Category: Biology
-

Colony: Definition, Meaning, and Examples
Continue ReadingColony Definition
• A group of organisms (usually of the same species) that live in close proximity to one another.
• A bacterial colony is a cluster of identical cells (clones) on the surface of (or within) a solid medium, often produced from a single parent cell.
What is Colony?
In biology, insect colonies are common examples of colonies. An ant colony, for example, is made up of ants who dwell close together for mutual benefits, such as greater defense.
Coenobium, a single-celled Volvox species colony, is an example of how single-celled organisms may form colonies.
When bacteria are cultivated in a solid medium, they form colonies. Because they are all descended from a single parent cell, the colony is actually (and ideally) a collection of bacterial clones.
The word colonia comes from the Latin word colonia.
Colony Citations
Share
Similar Post:
-
What is Symbiosis? Definition, Types and Examples
Continue ReadingWhat is Symbiosis
The word Symbiosis was coined by Anton de Bary which described about the interaction between two species to exist as long duration relationship. It is a type of a mutualistic relation between two species. When two different species come together in a relation where both of them in the interaction with each other get benefitted is called as Symbiosis. Both the species while living alone did not benefit in any way, thus the interaction of the species together will provide benefit to both of them. Similar to symbiosis there are other types of interactions as well such as Commensalism, Parasitism, Amensalism and others.
History and Etymology of Symbiosis
Symbiosis is a Greek word which means “living together”. It is believed to mean that symbiosis is the interaction of 2 different species. The term coined by Anton said that these relationships between two species can benefit as well as can cause harm to the species.
Later scientist began to explore whether the statement said by the scientist Anton was realistic. They realized that to fulfill the requirement of one and other species, two different species come together as one and stay in a relationship where both of them get benefitted or it could be where one species get benefitted and the other remains unharmed.
An example could be an organism, particularly eukaryotic living in conjunction with other organisms such as virus, archaea, bacteria are called as symbionts, whereas the larger one is called as host, which is the eukaryotic organism in this case.
However, at times to build a relationship, several obstacles are faced such as organelle differentiation which further leads to host and symbiont identification, followed by symbiont engulfment, host’s defense system is damaged, preventing the symbiosis, followed by physiological and genetic integration.
At times when two species stay together in a relationship for too long there are unique features and functions seen due to the evolvement of their relationship. These unique features are more clearly visible when they are in contact for longer duration.
Types of Symbiosis
There are 5 types of symbiosis and are:
a) Mutualism
One of the most common type of symbiosis is the mutualism. In mutualism, both the species get benefitted during the interaction. Although it could have an impact on the upcoming population and its survival. In such type of interaction, evolution takes place as they stay in conjunction to each other. Lichens are the example of mutualism.
Another example could be the relationship between algae and fungus, where fungus will provide support and protection and in return gets food from the algae, due to the photosynthetic pigment. Rhizobium legume symbiosis and arbuscular mycorrhizas are some examples of mutualism.
b) Commensalism
In this type of interaction one of the species gets benefitted while the other remains unharmed. This type of relationship is seen in organism found in the soil, where one organism provides the necessary requirements to the others.
Example of this type of interaction is when an organism produces antibiotic towards a pathogen, while protecting the plant. Bacillus and Pseudomonas are known to have such properties.
Another example in animals is remoras and sharks. To attract the prey towards itself remoras has a disk on which fishes such as bony fishes, sea turtle and others attach. Interaction between remoras and sharks make transportation, protection from preys possible to the shark and these remoras feed on small animals, zooplankton and host’s fecal matter.
c) Amensalism
In this type of interaction one species has a negative impact on the other, while the other species is hardly affected. Mussel beds incapacitates various species is an example of amensalism. Another example is taller plants which covers the shorter plant, thus the light reaching the shorter plant is very minimal or no light.
d) Parasitism
The relationship involving no mutual benefit is called as Parasitism. Majority of the species on earth are parasites. Example vampire, bats, nematodes, flatworms and etc. parasitism is the interaction where the parasite is dependent on the host to meet its requirement. Although the parasites are smaller than the host but they do not kill them instead feed on them. An example is tropical ants and a roundworm. Other example are tapeworms and fleas.
e) Predation
In this type of a relation, one species get rids of the other by killing them. In simple words the symbiont kills the host. An example of this interaction is sea anemone which are the host and the symbiont is the hermit crab.
Examples of Symbiosis
There are various example of symbiosis and they are:
a) Mycorrhizas
This is a very common type of interaction seen between plants and fungi. The fungi will form the arbuscular mycorrhizas (AM) and these fungi require host to outgrow, without the host they cannot grow. Thus, here one of them get the required nutrients whereas the other benefits from disease and drought occurrence.
b) Pinworm
Enterobius vermicularis, pinworm is the nematode causing infection to humans. This pinworm is an example of parasitic symbiotic relationship. These infections are seen in infants who are able to poop properly. The adult pinworms are found in the intestine and grow about a size of 1cm in size and these female adults come out of the host during the night move out and release eggs on the perianal skin. Within few hours the lifecycle of this worm is completed as the eggs are hatched and releases the infected larvae in the small intestine.
c) Amebiasis
This is a very dangerous issue in the countries developing due to the parasitic infection leading to major mortalities. The humans are the host and the protozoans interact with the host to slower the pace or fasten the disease. In children’s it causes diarrhea leading to death in various developing countries. When an infant is born, 1 out of 30 infants die every day due to diarrhea in developing countries like Bangladesh. The protozoan behind the disease is Entamoeba histolytica causing dysentery. However, other microorganism can also affect the interaction. When Entamoeba was cultured with other deadly bacteria, the effect of entamoeba might have increased or diminished.
d) Clownfish and Sea Anemones
There are various species which interact with sea anemones in various symbiotic relationship. However, the most commonly studied is the Clownfish. The interaction between the clownfish and the sea anemones is a mutualistic symbiosis one. Clownfish will deliver host with carbon, nitrogen and oxygen whereas the sea anemone will provide nutrition and protection. Thus, staying together and mutually get positively affected.
e) Oxpeckers and Mammals
In order for oxpeckers to adapt itself to various climates and conditions other mammals helps oxpeckers and are as follows: to hide they have sharp claws that helps in clinging. To support the oxpeckers, it has long tails. This relation is beneficial to both the species as oxpeckers have beaks which is sharp and flattened to catch ticks serving food to the others.
f) Black Walnut Tree
In amensalism, there is competition as well and its example is the Black walnut tree. This plant gathers harmful chemicals after it has aged to 25 years of age and does not allow any other plant to grow near it. The chemical behind this behavior is juglone, thus competing from the other plants.
g) Rhizobium Legume
For plants, nitrogen is very vital. Although it is available in the environment but its in the form that cannot be used and eukaryotes do not have the machinery to convert inert nitrogen into the required for. Thus, different relationship have been employed between diazotrophic bacteria and eukaryotes. Nitrogen fixing bacteria, Rhizobium is capable of fixing nitrogen. Thus, many species have thought to come in conjunction with the rhizobacteria. In exchange one gets the nutrition required whereas the other gets the fixed nitrogen.
h) Crabs and Sea Urchins
In the Indo-West Pacific region is a crab called Echinococcus pentagonus. These adults reside in the sea urchin’s rectum. Thus, they get food and shelter from sea urchin, whereas the younger ones and the males freely move on the surface. This type of relation can be considered as commensalism as well as parasitism because they do not kill their host.
i) Human gut Microbiota
Humans and microorganisms have a direct relation. The human gut is huge and inhabitates various microorganism, commonly known as gut microbiota. It is a symbiotic relationship because these microorganisms get shelter and in return, they break down food and provides human energy. However, this microorganism could also turn opportunistic and cause diseases. If these microorganisms are present at unnecessary places could cause major damage in humans.
j) Viruses
Virus also requires host to completes its role. They are parasites which completes its lifecycle by replicating and infecting. A virus can be mutualistic where both of them benefits or even parasitic or a commensal where one benefits and other is unharmed. There are cases where organism requires virus such as polydnavirus and wasps.
Holobiont
Thus, we can say that symbiotic relationships can be seen various categories and types of species. Species lives in symbiosis for various reasons as we know to obtain, shelter, nutrition, to feed on the other one and various others reasons.
