinct.
The common factors affecting the plant growth are divided into;
A. External Growth Factors
(i) Biotic Growth Factors: interaction of plants with other plants their response are all the biotic factors.
(ii) Abiotic Growth Factors: interaction of plants with external non – living factors playing crucial role in plant growth and development
B. Internal Growth Factors
(i) Genetic Growth Factors: the hereditary material made of nucleic acid which assigns different protein molecule for different functions are the genetic factors.
(ii) Physiological Growth Factors: Mainly includes the hormones and enzyme present within the body and the plant requirement.
A. External Growth Factors
External growth factors are components which influence the growth of plants from outside the plant body.
(i). Biotic Growth Factors: biotic factor which influences the plant growth from external sides are just interaction of plants to other plants and competition among themself for the survival of them. These are managed by certain behaviors namely;
Mutualism, Herbivory, Parasitism
a. Mutualism: the interaction between plants for their cooperative mechanism for survival and yielding benefit to each other.
Example: lichens
b. Herbivory: it is the nature of animals where it depends upon plants for survival. When excessive grazing tales place other organism inhabiting the same region has low survival rate.
c. Parasitism: interaction between two organisms where one benefits from the interaction others not and are deprived from nutrition making it hard to survival.
(ii). Abiotic Growth Factors: Factors which does not involve biologically but are essential for growth. Different factors that influence the plant growth are:
a. Climate: each plant has its suitable climate at which they grow well. The climatic factors include: Precipitation, Temperature, Humidity, Solar radiation, Wind velocity and Atmospheric gasses.
1. Precipitation: is of all forms such as Rain, Fog, Haze, Dew, Snow, etc., out of which rain fall is crucial in plant growth. Precipitation is completely dependent on the geography of a region. The slopes of Western Ghats receive high rainfall than the plains therefore considering the rainfall plantation crops are grown at the slopes of Western Ghats. Similarly drier regions support drought resistance plants such as sorghum, wheat, millet etc.,
2. Temperature: temperature is determined by the topography of the region. An ideal range for any plant is between 15° C and 38° C. But for the ideal plant growth each species is unique. The temperature also influences other body activity such as diffusion of the gasses, solubility of different materials, etc.,
3. Humidity: Humidity is the presence of water molecule n the form of water vapor. Higher the humidity lowers the rate of transpiration. Hence water accumulates causing decay of plants.
4. Solar Radiation – Light: Respiration is the process where the CO2 consumed to produce O2. This takes place by the process called photosynthesis. Incident of light is essential for synthesis of energy for plants survival. The radiation controlled the situation by determining the temperature of the region.
5. Atmospheric Gasses: in atmosphere the ratio of Carbon, Oxygen and Nitrogen must be balanced properly other wise imbalances can causes destruction to entire living system.
b. Edaphic Growth Factors: is noting but the specificities of soil for plant growth. The soil has several criteria namely: soil moisture, air, temperature, pH, mineral content, organic content and microorganism.
1. Moisture content makes the availability of nutrients to the plant easily attainable.
2. Soil Air provides aeration which removes any accumulation of undesirable gases, remove the dampness of the soil thereby providing an ideal environment which is free from infections.
3. Temperature, affects the physico chemical process taking place inside the soil and keeps the microbial activity under control and prevent microbial accumulation
4. Soil Organism, microbial growth is well associated with root nodules present in the plant where they fix atmospheric nitrogen to fulfil the nitrogen need for plants.
5. Other, factors associate well with the above factors provide an ideal internal environment for plant growth.
B. Internal Growth Factors
Factors which are present inside a plant body which are responsible for the growth of the plant.
The internal factors are a. Genetic factors and b. Physiological factors.
i. Genetic Growth Factor: the hereditary material becomes responsible for the blueprint of the organism, its productivity, survival capacity and others. In plant breeding technology new methods are employed to produce an ideal variety for better yield. Such efficiencies and capacities are present inside the cell and does not require other factors to promote it.
ii. Physiological Growth Factor: physiological factor is the hormonal and other factors which influence the plant growth. The growth of plants are dependent on the GROWTH REGULATORS, which are hormones which promotes or inhibits the growth.
These are done by 5 major hormones:
a. Auxins: enhance the cell elongation, enlargement, phototropism, geotropism, flower, root initiation, development of flower, root, fruit seeds etc.,
b. Gibberellins: affects the enlargement of organism, resisting the growth of plants as a whole.
c. Cytokinin: Cytokinin works along with auxin helps in cell enlargement
d. Ethylene gas: they diffuse easily throughout the body and ripens the fruit, seeds and are present in meristematic tissues,
e. Abscisic acid: intervene the growth promoting effect by reducing the growth promoting factors.
Growth Factors Citations
- The Pivotal Role of Ethylene in Plant Growth. Trends Plant Sci . 2018 Apr;23(4):311-323.
- Auxins as one of the factors of plant growth improvement by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Pol J Microbiol . 2014;63(3):261-6.
- Cytokinin signaling in plant development. Development . 2018 Feb 27;145(4):dev149344.
- Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci China Life Sci . 2020 May;63(5):635-674.
- Brassinosteroids: Multidimensional Regulators of Plant Growth, Development, and Stress Responses. Plant Cell . 2020 Feb;32(2):295-318.
Share
Similar Post: