What is Primary Cell Wall?
Plants possess 2 cell wall primary and secondary cell wall and surrounding the secondary cell is the primary cell which is to the exterior. Primary cell wall are made up of hemicellulose, chitin, pectin and is flexible as well as thin in structure.
Plant cell has various components like various organelles, plastid, cell wall, cell membrane and vacuole. Encapsulating the protoplasm is the cell membrane, which distinguishes the outer environment from the interior.
On top of the cell membrane is the cell wall, which is seen in plants, fungi, algae and others, although the cell wall composition and structure varies from organism to organism.
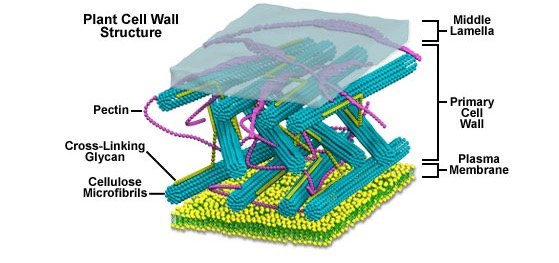
Primary cell wall is formed from hemicellulose, chitin, pectin and is flexible as well as thin in structure and the secondary cell wall is formed from lignin which is quite thick thus making it firm and does not allow water penetration and will stop increasing in size after the cell has matured.
The nearby cells are sticked to each other by middle lamella which comprises of pectin and lies between the walls. The osmotic pressure is maintained by cell wall.
Bacteria comprises of cell wall formed from peptidoglycan and there exist two bacteria types; Gram positive and Gram negative, where in gram positive there is a thicker peptidoglycan layer along with teichoic acid and in thinner in gram negative bacteria, whereas archaea have pseudopeptidoglycan layers made up of S glycoprotein. Chitin is the polysaccharide forming the cell wall and in algae it comprises of glycoproteins.
Features of Primary Cell Wall
There are two cell walls in plant called the primary and secondary cell wall and in between these lie the middle lamella. Primary cell wall are made up of hemicellulose, chitin, pectin and is flexible as well as thin in structure.
Secondary cell wall is formed from lignin which is quite thick thus making it firm and does not allow water penetration and will stop increasing in size after the cell has matured.
The nearby cells are sticked to each other by middle lamella which comprises of pectin and lies between the walls. Thus, the outermost layer is primary cell wall and after that is middle lamella and the last is the secondary cell wall.
You may like to read;
Top 20 Best FREE Plagiarism Checker Software
Top 20 Best Data Analysis Software Tools for
Biological Process of Primary Cell Wall
Expansion of a plants cell wall occurs through acid- growth mechanism, where the wall expands and this occurs at a low pH. Example is under acidic conditions, cell wall of a plant hormone auxin results in expansins which are proteins which relaxes the microfibrils of cellulose in the cell wall. Thus, volume of cell is increased and its extensibility also increases.
Primary Cell Wall Functions
Functions are to protects the plant from the outer environment such as mechanical stress, osmotic pressure, rigidity, strength and others.
As the cell wall cannot grow, thus by acid growth mechanism, cell wall extensibility can be increased. The surface of leaves and shoots which are juvenile are coated by wax and cutin, thus permeability barrier is formed by cell wall.
Primary Cell Wall References
Plant Cell Wall: https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plants/cellwall.html