A term called “Holobiont” was later discovered in 1991 by Lynn Margulis which meant a relation between the symbiont and the host, which was later stretched to determine the interaction between the host and various microorganisms. A holobiont comprises of microbiota and the host. A holobiont constitutes of all the interactions and is been studied in various fields of plants, animals and humans.
Symbiosis Citations
- What have we learnt from studying the evolution of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis? Curr Opin Plant Biol . 2018 Aug;44:49-56.
- The first thousand days – intestinal microbiology of early life: establishing a symbiosis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol . 2014 Aug;25(5):428-38.
- Nitrate-mediated control of root nodule symbiosis. Curr Opin Plant Biol . 2018 Aug;44:129-136.
- Secondary metabolism in the lichen symbiosis. Chem Soc Rev . 2018 Mar 5;47(5):1730-1760.
- Symbiosis. Curr Biol . 2006 Oct 24;16(20):R866-71.
- Symbiosis genes for immunity and vice versa. Curr Opin Plant Biol . 2018 Aug;44:64-71.
- Precarious Symbiosis Between Host and Microbiome in Cardiovascular Health. Hypertension . 2019 May;73(5):926-935.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Definition, Types, and Examples
Continue ReadingWhat is Stratified Squamous Epithelium?
A stratified squamous epithelium is a stratified epithelium with squamous (flattened and scale-like) epithelial cells in the top layer. Cuboidal or columnar cells may be seen in the deeper layers. Some stratified squamous epithelia are extensively keratinized, whereas others are keratinized either minimally or not at all.
Keratin is generated by keratinocytes, a highly specialised kind of epithelial cell. Keratin filaments grow increasingly numerous near the surface of highly keratinized epithelium, which on the dry surfaces of the body may consist of a layer of dead corneocytes.
The epidermis of the palm of the hand, the sole of the foot, and the masticatory mucosa are examples of keratinized squamous epithelial tissues. The mucosa of the oral cavity, anal canal, ectocervix, foreskin, and other linings of squamous epithelial surfaces that are mildly (or non-) keratinized are examples. This tissue is largely responsible for providing abrasion resistance.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Diagram
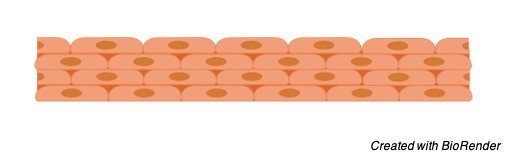
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Structure
The outermost layer of the skin and the linings of the oesophagus, mouth, and vaginal canal are examples of stratified epithelia in which the uppermost layer is made up of squamous epithelial cells.
An epithelial tissue comprised of more than one layer of epithelial cells is known as a stratified epithelium. The difference between it and a simple epithelium is that the latter has just one layer of epithelial cells.
The stratified epithelium’s basal layer is the only one in touch with the basal lamina. The cells in the basal layer divide mitotically, resulting in an increase in the number of cells on top of the basal layer. Mitosis produces new cells that replace the apical cells on a regular basis.
The stratified epithelium can be further divided into squamous, columnar, or cuboidal cells based on the kinds of cells found at the surface.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Citations
Share
Similar Post:
-

Living Things: Definition, Characteristics, and Examples
Continue ReadingLiving Thing Definition
A living thing is any creature or life form that possesses or shows the attributes of life or being alive. The following are the basic characteristics of life: an ordered structure, the need for energy, the ability to respond to stimuli and adjust to environmental changes, and the ability to reproduce, grow, move, metabolize, and die.
Living organisms are currently divided into three domains: (Eu) bacteria (real bacteria), Archaea (archaebacteria), and Eucarya (archaebacteria) (eukaryotes).
Living Thing Etymology
The term “living” comes from the Old English word “lifende,” which means “to live” or “to have a life.” The word thing comes from the Old English word ing, which means “entity,” “being,” “body,” or “stuff.” Organisms, living forms, and creatures are all synonyms.
Living Thing History
While the Earth is estimated to be 4.54 billion years old, life on Earth began much later, most likely about 3.5 billion years ago, while some scientists believe life may have begun much earlier.
Abiogenesis
Abiogenesis, or the natural process of life arising from non-living materials, is referred to as the origin of life. Scientists are still debating how this might have happened. There has never been an agreement about how life on Earth originated.
Primordial Soup
The term “primordial soup” refers to a hypothesized model of the early Earth in which biological material and water collected in a soup-like state. This soup functioned as a laboratory for the creation of organic substances. The Miller–Urey experiment is a generally recognized scientific finding. Chemical synthesis of the cell membrane’s basic structure (e.g., phospholipids creating lipid bilayers) and organic molecules from inorganic sources appear to have favored the simulated-primitive Earth. The primordial soup is also declared by Alexander Oparin and John Burdon Sanderson Haldane’s heterotrophic hypothesis of life’s beginnings.
RNA World Hypothesis
It’s possible that the shift from non-living to living beings happened gradually. The RNA universe theory, which argues that primordial life was based on RNA since it can function as both a genetic material and a catalyst, is one of the most prevalent hypotheses today. This RNA-based life might have been the forerunners of today’s life on Earth.
The building components of RNA and DNA may have started and developed in asteroids from outer space before being transported to Earth through meteorites. RNA and DNA nucleobases such as adenine and guanine were discovered in meteorites, according to NASA. These nucleobases might have resulted in the formation of RNA and DNA on their own.
The early living forms may have utilized these organic compounds to exist and reproduce. Single-celled creatures that appeared around the end of the Hadean Eon or early in the Archean Eon might be the first living forms. This is based on the finding of biogenic graphite in Western Greenland, which is thought to be 3.7 billion years old. Organisms without membrane-bound organelles were most likely the first to rule the planet. Prokaryotes are a category of bacteria and archaea that includes bacteria and archaea.
Endosymbiotic Theory
Endosymbiosis between a bigger cell and a prokaryote is thought to have resulted in the first photosynthetic eukaryote, according to the endosymbiotic theory. According to this idea, the bigger eukaryote may have absorbed prokaryotes that evolved into semi-autonomous organelles inside the cell, such as chloroplasts and mitochondria.
Multicellularity
Multicellular life is thought to have first appeared 600 million years ago and has recurred numerous times throughout biological history. Haeckel’s Gastraea Explanation is the most widely accepted theory on the genesis of multicellularity. As a result, multicellularity began when cells from the same species gathered in a blastula-like colony. Certain cells in the colony begin to differentiate over time. This idea, however, falls short of understanding the origins of multicellularity.
During the Ediacaran epoch, about 600 million years ago, a biota of single-celled and multicellular creatures thrived. The first creatures initially emerged in this biota. They resemble sponges and range in size from 1 cm to less than 1 meter.
Cambrian Explosion
In the Cambrian era, approximately 541 million years ago, a rapid explosion of life erupted. The Cambrian Explosion is the name given to this phenomenon. Plants and animals of all kinds arose. Animals began to go onto land in the late Cambrian or early Ordovician periods. Animals developed and diversified in tandem with the emergence of terrestrial plants. They eventually invaded terrestrial environments, including inland areas.
Current Population
In May 2019, the total number of species on Earth was predicted to be about 7.674 billion. According to the Census of Marine Life, there are around 8.7 million eukaryote species on the planet. Unfortunately, many of the world’s living organisms (estimated to be over five billion species) have gone extinct.
Classification of Living Things
Originally, living things were divided into two categories: plants and animals.
Animals and plants are both eukaryotes, but they are characterized by their distinguishing traits, such as motility, manner of feeding, and cellular structures. Animals are non-motile, photosynthetic, and have a cell wall, whereas plants are non-motile, photosynthetic, and do not have a cell wall. Bacteria and archaea, on the other hand, are neither plants nor animals since they are prokaryotes.
The RNA polymerase is one of the distinctions between bacteria and archaea in terms of bacterial and archaeal classification. It has 10 subunits in archaea. It contains four types of bacteria. The composition of the cell wall is another example. The peptidoglycan in archaeal cell walls is absent, but peptidoglycan is present in bacterial cell walls.
The categorization of living organisms into three domains is now used in modern biological taxonomy: (1) domain Eukarya, (2) domain Bacteria, and (3) domain Archaea. According to Carl Woese’s 3-domain system of taxonomy, a biological domain is the highest taxonomic rank of organisms. There are seven primary taxonomic levels below the domain.
Descending order:
Domain » Kingdom » Phylum » Class » Order » Family » Genus » Species
All eukaryotic living entities are included in the domain of Eukarya. Animals, plants, fungus, algae, and protists are among them. Within their cells, they have membrane-bound organelles.
Characteristics of Living Thing
Organisms that exhibit the qualities of life are referred to as living entities. The following features distinguish living things from non-living things:
i. An Organised Structure
Living things are a well-organized system. It might be single-celled, like a bacterial cell, or multicellular, like animals and plants, which have several cells. A cell is an organism’s most basic biological unit. The cell orchestrates and systematizes a variety of cellular functions. Protoplasm and a plasma membrane make up a cell. Organelles and other cytoplasmic structures are hung in the cytosol of the cell, each having their own tasks and functions.
ii. Energy-Requiring
The survival of a living organism involves the use of energy. Energy is necessary since it fuels a cell’s myriad metabolic operations. Photosynthesis, in which light energy is transformed into chemical energy, is one way that organisms generate energy. Another method is cellular respiration, which involves extracting biochemical energy from an organic substance (such as glucose) and storing it in an energy-carrying biomolecule like ATP for later use.
iii. Reproductive Capability
A live thing has the ability to reproduce. Living creatures can reproduce copies of themselves in two ways: sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. In sexual reproduction, the two parents’ sex cells combine to form a zygote, which will eventually develop into a creature of their own species. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, is a method of reproduction that does not require the use of sex cells. Only one parent gave birth to the children. Binary fission, budding, vegetative propagation, sporogenesis, fragmentation, parthenogenesis, apomixis, and nucellar embryony are examples of these processes.
iv. Growth
A living being develops. At the cellular level, growth can be defined as an increase in quantity or size. Cell division is the process by which the number of cells grows. Animal stem cells and plant meristematic cells divide in order to produce new cells. The rise in cytoplasmic bulk is frequently blamed for the increase in cell size.
In the cell cycle, the cell passes through a succession of stages. Interphase is the stage in which the new cell created by mitosis spends the majority of its time. It is the stage of the cell cycle during which the cell expands in size. The cell could copy its DNA to prepare for the next cell division if it is not fully differentiated. New cells in plants expand their capacity by absorbing and storing water in a vacuole.
Between the primary cell wall and the plasma membrane, some plant cells develop a secondary cell wall. There are two forms of growth in vascular plants at the tissue level: primary and secondary. Primary growth is characterized by vertical growth as primary xylem emerges from the procambium, whereas secondary growth is characterized by lateral growth as secondary xylem emerges from the vascular cambium.
The growth of tissues in higher animals follows a pattern that is genetically set. Plants have infinite regeneration capacities, while humans don’t. The amount of regeneration varies depending on the species. Salamanders, for example, can regenerate new eyes or limbs, whereas humans cannot. Humans, on the other hand, can regenerate specific sections of their bodies, such as skin and liver tissue.
v. Metabolism
Metabolize is the process by which a living thing breaks down its food. Metabolism refers to the different processes involved in a cell’s or organism’s ability to maintain its alive state. Cell development, respiration, reproduction, reaction to stimuli, nourishment, biomolecular syntheses, waste disposal, and other homeostatic activities are examples of those involved.
Catabolism and anabolism are the types of metabolism. Catabolism is a process in which living things carry out degradative chemical reactions that result in the breakdown of complex molecules into smaller components and the release of energy. Energy-driven chemical reactions in anabolism create compounds from smaller units.
vi. Responsive to Stimuli
Living things respond to stimuli and adapt to changes in their environment. It can detect changes in the environment, particularly through receptor cells. Humans, for example, have five basic senses: sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste. Vestibular sense (detects body movement, direction, and acceleration), thermoception sense, kinesthetic sense (detects body component positions), internal sense (interoception), and so on are some of the other senses. It is capable of not only detecting but also adapting to changes in its environment.
vii. Movement
The living thing is in motion. A living organism can respond to stimuli in its environment because it can detect them. Animals, for example, travel to forage, avoid predators, and find a suitable partner. Plants have a restricted form of mobility known as nastic movement, which allows them to move at will (e.g., thigmonasty, nyctinasty).
viii. Death
Living things perish. A living creature has a life, and that existence will come to an end at some point. Biological ageing is referred to as senescence. It occurs when the health of a living organism deteriorates over time. The organism’s ability to function and deal with stimuli deteriorates over time. As a result, it is more susceptible to illnesses and malfunctions.
The cell no longer divides at the cellular level, but it may still be metabolically active. The shortening of telomeres, which leads to DNA damage, is one of the natural causes of cellular senescence. Some living organisms, on the other hand, are thought to be eternal because they appear to be immune to death. Turritopsis doohmii, an age-reversing jellyfish, regenerating flatworms, and seemingly invincible tardigrades are all examples.
Non-cellular Life
Is it possible for viruses to live?
For a long time, biologists have been divided on this issue. Because viruses appear to be alive when they are within their host, some people consider them to be living things. They have genetic material, multiply, and evolve through natural selection. Others, on the other hand, do not regard them as living creatures because they are essentially dead when they are not in contact with their hosts. Viruses are incapable of self-replication.
They rely on the machinery of the host cell to do so. Viruses are thus neither alive nor non-living. Viruses are passive and appear to be lifeless when they leave their host. They become active once inside their host, able to use the host cell’s structures and proliferate. Viroids are another category of organisms that appear to exist outside of cells. Short strands of circular, single-stranded RNA are infectious and harmful.
Living Things Citations
- From Animaculum to single molecules: 300 years of the light microscope. Open Biol . 2015 Apr;5(4):150019.
- Viruses in the sea. Nature . 2005 Sep 15;437(7057):356-61.
- The disparity mutagenesis model predicts rescue of living things from catastrophic errors. Front Genet . 2014 Dec 4;5:421.
- Endosymbiosis and Eukaryotic Cell Evolution. Curr Biol . 2015 Oct 5;25(19):R911-21.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Genotype: Definition, Characteristics, and Examples
Continue ReadingGenotype Definition
A cell’s, an organism’s, or an individual’s genetic makeup influences its traits or phenotype.
What is a Genotype?
The terms genotype and phenotype are used to describe an organism’s characteristics or traits which identify alleles that are linked to a single trait (e.g., Aa) or a group of traits (e.g. Aa Bb cc). The term can be used to refer to an organism’s entire gene pool (or a taxon) that shares some similarities with the term genome, which refers to all of an organism’s DNA at this level.
However, genes do not make up all of the DNA. A collection of characters encoding the alleles for each of the 20,000 or so known genes in the human genome would be required to completely write down an organismal genotype.
The phenotype is the result of the genotypes’ expression and describes the physical or physiological characteristics of an organism. The genotype, however, is not the only factor that influences an individual’s phenotype, but various environmental variables also play a role, and they impact gene expression to define an organism’s particular phenotype.
Genes, Genotypes, and Alleles
Genes in most eukaryotes come in pairs known as alleles, which are found on the same chromosome (called a locus). They’ll be in charge of the same trait as well. The term “allele” refers to a gene variation. Because most eukaryotes reproduce sexually, each parent contributes one of a gene’s two alleles.
Random replication faults and environmental interactions with DNA have resulted in various alterations of each parent’s genes because each parent is the product of a separate lineage of creatures. This distinction is the source of the term “allele,” (allo = other), which means “other” or “different.” If the trait is inherited in a simple Mendelian pattern, one of the alleles will be expressed and the other will not.
The allele that is expressed is known as the dominant allele, whereas the allele that is not is known as the recessive allele. When the dominant allele is lacking, the recessive allele takes its place. When the dominant allele is “A” and the recessive allele is “a,” three genotypes are possible: “AA,” “aa,” and “Aa.”
The term “homozygous” is used to characterize the pairings “AA” and “aa” since their alleles are identical, i.e. both dominant and recessive. The allelic pair “Aa,” on the other hand, is referred to as “heterozygous.” Individuals with genotypes AA or Aa will show the dominant characteristic, while those with genotype aa will show the recessive trait.
Many genes contain many allelic variations, and not all gene pairs have a simple dominant/recessive connection, hence not all attributes are determined by a single gene.
A non-Mendelian kind of inheritance includes codominance, incomplete dominance, and polygenic inheritance. Many of the observable qualities in humans are non-Mendelian; height and skin colour, for example, are determined by the interplay of multiple genes at multiple loci, not just a pair of alleles.
Genotypes Examples: Punnett Squares
The alleles for only one or a few attributes are given in simple genotypes. Two alleles, R and r, reflect the genotype of the gene that affects the colour of the flower, for example, in which the dominant allele is “R,” while the recessive allele is “r.” The Red flower trait is coded by the dominant allele, while the white flower trait is coded by the recessive allele. Take a look at the image below for a visual representation of the chart.
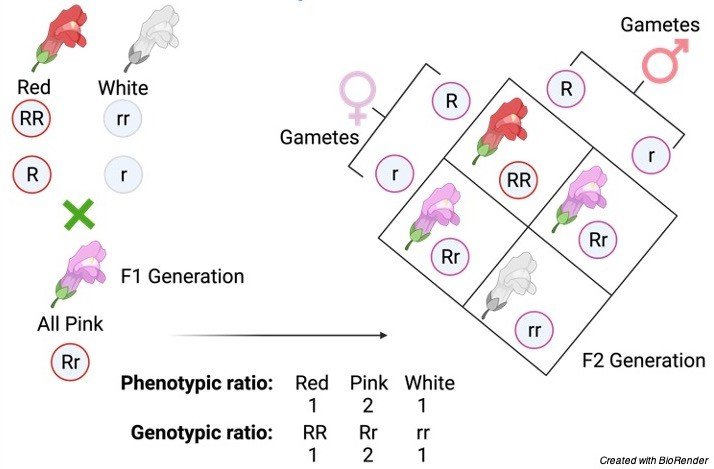
This is an example of a Punnett square, which was initially developed by Reginald Punnett after Mendel’s work was rediscovered. In genetics, the Punnett square is used to predict inheritance patterns and ratios. The genotype and phenotype of the offspring of two heterozygous (Rr) parents, both with pink blooms, are shown in this square.
The alleles contained in the parental gametes, as well as the progeny produced by various combinations of those gametes, are depicted in the diagram. Each parent creates two types of gametes (R and r), which are mixed together in every feasible combination.
Two of the four progeny are homozygous, one red (RR) and one white (rr), while the other two are heterozygous (Rr), both exhibiting pink as the dominant characteristic. This results in Mendel’s 3:1 phenotypic ratio of dominant: recessive phenotypes. It also tells us the genotypic ratio of RR, Rr, and rr genotypes, which is 1:2:1.
Genotype Citations
- Genotype and phenotype study of 34 Spanish patients diagnosed with oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. J Neurol . 2012 Aug;259(8):1546-52.
- Mechanisms of genotype-phenotype correlation in autosomal dominant anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia with immune deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2018 Mar;141(3):1060-1073.e3.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Chordata: Definition, Characteristic, and Examples
Continue ReadingWhat is Chordata?
Chordata is an animal kingdom phylum that comprises a diverse range of animals, including humans, and all creatures that have a notochord at some point in their lives belong to the Phylum Chordata.
A Phylum is a taxonomic classification that follows third in the hierarchy of classification after domain and kingdom. Creatures belonging to the same phylum possess similar features that distinguish them from organisms belonging to different phyla.
Chordata is a vast class of creatures that includes vertebrates, lancelets, and sea squirts, among others, and it includes several well-known vertebrates, such as reptiles, fishes, mammals, and amphibians.
What are Chordates?
Any animal belonging to the phylum Chordata is referred to as a “chordate.” “The chordates are the class of animals that, at least throughout some part of their development into adulthood, have four anatomical characteristics, namely;
(1) Notochord
(2) Dorsal nerve cord
(3) Post-anal tail
(4) Pharyngeal slits
Chordata Definition
a phylum of the animal world that includes all creatures with a notochord (a hollow dorsal nerve cord), pharyngeal slits, and a muscular tail reaching past the anus at some point in their lives. The subphyla Cephalochordata, Urochordata, and Vertebrata are included (vertebrates). From the Latin chorda, which means “cord” or “string.” chordate is a synonym for chordate.
Is it true that all chordates are vertebrates?
Chordates encompass all vertebrates. Not all chordates, however, are vertebrates.
Vertebrates have a post-anal tail, a notochord, pharyngeal slits, and a dorsal hollow nerve cord because they are chordates. Their notochord, on the other hand, develops into a spine, a column of bone vertebrae divided by discs.
Other common characteristics of chordates found in vertebrates include:
• Symmetry on all sides.
• Body with segments
• The firm’s full potential has been realized.
• A single nerve cord has a hollow dorsal end and a big anterior brain end.
• At any stage of growth, the tail projects far beyond the anus.
• There are pharyngeal pouches.
• A heart with a ventral location.
• A blood system that is completely closed.
• Blood vessels in the ventral and dorsal areas.
• A whole digestive system is available.
• Endoskeleton systems are cartilaginous and bony.
Chordates include pandas, crows, sharks, salamanders, alligators, sea squirts, and many others. So, to answer the question, which phylum contains amphibians, reptiles, and mammals, the answer is Chordata.
What about people... Are we chordates as a species?
Humans, too, are chordates. The human embryo generates a notochord, which eventually develops into a vertebral column, especially when the embryo develops into a baby. Any animal with a notochord at any time in its existence is called a chordate, as previously stated.
Chordata Characteristic
A notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail are all characteristics shared by animals in this phylum.
i. Notochord
The notochord is a flexible rod that runs down the organism’s body’s anteroposterior axis (from top to bottom) and is located dorsal to the stomach and ventral to the body’s central nervous system.
In reality, the chordates get their name from the notochord. This flexible, rod-shaped structure can arise at any time throughout chordate development and can even last until maturity.
Chordates with a notochord that lasts their entire lives use it for skeletal stability. The notochord is replaced by a vertebral column (spine) in other chordates, such as vertebrates, after the embryonic period.
Between the nerve code and the stomach tube is the notochord, which plays a crucial function in coordinating growth and development in vertebrates and is largely engaged in signalling.
The notochord of vertebrates, in particular, stimulates neural tube growth. The process of development is known as notogenesis.
ii. The Dorsal Hallow Nerve Cord
The dorsal hollow nerve cord is a hollow tube generated from the ectoderm and positioned posterior to the notochord during the embryonic stage of vertebrates.
In chordates, it may be observed near the top of the notochord. This tube is made up of nerve fibres that eventually grow into the central nervous system, which consists mostly of the brain and spinal cord. The vertebral column protects the dorsal hollow nerve cord.
The nerve cord, on the other hand, is not exclusive to chordates. Other animal phyla have it as well. In other species, it is ventral or laterally situated, as opposed to chordates, where it is dorsal to the notochord.
iii. Pharyngeal Slits
The pharyngeal slits are the apertures in the pharynx which are located below the mouth (or oral cavity) and extend to the outside (environment). Invertebrate chordates utilise these apertures for filter feeding. As water enters the mouth and leaves through the pharyngeal slits, it filters food particles.
The pharyngeal slits of aquatic animals, such as fish, are eventually converted into gill supports or jaw supports (as in jawed fishes). The pharyngeal slits are present in other animals, such as mammals and birds, at the embryonic stage and eventually integrate as portions of the ear and tonsils.
iv. Post-anal Tail
The post-anal tail is a posterior extension of the body that extends beyond the anus. The post-anal tail of aquatic chordates contains skeletal components and muscles, making it crucial for the organism’s movement in the aquatic environment.
By definition, locomotion refers to an organism’s ability to move from one location to another. Animal locomotion includes activities such as running, swimming, leaping, flying, and hopping. In this sense, the post-anal tail, for example, plays an important function in facilitating fish movement. The tail is utilised for balance and signalling in terrestrial chordates.
v. Reproduction and Life Cycle
The phylum Chordata encompasses the entire new and diversified class of vertebrates with a vertebral column, tunicates, and lancelets. Internal fertilisation and external fertilisation are the two methods employed for sexual reproduction.
The sperm and eggs (collectively known as the gametes) combine within the body during internal fertilisation. Because the sperm fertilises the egg outside the body in external fertilisation, this type of fertilisation is only found in aquatic creatures.
Many small species of lancelets, which are small fish-like organisms with a nerve cord supported by the notochord instead of a spine, are found in the Cephalochordata subphylum.
Males and females generate sperm and eggs, which are released at the same time for fertilisation during the mating season. The gametes are expelled into the water during spawning when the gonads eventually burst. Sexual or asexual reproduction is possible in the subphyla Urochordata and Vertebrata.
In fish, reproduction happens through external fertilisation, in which males and females release a high quantity of gametes to ensure successful reproduction. Amphibians, too, reproduce by relying on external fertilisation.
The breeding site is where the male and female generally meet (a pond or well of the leaf). Females lay a large quantity of eggs, whereas males lay a large number of sperm.
Evolutionary History of Chordata
The chordates first arose in evolutionary history around 530 million years ago, during the early Cambrian period, when jawless fish fossils first appeared. In 1995, the earliest fossil of the Chordata family was discovered in China, and it was identified as Yunnanozoon lividum.
The researchers estimate that the oldest fossils of tetrapods, mammals, and birds were found roughly 363, 80, and 208 million years ago, based on extensive research on chordate evolution.
The main reason for chordate evolution is large habitat changes, and the earliest chordates documented in the literature were all aquatic species like tunicates and lancelets. As a result of their progressions and evolutions, they eventually made their way to freshwater ponds and ultimately to land.
Many amphibians still choose to dwell in both terrestrial and aquatic settings, demonstrating the intermediary phase in which chordates transition from water to land. In addition, the expansion of the aerial population of birds resulted in a wide spectrum of chordate phylum diversities.
The researchers looked at the chordate’s evolutionary history in depth and came up with four major options, which are the Paedomorphosis theory, the Inversion hypothesis, the Aboral-dorsalization hypothesis, and the Auricularia hypothesis.
The first hypothesis argued whether chordates’ forefathers were free-living or intelligent. Similarly, the remaining three hypotheses shed information on the biology underlying chordate evolution and how they descended from a common ancestor. As a result, all four models are linked, and supporting arguments in each of them may occasionally overlap.
Phylogeny of Chordates
Urochordata (Tunicata), Cephalochordata, and Vertebrata are the three subphyla of Chordata (Craniata). The notochord, nerve cord, branchial slits, endostyle, postanal tail, and myotome are the distinguishing traits that have been used to classify these three types.
Chordata, along with the phyla Hemichordata and Echinodermata, is included in the superphyletic Deuterostomia. The chordates developed from deuterostomes as their common ancestor. As a result, the majority of scientists believe that the Urochordata was the first chordate phyla to emerge, followed by Cephalochordata, and finally Vertebrata.
In the phylogeny of chordates, the term protochordate has been widely used. On the other hand, there are numerous questions that readers frequently have about chordate evolution, and it has been demonstrated that an acceptable solution to all of these issues can be found using molecular phylogeny.
The researchers were able to reclassify the metazoan groups on a phylum level thanks to the broader classification in this field of science. The conventional classifications for Bilaterians and tripoblasts were protostomes and deuterostomes.
Based on the modes of diverse formations in the body cavity, the protostomes were separated into acoelomates, Platyhelminthes, and pseudocoelomates.
The molecular phylogeny did not actively support the indicated groups, instead relying on DNA sequences and protein-coding gene sequences. Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa were used to separate the protostomes into two primary groupings.
The echinoderms and hemichordates have established a clade. The urochordates, vertebrates, and cephalochordates make up another. The data from molecular phylogeny, mitochondrial and nuclear biology have all verified this. As a result, the Ambulacraria phylum is represented by the first clade, whereas the Chordata phylum is represented by the second.
In addition, cephalochordates were the first to develop in Chordata, with the remaining two species, urochordates and vertebrates, forming a sister class.
Chordata Classes
The phylum Chordata is divided into three subphyla: Urochordata, Cephalochordata, and Vertebrata. Only a few species are classified as Cephalochordata or Urochordata.
Most chordates, such as fish, animals, birds, and reptiles, are members of the Vertebrata (vertebrates) subphylum, with cartilage and bone backbones and a brain enclosed in a hard skull. There are over 50,000 species in this subphylum. They’re everywhere and can be found in a variety of environments, including marine, freshwater, and terrestrial.
Chordata have a unique feature: their bodies are bilaterally symmetric, making them different from other animal phyla. The chordates belong to the deuterostome family. The anus develops in the early embryonic stages before the mouth, which is one of the group’s hallmarks.
Fishes, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and mammals are only a few of the many kinds of vertebrates. Reptiles have scaly, water-resistant skins and are vertebrates which breathe air and lay shelled eggs. They are cold-blooded, which means they can not resist cold temperatures and rely on the temperature of their surroundings to keep their body temperature normal. They have four limbs in most cases. Some of the most frequent reptiles include turtles, chameleons, crocodiles, and snakes.
Amphibians are another well-known chordate group. The term “amphibian” refers to their ability to live in both terrestrial and aquatic environments. They are born in water and have tails and gills, but as they mature into adults, they develop lungs and legs, allowing them to live on land. Reptiles and amphibians have one thing in common: they are both cold-blooded animals, and the class includes frogs, newts, blindworms, salamanders, caecilians, and toads, among others.
The skeleton of chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) is made up of cartilage. They have an asymmetrical, upward-curling tail. Chondrichthyes have five to seven different gills on their bodies, and the reproductive cycle is carried out by modified fins that transfer sperm to the females. Rays, skates, sharks, and chimaeras are all members of the Chondrichthyes class. The Agnatha class of chordates, specifically vertebrates, is the oldest known class of chordates (jawless fish). The two main groups of Agnatha are hagifish and lampreys. Hagfishes are specialised scavengers, but lampreys are parasitic fishes that attach to other fishes and feed by sucking their blood.
Warm-blooded animals that make milk in their bodies and use it to feed their young are classified as Mammalia. They have the ability to regulate body temperature in any setting and keep the same temperature throughout their bodies. Their brains are larger than those of other vertebrates. Bears, camels, bats, dolphins, monkeys, and cheetahs are just a few of the most well-known Mammalia animals.
Ecological Importance of Chordata
Chordates play a critical function in maintaining the balance of our biosphere by preying on accessible insects and devouring algae and decaying plants that may flood ponds and streams, amphibians serve a critical role in wetland ecology. Furthermore, they serve as reliable markers of environmental health.
Similarly, the other chordates that are available are the primary source of sustenance for humans. Fish and a variety of other huntable creatures are examples of chordates. In addition, we have a variety of different mammals who live with us as pets and help us with a variety of daily activities. As a result, their utility and impact on our ecosystems are enormous.
Chordata Examples
As one of the many huge phyla present in our ecosystem, Chordata has many common instances. The lamprey, for example, is a vertebrate belonging to the Vertebrata subphylum. It’s a jawless fish that feeds on filter feeds and grows into an adult with an oral disc covered in sharp teeth that it uses to latch on to other fish (to obtain nourishment). Their bodies are made up of gills for breathing, a cartilage skeleton, a notochord, and a nerve cord. To capture the food particles, a mucus-secreting organ is used.
Sea squirts are another example of Chordata. They’re tunicates with a barrel-shaped body that’s linked to a substrate. Filter feeders, the adults of this species feed using specialised structures called syphons.
The vertebrates, such as bears, camels, bats, dolphins, monkeys, cheetahs, frogs, newts, blindworms, salamanders, caecilians, and toads, are among the chordates most of us are familiar with.
Chordates are organisms that have a structure called the notochord at some point during their development into mature organisms. The Chordata phylum is divided into three subphyla: Cephalochordate, Vertebrata, and Urochordata. Chordates have a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail, among other features.
Chordata Citations
- The vertebrate heart: an evolutionary perspective. J Anat . 2017 Dec;231(6):787-797.
- Chordate evolution and the three-phylum system. Proc Biol Sci . 2014 Nov 7;281(1794):20141729.
- Evolution of Allorecognition in the Tunicata. Biology (Basel) . 2020 Jun 16;9(6):129.
- Onto-phylogenetic aspect of myotomal myogenesis in Chordata. Folia Biol (Krakow) . 2004;52(1-2):1-12.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Cell Wall: Definition, Structure, and Function
Continue ReadingWhat is Cell Wall?
Outside the plasma membrane is another layer called as the cell wall. It is very important to the cell as it provides tensile strength, firmness and protection from the outer environment.
Cell membrane keeps the cell secured from the stress with the help of the cell wall and separates cell content from the outer environment. Cell wall is seen in plants, protist, fungi and majorly all bacteria excluding mycoplasma. Animals as well lack cell wall.
Cell wall can be defined as the structure which provides shape to the cell and is tensile and thick to protect the cell. Only cell membrane alone cannot protect the cell thus, there is cell wall which provides the aid to cell membrane.
Cell Wall vs Cell Membrane
The cell wall can be differentiated from cell membrane in various features and are:
a) Cell membrane thickness ranges from 7.5- 10nm in thickness and cell wall thickness is 0.1µm in thickness.
b) Cell membrane possess cell receptors whereas cell wall lack receptors.
c) Cell membrane is seen in all types of cells whereas cell wall is seen in protist, fungi, plants and other bacteria.
d) Cell membrane provides flexibility whereas cell wall provides rigidity.
e) Cell membrane is made up of carbohydrates, fatty acids and protein, however cell wall composition is dependent on the organism present.
Cell Wall Function
As the cell membrane is delicate, thus to protect the internal organelles and the genetic material, cell wall provides protection to the cell from outer environment. It also helps to provide shape to the cells.
Cell wall also has other function such as when too much of water has entered the cell, cell wall will prevent the cell from damage and contraction. Thus, to avoid this cell only permits tinier molecules to move, preventing unnecessary drugs and toxins to pass through.
Plant cell wall provides the cell from turgidness. In simpler words, whenever the cells internal pressure is too much due to the presence of fluids, cell wall protects the cell from bursting open by maintaining the pressure.
Thus, maintaining a balance. Some plants have single cell wall whereas others have two cell walls i.e., primary and secondary cell wall. The second layer of plant cell wall contains lignin and prevent water entering the cell.
Cell Wall Structure
Cell wall structure varies from species to species. In plant’s cell wall it consist of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin along with other polymers such as lignin, cutin and suberin. Algal cell wall are made up of agar and carrageenan such as polysaccharide, which are present in plants. Fungal cell walls are composed of N- acetylglucosamine, a chitin polymer. Bacterial cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan which is further composed of NAG and NAM residues.
Plant Cell Wall
Plants possess cell wall which protects the plant cell and provide support to the cell. Thus, the cell wall makes the plant cell stronger and rigid but not quite flexible when compared to animal cell.
Plant cell wall is made up polysaccharides such as hemicellulose, cellulose, pectin which encapsulates the cell making the cell survive the stress from the outer environment. Through glycan cross linkage are polysaccharide linked to each other forming a complex structure.
Some cells may also have another layer of cell wall underneath the other cell wall. Newly formed cell wall is the secondary cell wall whereas the old cell wall is the primary one.
The secondary cell wall is loaded with lignin and is thicker than the primary cell and doesn’t allow the movement of water across it. Between the two-cell wall is the lamella present which is rich in pectin and keeps the cells intact together.
What is the Function of Cell Wall in Plant Cells?
The various function of plant cell wall are:
a) Providing support to the cell
b) Maintaining shape
c) Encapsulates the cell
d) Movement of material from the cell and the environment
e) Maintains turgidity
Fungi Cell Wall
Fungi are eukaryotes and possess cell wall which safeguards them from being harmed. In fungi, the cell wall and cell membrane remain connected to each other. The basic function of cell wall is to protect the cell from the outer environment, stress, provides strength, rigidity, prevents from bursting open, controls the movement of solutes and integrity.
The cell wall possess receptors, which makes it possible to interact with the outer environment along with some other proteins. The proteins present on the cell wall will interact with the host during crisis to protect the cell. the cell wall of fungi is composed of glycoproteins such as chitins and glucans, which are absent in animal and human cells.
Thus, the antifungal drugs usually try to approach that area to obtain selectivity and specificity. Fungal cell wall possess a high molecular weight pigment called melanin, which is negatively charged. As melanin is hydrophobic to water it allows the cell to survive from high temperature, toxins, UV light. This is one of the major mechanisms of fungal cell to protect itself from host, however melanin could stop inducing phagocytosis and host immune response.
Cell wall of fungi can also be made up of another polysaccharide called glucan, which links itself to 1 and 3rd glucose molecule. Another polysaccharide found in fungi is chitin, having a dry weight of about 2% in yeast and in fungi around 10-20%. With the help of the enzyme N-acetylglucosamine chitin can be synthesized which gets piled in the extracellular space of cytoplasmic membrane. Proteins form a dry weight of about 20-30% in fungi and 30-50% of dry weight in yeast cell.
Algal Cell Wall
They resemble the plant cell wall, made up of polysaccharide and glycoprotein such as cellulose. Microfibrils are seen in the cell wall of red and green algae whereas alginic acid is contained in the cell wall of brown algae. In the cell wall of algae different compounds can assemble such as sporopollenin and calcium ions. For the synthesis of cell walls, a type of algae called diatoms uses silicic acid. Due to the synthesis of silica, energy of the cell is saved.
Molds Cell Wall
Molds are protist which looks like fungi. They could be seen on walls or in water ex slime molds and water molds. As they look like fungi they lack chloroplast, feed on dead matter but possess cell walls, made up of cellulose but does not contain chitin, which is a common feature of fungi.
Bacterial and Archaeal Cell Wall
Both bacteria and archaea are both prokaryotes. The cell provides tensile strength and is rigid. The cell wall of prokaryotes also serves as the site of action to check the activity of the drug.
There are two types of bacteria, such as gram positive and gram negative and these bacteria can be distinguished from the cell wall. Bacteria with gram positive cell wall have a thick peptidoglycan layer. In between the cell wall and plasma membrane is the periplasmic space, which contains teichoic acid such as ribitol or glycerol found in gram positive bacteria cell walls.
Teichoic acid regulates movements of cations, prevents cell lysis. It also helps to detects the cell as it possess antigenic character. The peptidoglycan is composed of repeating unit of disaccharide forming a structure of NAG and NAM residues respectively.
These N-acetyl glucosamine and N- acetyl muramic acid repeating units form the backbone linked by polypeptides. The mechanism of action of penicillin is also the same, it attacks the cell wall by disrupting the linkage and damaging the cell due to loss of structure.
Gram negative cell wall consist of a thin peptidoglycan layer, followed by an outer membrane. In between these 2 layers lies the periplasmic space. As the peptidoglycan layer is thinner it has more chances of getting damage from the outer environment.
Lipoproteins, lipopolysaccharide and phosphate is present in the outer membrane. Outer membrane shows resistance to bile salts, antibiotics, enzymes, detergents and various other things. There are pores present on the outer membrane which allows the entry of biomolecules such as amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins and fluids.
There is a lipid molecule present in the outer membrane called Lipid A. After the cell has died, lipid A is released. As gram positive cell wall has teichoic acid, in gram negative lipopolysaccharide is attached to lipid A.
The function of lipid A is that it acts an endotoxin causing vessel dilation, fever, blood clotting and others. Archaeal cell walls are composed of not peptidoglycan but proteins and polysaccharide. When archaea is seen under microscope it resembles gram negative bacteria although they are devoid of peptidoglycan.
Although they do not peptidoglycan but they have pseudo peptidoglycan containing N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid.
Cell Wall Citations
- Cell wall polysaccharides: before and after autolysis of brewer’s yeast. World J Microbiol Biotechnol . 2018 Aug 20;34(9):137.
- Imaging Bacterial Cell Wall Biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem . 2018 Jun 20;87:991-1014.
- Plant cell wall-mediated immunity: cell wall changes trigger disease resistance responses. Plant J . 2018 Feb;93(4):614-636.
- The Fungal Cell Wall: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Function. Microbiol Spectr . 2017 May;5(3).
Share
Similar Post:
-
Organic Compounds: Definition, Types and Examples
Continue ReadingWhat are Organic Compounds?
A compound falls into the category of organic when it is attached to another group which is either carbon- carbon or carbon hydrogen is said to be organic compound. When 2 or more than 2 groups are attached to each other chemically it is called as chemical compound. A single atom could also be referred to an element. An element forms a compound when there is a bond holding them up together.
In chemistry, compounds are broadly categorized into organic and inorganic compound. If organic compound is defined as the one containing carbon, then a compound is said to be inorganic if it does not possess carbon atom.
Organic Compounds Vitalism
The roots of vitalism has been seen coming from Greek philosophy and ancient Egypt. The basic thought behind vitalism is that living things differ from non-living, thus making the living things to produce chemicals. As living organism are in the influence of vitalism, they have the ability to make such compounds.
Scientist such as Louis Pasteur who was working on pasteurization and spontaneous generation, assumed that there is some life which is responsible in the fermentation process, as only something living had the ability to make a process such as fermentation possible and referred to them as vitalism and the followers were called vitalist.
The reactions which required a bit of alterations to be made were called as inorganic compound. However, the theory was latter rejected by various experiments conducted further. In 1828, a scientist Friedrich Wohler identified that using inorganic salts urea could be formed. However, the vitalism theory considered urea as organic compound, produced from living person only.
Organic Compounds Ambiguities
A compound is said to be organic if it possess carbon atoms bounded via a covalent bond. This is the definition of organic compound according to the modern era. However, it was difficult for the scientist to come up with a proper definition as with carbon atom in an organic compound, inorganic compound could also come into picture.
Example of inorganic compound containing carbon are cyanides, carbonate, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, thiocyanates, and structurally different forms of carbon such as coal, diamond, graphite are all composed of only carbon, therefore cannot be categorized into the class of organic compound.
Organic Matter
Although organic compounds on the earth’s crust form a small percentage, they are significant and are of great value. Organic compound examples are proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates. As living things are made up of carbon, thus when they die it can be degraded as these organic compounds can be broken to smaller ones.
Organic material is also secreted by living beings and this matter is found in the environment such as in soil, water where it could provide nutrients to other living organisms.
Natural vs Synthetic Organic Compounds
Organic compounds can be divided in various ways such as on the basis of its synthesis.
a) Natural Organic Compound: As the name suggests organic compound which are produced through natural sources such as plants and animals. Making them artificially increases the overall cost. Natural compound example are sugars, enzyme, antigens, lipids, neurotransmitters like protein, vitamins, amino acids, lectins, alkaloids and terpenoids.
b) Synthetic Organic Compounds: From the name itself it can be said that it is artificially prepared by making some chemical alterations in the reaction. To obtain synthetic compounds they might take place in a chemical reaction. They could use natural compounds as well in the process. Example plastics are synthetically produced.
Small Organic Molecules vs Large Organic Compounds
On the basis of the size or the length of the molecule it can be broadly categorized into small organic molecules and large organic molecule.
a) Small Organic Molecule: A molecule is said to be small if it has a molecular weight of less than 900 Daltons. Small molecules play a role in various processes example pharmaceutical drug. However, small molecules should not be misinterpreted with biomolecules such as protein, DNA, RNA and amino acids as they are huge.
b) Large Organic Compound: It is a macromolecule, or in simpler terms a huge molecule. This polymer is formed when many repeating subunits complete a large organic compound.
Organic Compounds Citations
Share
Similar Post:
-

Osmosis: Definition, Mechanism, and Examples
Continue ReadingWhat is Osmosis?
The net flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane is referred to as osmosis. It’s comparable to diffusion in that it moves downhill, from a higher to a lower concentration. However, in osmosis, the movement must take place over a semipermeable barrier.

Osmosis cannot be called osmosis without this component. While diffusion refers to the net movement of solutes between two solutions, osmosis is concerned with the net movement of solvent molecules, such as water molecules. The difference in water molecule concentration between the two sides of the membrane is what causes the water to migrate in order to bring the concentrations of the two sections closer together.
Osmosis Definition
Osmosis is defined in biology as the net transfer of water molecules from a higher to a lower water potential area through a semipermeable membrane (e.g., the cell membrane).
Other osmosis definitions are as follows:
1. The process of a solvent diffusing from a low-solute-concentration area to a high-solute-concentration area via a semipermeable barrier.
2. The ability of water to flow through a semipermeable barrier from a hypotonic solution (low concentration of dissolved chemicals) to a hypertonic solution (high concentration of dissolved substances).
Osmosis is characterized similarly in chemistry. When two solutions are separated by a membrane that selectively inhibits the passage of solute molecules while allowing the passage of solvent molecules. It is the passage of a pure solvent from one with a lower concentration of solutes to another with a higher concentration of solutes.
Osmosis Etymology
The word osmosis is a Latinized version of the now-defunct osmose. Osmotic is a derived word that means “pertaining to or of the character of osmosis.” Osmotic pressure, for example, is a pressure that occurs as a result of osmosis.
How Osmosis Works?
(1) net downhill flow of water molecules, (2) a selectively permeable membrane, and (3) an osmotic gradient are all required for osmosis to occur. Water molecules tend to migrate downhill, from a high-water concentration (or fewer solutes) to a low water concentration (or vice versa) (or greater solutes).
It cannot be considered osmosis if there is no net flow of water. It should also include a semipermeable barrier to allow for movement. Without it, the process is only diffusion rather than osmosis. Because water molecules are polar, channel proteins are required for them to travel along their concentration gradient.
These channel proteins are implanted in the cell membrane and create a hydrophilic conduit for water to flow through. The osmotic (pressure) gradient, or the difference in osmotic pressures between the two solutions, is what causes the water molecules to migrate.
Water potential is a measurement of the relative tendency of water to migrate from one location to another. The Greek letter Ψ is often used to symbolise it (Psi). Different tonicities of solutions produce a net flow of water across the cell membrane.
A solution consists mostly of the solute (material to be dissolved) and the solvent (the component that dissolves the solutes). The concentrations of components in two solutions will decide whether one is isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic in comparison to another.
Isotonic Solution
An isotonic solution is one in which the number of solutes in one solution is about equal to the number of solutes in another solution. A cell that is isotonic to the outside solution, for example, indicates that the internal fluid and the outside fluid have the same osmotic pressure and water potential. There will be no net flow of water molecules between the cell and the surrounding fluid in this instance.
Hypotonic Solution
A hypotonic solution is one that has a lower osmotic pressure (or contains fewer solutes) than the solution it is compared to. To dilute the solution, water flows toward the area with less water concentration or towards the more concentrated portion. Water will flow across the membrane and into the cell’s more concentrated solution if the fluid around the cell is hypotonic, for example.
Hypertonic Solution
A hypertonic solution is one that appears to be the polar opposite of a hypotonic solution. In comparison to the other solutions, a hypertonic solution contains more solutes and less water. Water will exit a cell submerged in a hypertonic solution to dilute the solution outside.
Osmosis Examples
i. Osmosis in Animal Cells
Osmosis is important in biological systems because many biological membranes are semipermeable, and it has a variety of physiological consequences. When animal cells are exposed to a hypertonic (lower water concentration) environment, the water leaves the cells, causing the cells to shrink. Crenation is the medical term for this ailment. When animal cells are put in a hypotonic environment (i.e., one with greater water content), water molecules migrate into the cells, causing them to expand. Cells will eventually rupture if osmosis persists and becomes extreme.
ii. Osmosis in Plant Cells
Plant cells do not rupture owing to an excessive amount of water input. Plants use their cell walls and vacuoles to protect themselves against excessive osmosis. The plant cell is stabilised by osmotic pressure exerted by the cell wall. Osmotic pressure, in fact, is what keeps plants upright. The big vacuole inside the plant cell aids osmoregulation, a regulatory process in which water potential is controlled to keep the osmotic pressure inside the cell within the optimal range.
Water efflux, on the other hand, does not protect plant cells. When a plant cell is put in a hypertonic environment, the cell wall is unable to prevent water loss. Cells shrink or become flaccid as a result of this.
Osmosis Citations
- Reverse osmosis desalination: water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res . 2009 May;43(9):2317-48.
- Brackish water desalination using reverse osmosis and capacitive deionization at the water-energy nexus. Water Res . 2020 Sep 15;183:116064.
- Emerging thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes for reverse osmosis: A review. Water Res . 2020 Apr 15;173:115557.
- Forward osmosis membrane technology for nutrient removal/recovery from wastewater: Recent advances, proposed designs, and future directions. Chemosphere . 2021 Jan;263:128116.
- Forward osmosis membrane processes for wastewater bioremediation: Research needs. Bioresour Technol . 2019 Oct;290:121795.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Decomposer: Definition, Types, and Examples
Continue ReadingDecomposer Definition
Decomposers are the organisms that have the ability to decay or break down the dead organisms. Decomposers are also defined as those organism that have the ability of decomposition.
What is a Decomposer?
The decomposers break down dead material of both animals and plants in the ecosystem. Decomposition is the process of breaking down the complex organic matter into simpler substances.
The examples of decomposers are bacteria and fungi. These organisms feed upon the dead organic material and convert the matter into simpler substances. They break down the nutrient matter of the ecosystem and play an important role in the food chain. This decomposed organic matter is recycled and absorbed by plants and other primary producers.
In ecological pyramid, they found in lowest position. Decomposers are heterotrophic organisms and get nutrients from the dead organic material.
Decomposers are mainly saprophytic in nature. The word saprophyte is made up of two words, sapro meaning “rotten material” and phyte meaning “plant”. Saprophytes are those organisms which feed upon the dead plant material or plant litter. The break the plant litter into molecular elements like carbon, calcium, and nitrogen etc. They convert the organic dead mass into simpler substances with some digestive enzymes.
For example, proteins are broken down into amino acids and carbohydrates are converted into simple sugars like glucose and fructose. They can survive in high humid conditions, and in presence of oxygen. Some common features of saprophytes include-
• Have filaments
• Heterotrophic in nature
• Reproduce by means of spores
Importance of Decomposer
There are various crucial functions carried out by the decomposers. In ecosystem, they have some major functions like decomposition or disintegration of the dead organisms.
Ecological Cleansers and Balance Providers: Decomposers play an important role in cleansing the environment by decomposing the dead material and also help to create a biosphere for the new life. Thus they have an important role as ecological cleansers and also in balancing the ecosystem.
Recycling of Nutrients: Decomposers convert the dead material into molecular elements like carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc. These elements are then absorbed by the primary producers like plants, algae etc., thus, decomposers helps in recycling the nutrients. The essential elements for the survival of producers are provided by decomposers.
Types of Decomposer
The decomposers are categorized into four types, namely fungi, insects, earthworms, and bacteria.
i. Fungi
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms that do not perform photosynthesis and feed on other organisms. Several fungi are saprophytic that feed upon dead material and principal decomposers in the ecosystem. Fungi secrete some enzymes in the environment to break down the plant litter into simpler molecules. These enzymes digest the material, which is absorbed by the fungi itself and thus, it get nutrient from the litter. Fungi grow in high humid conditions.
ii. Insects
Several insects like flies, maggots, dung beetles, and ants also help in decomposition. These insects are categorized as detritivores because they digest the dead material in their intestinal tract. Based upon the type of organic matter, the decomposers (insects) are classified into different categories-
• Dead plant tissue feeding insects
• Dead animal tissue feeding insects
iii. Earthworms
Earthworms are also considered as detritivores that orally feed upon the dead material. They are also known as friendly worms because of their ability to enrich soil by decomposition of litter. They release nutrients like phosphorus and calcium in the soil and helps to improve soil quality.
iv. Bacteria
Bacteria are microscopic, prokaryotic organisms that are ubiquitous in nature. They also involved in the process of decomposition. Bacteria also decompose the litter into carbon, nitrogen, etc. and helps in recycling of these nutrients. These nutrients are then absorbed by the producers of the food chain.
Decomposers and Detritivores
A group of organisms that break down the dead organic material into simpler molecules are called decomposers. The decomposers are categorized into two major groups: Detritivores and saprotrophs.
Detritivores are the type of decomposers including some animals like, worms and insects, whereas saprotrophs include fungi and bacteria. Sometimes, decomposers and detritivores are used as synonyms.
Decomposers Detritivores A group of organisms that decay the dead material. A class of decomposers that feed orally in the dead material. They act by secreting some digestive enzymes. Act by digesting the matter in their digestive tract. Cannot digest the large clumps of dead organic matter. They can digest upon large clumps. Examples- Fungi, bacteria, earthworms Examples- Earthworms, insects Decomposer vs Scavengers
Scavengers are the organisms that initiates the process of decomposition. There are some differences between Scavengers and decomposers-
Scavengers Decomposers The process of decomposition has initiated by scavengers. They act on the particles that are decomposed by scavengers. Act as initiators Act as finishers Example- Vultures, Flies Examples- Fungi, Bacteria, earthworms Decomposition Definition
Decomposition is the process of breaking down the dead organic material into simpler molecules. The process completed by some organisms called decomposers. Some common decomposers are fungi, bacteria.
Stages of Decomposition
The process of decomposition completes in five stages:
i. Fragmentation
The organic material is fragmented in this stage. The process initiates by detritivores to increase the surface area for decomposers. The detritivores feed upon the dead material and digest it with their digestive tract. Detritivores converts the matter into fragments for decomposers to act upon.
ii. Leaching
The fragmentation is followed by Leaching. In this stage, the water soluble nutrients present in the fragmented detritus are percolates through the soil.
iii. Catabolism
Third stage include secretion of enzymes by decomposers. These enzymes catabolize the decomposition process and convert the organic material into simpler substances.
iv. Humification
The formation of humus by dead matter is called humification. The amorphous substances form humus, which is very fertile.
v. Mineralization
It is the last step of decomposition. In this step the minerals are released in soil. The minerals or organic substances includes calcium, potassium, carbon, nitrogen etc.
Factors Affecting Decomposition
• Quality of Litter: Decomposition is affected by the structural and chemical properties of the litter.
• Temperature: The decomposition slower down with low temperature. Low temperature also decrease the microbial growth.
• Aeration: Aeration is essential factor for decomposition, thus oxygen is very important.
• Inorganic Chemicals: The process of decomposition decreases with presence of inorganic minerals.
• Moisture: moisture is essential factor that increases the rate of decomposition.
Decomposer Examples
i. Decomposers in Aquatic Ecosystem
1. Oceans / Seawater Decomposers: They are found in oceans and in seawater.
Some common examples are:
• Christmas tree worms
• Crabs
• Hagfish are the scavengers
• Sea urchin
• Tube worm
2. Freshwater Decomposers: Mostly found in fresh water bodies like rivers, ponds, etc.
Examples:
• Mildew
• Trumpet snail
• Water mold
• Yeast
ii. Terrestrial Ecosystem Decomposers
1. Forest Ecosystem Decomposers: Beetle, Earthworms, Millipede, Mushroom, Slime mold, Slug, etc.
2. Desert Ecosystem Decomposers: Dung beetle, Fly, Millipede, Saharan silver ant
3. Grassland Ecosystem Decomposers: Acidio bacteria, Termite
4. Mountain Ecosystem Decomposers: Mountain pine bark beetle, Purple fairy fingers
Decomposer Citations
- Role of phyllosphere fungi of forest trees in the development of decomposer fungal communities and decomposition processes of leaf litter. Can J Microbiol . 2006 Aug;52(8):701-16.
- Methods for assessing the impact of avermectins on the decomposer community of sheep pastures. Vet Parasitol . 1993 Jun;48(1-4):87-97.
- Stoichiometric imbalances between terrestrial decomposer communities and their resources: mechanisms and implications of microbial adaptations to their resources. Front Microbiol . 2014 Feb 3;5:22.
- Thermal adaptation of decomposer communities in warming soils. Front Microbiol . 2013 Nov 12;4:333.
- Current trends in forensic odontology. J Forensic Dent Sci . Sep-Dec 2017;9(3):115-119.
Share
Similar Post: