Author: Admin
-
Histone Protein: Definition, Modification, and Structure
Continue ReadingWhat is Histone Protein?
Generally, in biology, histones refer to the proteins of superior quality which is most abundantly found in lysine and arginine residues, which is abundantly present in eukaryotic cell nuclei.
Histones generally acts as a spool around DNA, which winds to create the structural units commonly known as nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are wrapped into a fibre of length 30 nanometre which forms a tight wrap around the chromatin.
Histones also prevent the DNA from becoming tangled or damaged. In addition to this histone also plays an important role in regulation of gene and in DNA replication.
Without the histones, unwinding of DNA in the chromosomes take a great time. For Instance, human cell contains about 1.8 meters of DNA, if it is stretched out completely.
When it is wounded with histones its size is reduced to about 90micrometers which is of 30nm in diameter of chromatin fibres.
Generally, histones are classified into five families, which are designates as H1, H2, H3, H4 and H5. These core formation of nucleosome has two H2A-H2B dimers and a tetramer as H3-H4.
During the tight wrapping of DNA with histones its extents to a large degree of electrostatic attraction between the positively charged lysine which thereby weakens the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged histones and a negatively charged phosphate which forms the backbone of DNA.
Chemical Nature of Histones
Histones are chemically modified with the help of enzymes which regulates the transcription in the genes. The most usual modifications are methylation of arginine or lysine residues or sometimes the acetylation of lysine.
Methylation effects the proteins of transcriptions factors which interact with the nucleosomes.
Acetylation of lysine weakens the electrostatic attraction between the histone and the DNA; which results in unwinding of DNA and makes it more accessible for the expression of genes.
Classes and Variants of Histones
As mentioned earlier histones are composed of five major families ranging from H1 TO H5. Where as the histones H2, H3, H4 are known as core proteins and the histones H1 and H5 are known as linker histones.
The core histones exist as dimers that are similar to that histone fold domain. Two alpha helixes are linked by two loops, which is the helical structure that allows the interaction between distinct dimers especially in between head and tail regions.
Then the resultant four dimers come together to form one octameric nucleosome core, which weighs approximately of Angstroms.
The linker H1 binds the nucleosome at the entry till the end sites in the DNA, which helps in locking the DNA in its place and allows the formation of higher order structure.
The most basic such formation results in the formation of string conformation with beads which is of 10nm as a fibre, which helps in wrapping of chromosome around the nucleosomes with an approximate of 50 pairs which separates the pair of nucleosomes.
Structure of Histones
The nucleosome core is made up of two dimers namely H2A-H2B and H3-H4which are nearly symmetrical halves by a tertiary structure.
The H2A-H2B dimers and H3-H4 tetramer also show the pseudodyad symmetry. Whereas the four-core histone are relatively similar in structure and they are highly conserved through elevation, which features a helix to turn into helix motif.
They also have a feature of long tails at one end which carries an amino acid structure of being the location of post-translational modification.
Archael histones contains H3-H4 like dimeric structure which stacks it into a tall superhelix onto which DNA coils similar to that of nucleosome spools.
Only few archael histones have tail. The distance between the spools in the eukaryotic cells ranges from 59 to 79 angstrom which winds the DNA.
Histones and their Interactions with DNA
All histones have the capability to make five types of interactions with histones. They are as follows, Salt bridges and hydrogen bonds between the chains of amino acids and phosphates of oxygen in DNA.
Helix-dipoles forms alpha-helixes in h2b, h3 and h4 which causes a net positive charge to accumulate at the point of interaction with the negatively charged groups of phosphate on DNA.
Hydrogen bonds between the backbone of DNA and the amide group in the main chain of histone proteins. Nonpolar interactions between the histone and deoxyribose in the DNA.
Non-specific minor grooves intersect into the two minor groove on the DNA molecule. Generally, genes are active and are less bound to histone, where inactive genes are highly associated with histones during the period of interphase.
It is also confirmed that structure of histones is evolutionarily conserved though the deletion mutations are severely maladaptive.
All histones are highly positively charged with lysine’s and arginine residues.
Function of Histone
Histones generally acts as a spool which winds around the DNA. Thus, enabling to fit the large genomes of eukaryotes inside the nucleus of the cell. Where the compact molecule is 40,000 timed shorter than the unpacked molecule.
Regulation of Histones
Histones undergoes pot translational modifications which alters the interaction between DNA and the nuclear proteins.
The H3 and H4 histones contains longer tails which protrudes out of the nucleosome, which is modified covalently at several places.
Modifications takes place through methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, SUMOylation, citrullination and ribosylation with ADP.
The core of histones can also be modified. Combinations of modifications constitutes a code which is known as histone code.
These modifications act in diverse biological processes like gene regulation, DNA repair, condensation of chromosome and in spermatogenesis.
Histones Citations
- Overview of Histone Modification. Adv Exp Med Biol . 2021;1283:1-16.
- Histones and genome integrity. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) . 2012 Jan 1;17:984-95.
- Linker histones: History and current perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta . 2016 Mar;1859(3):431-5.
- The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature . 2000 Jan 6;403(6765):41-5.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Nucleosome: Definition, Structure, and Function
Continue ReadingWhat is Nucleosome?
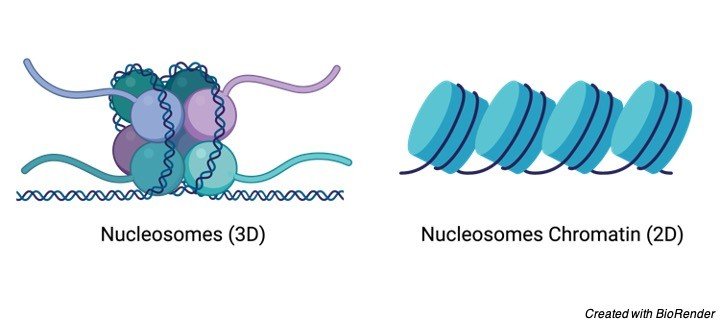
Nucleosome is one of the sections of DNA, which is wrapped around a core of proteins. Where the DNA forms a complex with protein inside a nucleus which is called as chromatin.
This chromatin allows the DNA to get condensed and thus reduces its volume. When this chromatin is extended and observed under a microscope, it resembles a structure of beads on a string.
Where these tiny beads are called as nucleosomes which has an approximate diameter of about 11nm. The nucleosome is one of the fundamental subunits of chromatin.
Each nucleosome constitutes a set of eight proteins which are wrapped around a DNA. And this is commonly referred to as histone octamer. Thus, each histone octamer has two copies of histone proteins of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4.
This chain of nucleosomes is further compacted and made into a highly organised complex structure of DNA and a protein named chromosome.
Nucleosome is a Unit of Chromatin
Nucleosomes are considered as the basic unit of chromatin as if the cells are the basic unit of life. Thus, the basic structural and functional unit of chromatin is the nucleosome which is made up of eight histone proteins, so it is also called as histone octomer.
While observing chromatin under an electron microscope it looked like a bead present on the string. It gave a clue that nucleosomes exist and the other clue is got by chemical cross-linking of histones in chromatin.
Structure of Nucleosome
When chromatin or whole chromosomes are let to read in air or water interface and examined under an electron microscope, a fibres of length 250 Angstrom are noted.
These fibres are generally known as deoxy-nucleosome proteins fibres which is present in the DNA complex along with the proteins.
This removal of protein can be carried out by several methods which reveals the fibre of 10nm, which acts as a subunit of chromatin.
Pronase is used in the digestion of 10nm fibre which leaves the sensitive DNAs of 2nm with the single DNA double helix.
It is now found that only a small fraction of eukaryotic chromatin is found in an active form and the remain part in a particular nucleus remains inactive.
Actually, there are two kinds of active regions which are recognised as the nuclear regions for coding the rRNA. And non-ribosomal cistrons.
Here the active chromatin shows the molecules of nascent RNA along its axis of DNA. Which is separated by the non-transcribed spacers.
Where as the inactive chromatin has a structure, which looks alike of beads present on the strings, and finally this is called as nucleosomes.
In the year 1974, researcher Olins and Olins experimented chicken embryo with the Millers technique and found the numerous fibres present along with a knob like structure which are released out with the nuclei. Beaded structures were also called as nu bodies.
Where as the other researchers, Oudet, Grosss-Bellard and Chambon seen many similar beads in the chromatin preparation which is collected from many vertebrates, in the year 1975. And they introduced them into nucleosome.
It is generally present in all eukaryotic cells and they are studied in plants and animals in their mitotic and polytene chromosomes.
The bead connecting to the strings constitutes one repair unit and it is structurally made up of about 200 base pairs in the DNA along with all the five histone proteins.
This bead consists of about 140 base pairs of DNAs which is wound in to two complete super-helical turns which is around a protein core and consists of 2 molecules of the histones each. H2A, H2B, H3 and H4.
There are about 60 base pairs that are present in the DNA which connects the strings with the histone H1. Where as the core particles are used for the construction of beads. And the connecting filaments are present in the linker region.
Thus, the DNA in the chromatin is packed with a series of repeated units of two distinct parts such as core particles and a liker region.
Where the chromatin present in the protozoans and in lower eukaryotes shows the similar length of 140 base pairs in the DNA.
But the length of the linker is variable even within the same tissues comparing with different species.
The nucleosome model of chromatin structure is attractive as it explains the packing of long strands of the DNA as the smaller repeat units which are known as nucleosomes.
Chromatin and Nucleosomes Structure
On analysing chromatin biochemically, it supports the concept of nucleosome. When chromatin is digested with the micro-coccal nuclease, it produces an oligomeric fragment of DNA with the specific lengths which corresponds with the repeat units which is being observed in electron microscope.
X-ray diffraction and scattering studies on crystallised DNA also proved the existence of nucleosomes.
In the diffraction of x-rays, it has been shown that it consists of a double helical DNA which is wound around a core of histone proteins with the super helix having a pitch of about 28A with the 1.75 windings around the DNA.
Function of Nucleosome
Nucleosomes are considering as the basic packaging unit in the DNA which is built with histone proteins and it is coiled around the DNA.
It generally serves as a scaffold for the formation of higher order of the structure of chromatin. It also acts as a lyre for controlling the expression of genes by following the concept of gene expression.
This functions smartly in reducing the over all length of the DNA which is present in the nucleus and help to keen the chromatin in an organised manner.
It is also known for its three primary functions first they provide space for packing and stabilising the negative coiling of the genomic DNA, through invivo.
The histones in a nucleosome are post transitionally replaced by the variants of histones for providing an additional epigenetic layer of information to get associated with the genome.
The third thing is that nucleosomes have the capability to regulate the transacting factors directly to function the elements in the chromosomes by virtue.
Nucleosome Citations
- The nucleosome: from structure to function through physics. Curr Opin Struct Biol . 2019 Jun;56:119-130.
- Histone core modifications regulating nucleosome structure and dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2014 Nov;15(11):703-8.
- A brief review of nucleosome structure. FEBS Lett . 2015 Oct 7;589(20 Pt A):2914-22.
Share
Similar Post:
-

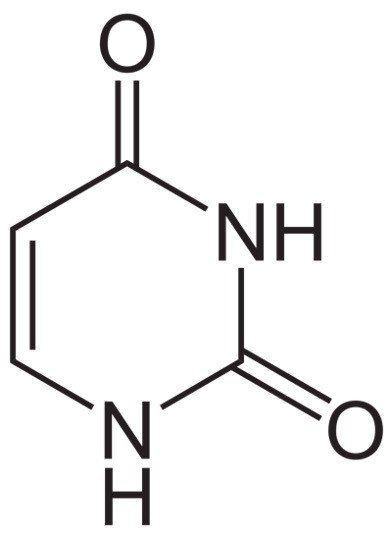
Uracil: Structure, Definition, & Functions
Continue ReadingWhat is Uracil
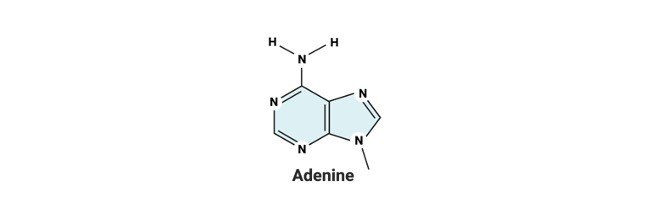
Uracil is one of the nucleobases in the RNA, such as adenine, Guanine and cytosine where as in all living beings that contains DNA, lack uracil in its nucleotide base pairs.
It has adenine, thymine, Guanine and Cytosine, where adenine pairs up with thymine and guanine pairs up with cytosine, in case of RNA, thymine is replaced by the base pair uracil.
Uracil is also said to be the demethylated form of thymine. Uracil combines with the adenine through two hydrogen bonds.
Generally, Uracil is considered as one of the natural derivatives obtained from pyrimidine.
The term uracil was first coined by a German Chemist named Robert Behrend during his attempt of synthesizing derivatives in the uric acid. But it was first discovered by Albert Ascoli in the year 1900 during the process of isolating yeast nuclei by hydrolyzing.
Uracil have also been found in bovine thymus, spleen, herring sperm and in germ of wheat. It is basically a planar, unsaturated compound which has the ability to absorb light.
Based on the carbon ratios present in the organic compounds,12C/13C is considered as isotopic ratio; there are observed to be in the Murchson metrorite.
It also said that Uracil and Xanthine are mostly related molecules. and they have the ability to form during extraterrestrials.
On other analysis during the collection of data from orbiting the Saturn. It is also observed that Titan’s surface may also contain an uracil.
Properties of Uracil
Usually in the nucleic acid RNA, Uracil combines with adenine and it is further replaced by thymine during the transcription of DNA.
This evolutionary substitution of thymine instead of uracil increases the stability of the DNA. And it improves the efficiency of DNA replication.
Uracil pairs with adenine with the help of two hydrogen bonds. When this base pair occurs uracil act as a both donor and acceptor of a hydrogen bond.
Where as in RNA Uracil binds with the ribose sugar to form a ribonucleoside uridine. When a phosphate attaches to uridine, it results in the production of 5’-monophosphate.
Uracil undergoes the tautomeric shifts of amide-imidic acid because lack of nuclear stability of the molecule leads to the unformal aromaticity during cyclic-amidic stability.
Here the tautomer of amide is referred to as lactam in structure and the imidic tautomer is referred to as lactim in structure.
These tautomeric forms are mostly predominant only at the ph. of 7. This lactam structure is the basic and common form of uracil. Uracil recycles itself to form nucleotides by undergoing series of phospho- ribosyl transferase reactions.
Degradation of these reactions results in the formation of substances like aspirate, carbon dioxide and ammonia. Uracil is generally considered as a weak acid.
Uracil and DNA
Uracil is most rarely found in the DNA. Because it often undergoes evolutionary changes which helps in increasing the stability through generations.
Because in cytosine diamines spontaneously produces uracil. By the process of hydrolytic deamination.
So, it can be said that if any organism uses uracil in DNA, the cytosine deaminates and leads to the formation of thymidine.
During the process of synthesis of DNA, the deamination of cytosil occurs which leads to the formation of uracil. During this process uracil-DNA bases excises from the double stranded DNA.
This enzyme recognises and cut the both types of uracil, where as the one is formed due to the cytosine deamination and the other would trigger unnecessary and unappropriated repair processes.
During the process of evolution, this is been solved by methylating uracil. This methylated uracil is being identical to thymine; hence this hypothesis states the reason for thymine being replaced by uracil.
So, the cells continue to use Uracil in RNA and it is not used in DNA, because RNA lives shorter than that of DNA.
If any potential errors occur in case of uracil, it leads to the damage in a particular strand.
There is also no evolutionary pressure in the RNA, to replace uracil with complex thymine’s, Some DNAs which consists of uracil still exists in some cases such in; DNA of several phages, end pterygote development, Hypermutations occurs during the synthesis of vertebrate antibodies.
Uses of Uracil
Uracil helps our body to carry out the synthesis of many enzymes which are necessary for the cell to function while bonding with ribose’s and phosphates.
Uracil serves as allosteric regulator and coenzyme for the reactions in plants and animals. UMP (Uridine Monophosphate) helps in controlling the activity of carbamoyl phosphate synthesis and in aspirate transcarboxylase in the plants while UDP and UTP helps in regulating the Cause II activity in the animals, where as UDP-glucose regulates the conversion of glucose into galactose in the organs such as liver and other tissues in the process of carbohydrate metabolism.
Uracil is also involved in the in the biosynthesis of polysaccharides and in the transportation of sugars containing aldehydes.
Uracil is also important in the detoxification of many carcinogens which is found in the cases of people who consume tobacco and smoke.
Uracil is also required in the process of detoxifying the drugs such as cannabinoids and other morphines.
If the body faces extreme deficiency of folates, it increases the risk of cancer, because the deficiency of folate the increases the ratio of deoxy uridine monophosphate or deoxythymidine phosphate and leads to misincorporation into the DNA which in turn results in low production of DNA.
Uracil has also been used in drug delivery in pharmaceuticals and also in medicines.
Uracil can also be used to determine the microbial contamination of tomatoes by indicating the lactic acid contamination in the fruit.
The mixtures containing uracil are most commonly use to test the reverse phase of HPLC columns.
Uracil Citation
- Uracil within DNA: an actor of antiviral immunity. Retrovirology . 2008 Jun 5;5:45.
- Uracil DNA glycosylase uses DNA hopping and short-range sliding to trap extrahelical uracils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2008 Aug 5;105(31):10791-6.
- Therapeutic potential of uracil and its derivatives in countering pathogenic and physiological disorders. Eur J Med Chem . 2020 Dec 1;207:112801.
Share
Similar Post:
-
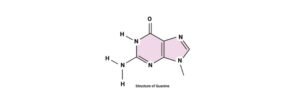
Guanine: Structure, Definition, & Functions
Continue ReadingDNA and Guanine
Generally, all complex substances are made up of smaller building blocks, considering an example where our house is built with bricks, stones, woods, etc. and as the same; our body is made up of cells which form the basic unit of live.
Likewise, DNA is also made up of smaller molecules which together functions as the important substance to live in.

We know that DNA is a complex molecule made up many substances like phosphoric acid, sugar (5-carbon) and nucleobases.
There are five nitrogenous bases which serves as the most vital and important component in the functioning of the DNA.
The nuclear bases are mostly of adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine, and uracil in case of RNA.
These bases are generally classified into two types namely purine and pyrimidine.
History of Guanine?
Guanine was first isolated by Julius Bodo Unger a German chemist in the year 1844. It was first obtained by him in the form of mineral which is extracted from the excreta of sea birds. Which is commonly refers to as guano. It is was then used as a source of fertilizer.
It was later named as guanine in the year 1846. In between the years 1846 and 1906 the scientist named Fischer showed the structure and described the conversion of uric acid into guanine.
What is Guanine?
Guanine is a purine nucleobase. The chemical formula of guanine is C5H5N5O. Where the purines are heterocyclic aromatic compounds which are organic in nature.
As these purine and adenine is composed of two carbon rings namely pyrimidine ring and an imidazole ring.
Guanine can be seen in both DNA and RNA. Its complementary base pair is cytosine which combines with it in a DNA or RNA with the help of three hydrogen bonds.
Guanine is one of the groups of organic compounds which belongs to the group of purines.
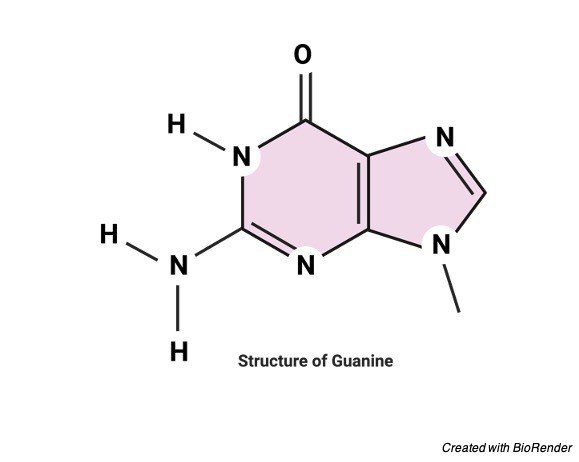
It is generally characterized by its two-ring structure which is made up of carbon. And nitrogen atoms and other free occurring or combines diverse group of substances like dead bodies of other lower vertebrates like bats, birds and sealed and sugar beets, yeasts and scales of fish.
It is one oof the component of nucleic acid and one of the vital cellular components in storing and transmitting hereditary characters to the next generation.
It was first discovered by the scientist named Guano in the year 1846 and was first isolated from the nucleic acid in the year 1891.
The other complex molecules that are obtained from nucleic acids include the nucleoside, guanosine and deoxyguanosine where guanine is combined with the sugar molecules like ribose and deoxyribose and it also includes other nucleotides like guanylin acid and other dioxygenyl acid, where the phosphoric acid diester bonds of guanosine and deoxyguanosine.
Nucleotides are the molecules that constitute the fundamental and structural units of nucleic acids.
Nucleotides are the smallest subunits lacking the phosphoric acid.
Characteristic of Guanine
Along with other nucleosides guanine is present in both nucleic acids like DNA and RNA.
Guanine usually have two tautomeric forms, where as the one is commonly present keto group and the other is rarely present enol form.
Guanine always pairs up with cytosine of the amino group which acts a bond donor for hydrogen.
This nucleotide is hydrolyzed with the strong acid like glycine, ammonia, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
First the guanine is deaminated to become xanthin. Guanine then readily oxidizes adenine which is the other purine derivative in the basses of DNA.
Guanine has a melting point of about 350ºC which reflects the intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the amino groups in the molecule of crystal.
Due to its intermolecular bonding of hydrogen between these two oxo and amino groups guanine is relatively insoluble in water but it is soluble in other dilute acids and bases.
Biological Uses of Guanine
The word Guanine was being derived from the Spanish word guano. Guanine has a wide variety of biological functions ranging from its complexity and versatility. Which includes the display, camouflage and vision and also for many other purposes.
Albburns is extracted from the scales of fish and is commonly called as pearl essence and it is generally a crystalline guanine. This crystalline guanine is used in a cosmetic industry for additive purposes in the manufacturing of shampoos which is the main reason for their iridescent pearly effect.
This is also being used in the metallic paints, synthetic pearly and also in plastics.
It is also being used in eye shadows and in nail polishes artificially.
Guanine is also used as substrate in spray paintings and in the lustrous paint materials. Whereas spiders, scorpions and some other amphibians converts the ammonia into guanine by a protein metabolism, which takes place in the cells.
In such case guanine is excreted with the minimum loss of water. Guanine is also found in the specialized skin cells which are found in fishes and in some amphibians namely iridocytes.
It is also being present in the deposits of eyes in the deep-sea fishes and in some reptiles such as crocodiles.
Guanine Citations
Share
Similar Post:
-
Cytosine: Structure, Definition, and Functions
Continue ReadingDNA and Cytosine
Generally, all complex substances are made up of smaller building blocks, considering an example where our house is built with bricks, stones, woods, etc. and as the same; our body is made up of cells which form the basic unit of live. Likewise, DNA is also made up of smaller molecules which together functions as the important substance to live in.

We know that DNA is a complex molecule made up many substances like phosphoric acid, sugar (5-carbon) and nucleobases.
There are five nitrogenous bases which serves as the most vital and important component in the functioning of the DNA.
The nuclear bases are mostly of adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine, and uracil in case of RNA.
These bases are generally classified into two types namely purine and pyrimidine. As every large molecule are made up of smaller sub units DNA is also made up of sugar and phosphate bonds and nucleotide bases.
One such nucleotide base pair is cytosine. Cytosine bases is one of four chemical bases present in the DNA, whereas the other three are adenine, Guanine and Thymine.
Inside a DNA molecule cytosine strands are located on one strand of DNA with the help of chemical bonds it pairs up with guanine in the opposite part of the strand. These sequences help in coding the genetic instructions to the cell.
Cytosine is first named by Albercht Kossel and Albert Neumann in the year 1894 from the thymus tissues of calf. The structure of cytosine as first described in 1903
What is Cytosine?
Cytosine is considered as one of the bases that are present in the nucleic acid of a molecule. Nucleic acids are usually composed of five carbon sugar bond which is combined to that of a phosphoric acid, with its nitrogenous bases deoxyribonucleic acid which is considered as an important hereditary material.
Such nucleobases are needed and found as most vital thing in all the organisms which is consisting of five carbon sugar deoxyribose with phosphate bond linked to it by a cytosine or other three bases to join together to form a complementary base with the guanine.
Where Cytidine is a structural and functional unit of ribonucleic acid which consists of cytosine and the sugar ribose.

Cytidine triphosphate an ester of cytidine and also with a triphosphoric is considered as an important substance that is utilized by the cells to introduce the cytidylic acid and further converts them into ribonucleic acids.
Cytidine triphosphate also reacts with nitrogen-which contains alcohols to form coenzymes which participate in the forming the phospholipids.
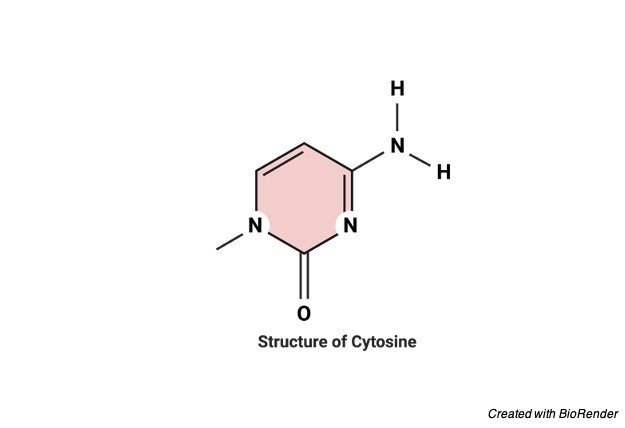
Chemical Nature of Cytosine
Cytosine is usually found as a part of DNA. Or of RNA. As a nucleotide in the form of cytidine triphosphate which acts as a co-factor of an enzyme and helps in transferring a phosphate to convert into adenosine triphosphate which is commonly referred to as ATP.
In DNA and RNA cytosine is paired up with guanine. However, in some cases if it is inherently unstable it changes its pairing to uracil which many leads to many disorders due to point mutation.
If it is not paired by DNA repair enzymes such as uracil glycosylase, it results in cleavage of uracil in DNA.
Cytosine is methylated and converted into 5-methylocytosine with the help of an enzyme DNA methyl transferase. And in some cases, cytosine is methylated and further hydroxylated to form 5-hydroxymethylcytosine.
Thus, cytosine is determined by the rate of deamination of cytosine and 5-methylcytosine which forms the basis of bisulphite sequencing.
Biological Function of Cytosine
When this cytosine is present in the third on the codon of RNA, Cytosine is present on the opposite side of uracil, since it is interchangeable with the third base.
If it is present in the second base of a codon. It is also interchangeable in the third codon which forms the serine groups like UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG.
Active deamination of the enzymes of cytosine or 5-methylcytosine in the family of APOBEC, of cytosine deaminase could have both beneficial and detrimental implication in various cellular processes as well as in the organismal evolution.
The implications that are present in the deamination of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine remains complicated.
Properties of Cytosine
Cytosine is considered as one of the important pyrimidine nucleobases with a chemical formula of C4H5N3O.
Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic aromatic compound and it is organic and forms single ring with the alternative carbon and nitrogen atoms. It has a molar mass of 111.10 gram per mole and a melting point of 320 to 325 ºC.
It can also be found as an important component in nucleoside base pairs and in forming nucleotides along with nucleoside and phosphate sugars.
Whereas in DNA and RNA cytosine matches with guanine which forms three hydrogen bonds while pairing.
Though cytosine is considered as relatively unstable it can be converted into uracil through the process of spontaneous deamination. This change can be correctly deamination.
This alteration in the nucleoside pair can be corrected by the process of DNA pair systems which uses the enzyme uracil glycosylase if this repair process is not being followed which results in point mutation.
Cytosine Citations
Share
Similar Post:
-

Thymine: Structure, Definition, and Functions
Continue ReadingDNA and Thymine
Generally, all complex substances are made up of smaller building blocks, considering an example where our house is built with bricks, stones, woods, etc. and as the same; our body is made up of cells which form the basic unit of live.
Likewise, DNA is also made up of smaller molecules which together functions as the important substance to live in.
We know that DNA is a complex molecule made up many substances like phosphoric acid, sugar (5-carbon) and nucleobases.

There are five nitrogenous bases which serves as the most vital and important component in the functioning of the DNA.
The nuclear bases are mostly of adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine, and uracil in case of RNA. These bases are generally classified into two types namely purine and pyrimidine.
What is Thymine?
Thymine is one of the four bases which is needed for the DNA, to make it as one of the structural and functional unit. Whereas the other three bases such as adenine, guanine, and cytosine also play an important role.
Thymine is located in one strand and always pairs up with adenine which is present on its opposite strand.

These bases in a sequentially manner greatly helps in instructing and transferring the genetic information for the present generations and it is later carrying out to future generations.
Thymine is abbreviated and it is referred to as the nucleotide T.
It is also chemically known as 5-methyluracil. It was first isolated by Albrecht Kossel and Albert Neumann from the thymus gland in the year 1893.
Structure of Thymine
A ring-shaped pyrimidine molecule is generally considered as the chemical structure of thymine. Which is equally shared among each of the molecules.
At the time of formation of DNA, thymine always combines with thymine with the help of two hydrogen bonds.
These hydrogen bonds create a stabilizing nature for the structure of nucleic acid.

Following the same way guanine and cytosine pairs up with each other. While moving forward to each generation.
However, when these molecules are exposed to ultra violet and some other heavier radiation it causes mutations in the DNA which leads to several disorders. Where thymine dimer also occurs during this condition.
But thymine is not present in RNA, whereas there it is replaced by Uracil.
The chemical name of thymine is 5-methyluracil. Which implies that it has been derived from methylation of uracil in the 5th position of carbon, in that case methyl (-CH3) is added to the ring of pyrimidine so that the thymine is scientifically referred to as 5-Methyluracil.
Features of Thymine
Thymine usually has a pyrimidine nucleobase with a chemical formula C5H6N2O2. It belongs to the group of pyrimidine which is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound having a single ring, which combines with an alternating carbon and nitrogen atoms.
This ring is generally known as pyrimidine rings. It has its molar mass of 126.115 gram per mol and it has a melting point of 316 to 317ºC. It usually occurs as one of the compounds in nucleoside which is made up of nucleobase and a sugar component namely deoxyribose or ribose.
It may occur in nucleotide. Thymine is considered as of the primary nucleobases out of five nucleobases that are found in the nucleic acids. Where thymine and uracil are considered as complementary pairs with Adenine.
Thymine Phosphorylation
On combining thymine with deoxyribose, it results in the formation of nucleoside deoxythymidine and is commonly referred to as thymidine.
This thymidine often undergoes phosphorylation when phosphoryl acid groups are added to it, it forms monophosphate thymidine, diphosphate thymidine, triphosphate thymidine accordingly. With the number of phosphoric acid groups added to it.
Thymine Mutation and Cancer
When the chemical nature of thymine gets mutated it becomes defective in such cases the DNA becomes mutated and it leads to the formation of melanoma.
A common cause for mutation that occurs due to the defect in thymine is mostly due to ultra violet radiations because these light waves cause the thymine bases to form a dimer which are located on its adjunct sides.
This changes the nature of the structure of the DNA and it results in the formation of mutation by affecting the functions of DNA.
This alteration in the function of DNA may cause deregulation in the cell division and its functioning which has a high risk of developing cancers and other tumors.
The usual treatment for cancer is done by introducing fluorouracil which on incorporating into the DNA can inhibit the function of cancer cells and it also helps in the formation of healthy new DNA in the newly formed cells.
Biological Reactions of Thymine
Thymine is almost similar to that of other bases which are present in the DNA. It is formed in several steps. First step in the formation of thymine involves a formation of carbamoyl phosphate from a reaction of bicarbonate, glutamine, ATP and water molecule.
This process is being catalyzed by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Which helps in converting carbamoyl phosphate into carbonyl aspartate by again undergoing a catalytic activity with the enzyme aspartate transcarboxylase which is further converted into 5-phospho-α-D-ribosy-1-phosphorylate.
Whereas this phosphate orates to form an oratidine 5- monophosphate. Which is further decarboxylated by the enzyme OMP decarboxylase and helps in yielding uridine monophosphate (UMP).
At the same time Uridine diphosphate and uridine triphosphate are synthesized by the biosynthetic process with the help of kinase along with the dephosphorylation of ATP molecules.
To produce thymine, uridine is reduced to deoxy uridine with the help of an enzyme ribonucleic reductase which is further methylated by the enzyme thymidyl synthetase to produce thymine.
Function of Thymine
Thymine is considered as one of the important base pair in the primary nucleobases among five base pairs. This is considered as one of the base pair which helps in forming the fundamental genetic code of DNA.
Where as the nucleic acids like DNA and RNA which have their own genetic functions, which helps in coding the particular sequence of proteins that are very much important for the functioning of the body.
Where as these nucleic acids like thymine plays a great role in maintaining the hereditary of the organism which helps in function of the cell and its metabolic activities.
Thymine Citations
Share
Similar Post:
-

Peroxisomes: Function, Definition, Structure, and Formation
Continue ReadingWhat are Peroxisomes?
Peroxisomes initially were characterized as organelles that complete oxidation responses prompting the creation of hydrogen peroxide.
Peroxisomes are little, layer encased organelles that contain enzymes associated with an assortment of metabolic responses, including a few parts of energy digestion.
These miniature bodies are little single unit film bound vesicles of o.2-o.8 µm in distance across.
Since peroxisomes co-silt with lysosome in thickness inclination centrifugation, they are morphologically like lysosomes, nonetheless, they are gathered like mitochondria and chloroplasts, from protein that are incorporated on free ribosomes and afterward brought into peroxisomes as finished polypeptide chains.
Their reality as a different intracellular organelle turned out to be for the most part perceived uniquely in 1960s by De Duve et.al. Beaufaytt and Berther gave the name peroxisome to it.
Function of Peroxisomes
Their principal work is combination and capacity of fats and oils. They contain something like 50 distinct enzymes, which are engaged with an assortment of biochemical pathways in various sorts of cells.
They complete oxidation responses prompting the combination of hydrogen peroxide and in light of the fact that it is unsafe to the cell, peroxisomes additionally contain the enzyme catalase, which deteriorates hydrogen peroxide either by changing it over to water or by utilizing it to oxidize another natural compound.
An assortment of substrates are separated by such oxidative responses in peroxisomes, including uric corrosive, amino acids, and unsaturated fats. The oxidation of unsaturated fats is an especially significant model since it gives a significant wellspring of metabolic energy.
In creature cells, unsaturated fats are oxidized in both peroxisomes and mitochondria, however in yeasts and plants unsaturated fat oxidation is confined to peroxisomes.
As well as giving a compartment to oxidation responses, peroxisomes are engaged with lipid biosynthesis. In creature cells, cholesterol and dolichol are integrated in peroxisomes just as in the ER. In the liver, peroxisomes are additionally associated with the amalgamation of bile acids, which are gotten from cholesterol.
What’s more, peroxisomes contain enzymes needed for the union of plasmalogens—a group of phospholipids wherein one of the hydrocarbon ties is joined to glycerol by an ether bond as opposed to an ester bond.
Plasmalogens are significant film segments in certain tissues, especially heart and mind, despite the fact that they are missing in others.
Peroxisomes assume two especially significant parts in plants. To start with, peroxisomes in seeds are liable for the change of put away unsaturated fats to sugars, which is basic to giving energy and crude materials to development of the growing plant.
This happens through a progression of responses named the glyoxylate cycle, which is a variation of the citrus extract cycle. The peroxisomes in which this happens are now and then called glyoxysomes.
Second, peroxisomes in leaves are associated with photorespiration, which serves to use a side item shaped during photosynthesis. CO2 is changed over to starches during photosynthesis through a progression of responses called the Calvin cycle.
Peroxisome gathering: Proteins bound for peroxisomes are deciphered on free cytosolic ribosomes and afterward shipped into peroxisomes as finished polypeptide chains.
Phospholipids are likewise imported to peroxisomes, by means of phospholipid move proteins, from their significant site of union in the ER.
The import of proteins and phospholipids results in peroxisome development, and new peroxisomes are then framed by division of old ones.
It is a solitary layer bound vesicle with a breadth of about 0.5 mm having a gathered wellspring of something like three oxidative enzymes in liver cells: D-amino corrosive oxidize, urate oxidize and catalase.
Types of peroxisomes
Sphaerosomes: Sphaerosomes were recently considered as lysosomes of plant cell as they contain enzymes a large portion of which are indistinguishable from those of lysosomes.
In any case, presently it is realized that sphaerosomes contain some extra enzymes. These miniature bodies are little single unit film bound vesicles of o.2-o.8^m in measurement. Their primary capacity is combination and capacity of fats and oils.
Lomasomes: Lomasomes are little vesicles present between the cell divider and plasma film in plant cells. They are related with the union of cell divider materials.
Metabolic Activities of Peroxisomes
Disengaged peroxisomes are porous to little molecules like sucrose. During the separation cycle, they regularly lose proteins that are ordinarily bound to the peroxisomal lattice.
In every living cell, peroxisomes are the fixed vesicles encircled by a solitary layer.
Little peroxisome or microperoxisomes with a measurement of about 0.15 – 0.25 µm are omnipresent in mammalian cells.
Photosynthetic plant cells may have around 70 – 100 peroxisomes where it performs photorespiration being related with chloroplasts and mitochondria.
Like mitochondria peroxisome is a significant site of oxygen use. Indeed, peroxisomes are believed to be the remnant of some antiquated organelle engaged with completing all sort of the oxygen digestion.
Later on Mitochondria developed with a component of coupling oxygen digestion with ATP blend. The oxidative responses completed by peroxisomes are as yet valuable to cell in spite of the presence of the mitochondria.
It is felt that specific vital layer proteins exceptional to the peroxisomes are orchestrated in the ER film to from a pre-organelle. This pre-organelle then, at that point shapes a bud from the area of smooth ER.
A few significant peroxisomal enzymes including catalase and urate oxidize are incorporated in the cytosol and shipped into peroxisome as it is framing.
The vast majority of the develop peroxisomes stay connected to smooth ER by a slim sleeve like projection. Oxidative enzymes contained in peroxisomes eliminate hydrogen particles from explicit substrates utilizing atomic oxygen and shaping hydrogen peroxide.
Hydrogen peroxide is poisonous and is along these lines separated to water and atomic oxygen by the catalase enzyme present in peroxisomes.
Importance of Peroxisome
The fundamental capacity of peroxisome is the lipid digestion and the handling of responsive oxygen species.
Other peroxisome capacities include:
• They partake in different oxidative cycles.
• They partake in lipid digestion and catabolism of D-amino acids, polyamines and bile acids.
• The responsive oxygen species, for example, peroxides delivered in the process is changed over to water by different enzymes like peroxidase and catalase.
• In plants, peroxisomes work with photosynthesis and seed germination. They forestall loss of energy during photosynthesis carbon obsession.
Some Uncommon Feature of Peroxisome
1. In photorespiration in C3 plants where glycolate from chloroplasts enter peroxisome get oxidized with sub-atomic 02 to frame glyoxylate. Hydrogen peroxide is the result, which is parted by catalase. Glyoxlate is then changed over to amino corrosive glycine that gathers to frame serine and C02.
2. Long chain and extended unsaturated fats are separated in peroxisome.
3. An uncommon sort of peroxisomes called glyoxysomes is found in plant tissues like growing seeds. Here it serves to change over the unsaturated fats put away in the seed into sugars required for the youthful plants.
This is refined through a progression of responses called glyoxylate cycle.
Two molecules of acetyl COA delivered by unsaturated fat breakdown in peroxisome, are utilized to make succinic corrosive which is changed over to glucose.
4. In creature cells peroxisome detoxify various substances like phenols, methanol, ethanol and so forth. The liquor devoured by an individual is incompletely detoxified in the liver cell peroxisomes.
Peroxisome Citations
- Peroxisome: Metabolic Functions and Biogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol . 2020;1299:3-17.
- Peroxisome biogenesis and human peroxisome-deficiency disorders. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci . 2016;92(10):463-477.
- Human disorders of peroxisome metabolism and biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta . 2016 May;1863(5):922-33.
- The peroxisome: an update on mysteries 2.0. Histochem Cell Biol . 2018 Nov;150(5):443-471.
- The Peroxisome-Mitochondria Connection: How and Why? Int J Mol Sci . 2017 May 24;18(6):1126.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Ribosomes: Function, Definition, Structure, and Formation
Continue ReadingWhat are Ribosomes?
A ribosome is a complex structure found inside the living cells that produce proteins from amino acids during the interaction called protein union or interpretation.
The interaction of protein amalgamation is an essential capacity, which is performed by all living cells.
Ribosomes are specific cell organelles and found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Each living cell requires ribosomes for the creation of proteins. This cell organelle additionally works by restricting to a courier ribonucleic corrosive (mRNA) and interpreting the data conveyed by the nucleotide arrangement of the mRNA.
The exchange RNAs (tRNAs) involving amino acids, go into the ribosome at the acceptor site. When it gets tie up, it adds amino acid to the developing protein chain on tRNA.
Features of Ribosomes
A ribosome is a complex of RNA and protein and is, in this manner, known as a ribonucleoprotein.
It is made out of two subunits – more modest and bigger. The more modest subunit, where the mRNA ties and is decoded and in the bigger subunit, the amino acids get added. Both of the subunits contain both protein and ribonucleic corrosive parts.
The two subunits are joined to one another by associations between the rRNAs in one subunit and proteins in the other subunit.
Ribosomes are situated inside the cytosol found in the plant cell and creature cell. The ribosome structure incorporates the accompanying: It is situated in two spaces of cytoplasm. Dissipated in the cytoplasm.
Around 62% of ribosomes are included RNA, while the rest is proteins. The construction of free and bound ribosomes is comparative and is related with protein combination.
Ribosomes Function
It gathers amino acids to shape proteins that are fundamental for complete cellular capacities. The DNA produces mRNA by the cycle of DNA record. The mRNA is combined in the core and moved to the cytoplasm for the interaction of protein union.
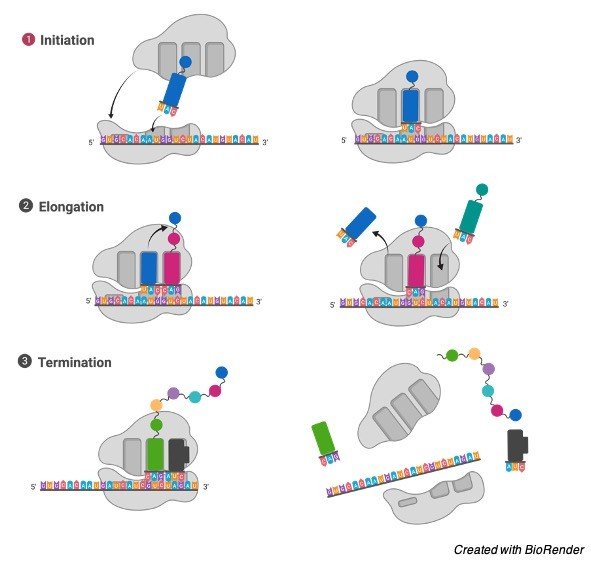
Ribosomes during protein synthesis
The ribosomal subunits in the cytoplasm are bound around mRNA polymers. The tRNA then, at that point combines proteins. The proteins blended in the cytoplasm are used in the actual cytoplasm, the proteins orchestrated by bound ribosomes are moved external the cell.
Structure of Ribosome
• Ribosomes are non-layer bound cell organelles made of RNA and proteins.
• Ribosomes are mind boggling atomic machine that make proteins from amino acids in the measure called protein union or interpretation.
• Every cell needs ribosomes to produce proteins. Ribosomes are found in both prokaryotic also, eukaryotic cells.
• Ribosomal construction and capacity are strikingly comparative in all organic entities and organelles.
• In eukaryotic life forms, ribosomes are found in cytoplasm, mitochondria, and chloroplast.
• The cytoplasmic ribosomes are discovered free in the cytoplasm and appended to the endoplasmic reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum related with ribosomes are called rough endoplasmic reticulum.
• The ribosome found in mitochondria and chloroplast are fundamentally like the prokaryotic ribosomes.
• All prokaryotic ribosomes are discovered free in the cytoplasm of the cell.
• Each E. coli cell contains at least 15,000 ribosomes, which involve almost a quarter of the dry load of the cell. Mammalian cells contain around 10 million ribosomes.
• The ribosomes are made of two subunits, the enormous and the little subunit which involves ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins.
• In prokaryotes, ribosomes are made up from three distinct rRNA molecules, while in eukaryotes ribosomes are made up from four unique rRNA molecules.
• rRNA furnishes the ribosome with its essential structure and capacity and proteins in ribosomes help fill in primary holes and upgrade the amalgamation of proteins.
• The mass units of ribosomes are their Svedberg (S) values, which depend on how quickly the subunits settle to the lower part of test tubes under the centripetal power of a rotator.
• The ribosomes of eukaryotic cells typically have Svedberg upsides of 80S and prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes.
Prokaryotic Ribosome Assembly
Prokaryotes contain 70S ribosomes whilst eukaryotes contain 80S ribosomes. In any case, the construction what’s more, capacity of ribosomes is comparative in the two prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Bacterial ribosomes contain about 65% rRNA and 35% proteins. The measurement of ribosomes is around 18 nm and are made out of two inconsistent subunits with sedimentation coefficients of 30S and 50S and a joined sedimentation coefficient of 70S.
In the last part of the 1960s Masayasu Nomura and partners showed that both ribosomal subunits can be separated into their RNA and protein parts, then, at that point reconstituted in vitro.
The rRNA and proteins precipitously reassemble to frame 30S or 50S subunits almost indistinguishable in construction and action to local subunits.
The primary high-goal designs of bacterial ribosomal subunits were clarified by Thomas Steitz, Ada Yonath, Venki Ramakrishnan, Harry Noller and others. They clarified that the ribosomal subunits are tremendous RNA molecules and the customary spotlight on the protein segments of ribosomes was moved.
In the 50S subunit, the 5S and 23S rRNAs structure the primary center. The proteins are auxiliary components in the complex, finishing the surface.
There is no protein inside 18 Å of the dynamic site for peptide bond development. The high goal structure affirms, the ribosome is a ribozyme notwithstanding the knowledge that the itemized designs of the ribosome and its subunits give into the component of protein amalgamation, they have invigorated another glance at the advancement of life.
The bacterial ribosome is unpredictable, with a consolidated atomic load of approx. 2.7 million.
The two sporadically molded ribosomal subunits fit together to shape a separated through which the mRNA passes as the ribosome moves along it during interpretation.
The 57 proteins in bacterial ribosomes change massively in size and construction. Atomic loads range from around 6,000 to 75,000.
Most of the proteins have globular spaces organized on the ribosome surface. Some additionally have snakelike expansions that jut into the rRNA center of the ribosome, settling its structure.
Eukaryotic Ribosome Assembly
The ribosomes of eukaryotic cells (other than mitochondrial and chloroplast ribosomes) are bigger and more unpredictable than bacterial ribosomes, with a width of around 23 nm and a sedimentation coefficient of about 80S.
They additionally have two subunits, which fluctuate in size among species however on normal are 60S and 40S. Eukaryotic ribosomes contain in excess of 80 unique proteins.
The ribosomes of mitochondria and chloroplasts are to some degree more modest and more straightforward than bacterial ribosomes.
Ribosomes Citations
- Nascent ribosomes. Cell . 2001 Oct 19;107(2):133-6.
- The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Ribosomes: From Injury to Regulation. Cells . 2019 Nov 2;8(11):1379.
- One core, two shells: bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes. Nat Struct Mol Biol . 2012 Jun 5;19(6):560-7.
- Functions of ribosomal proteins in assembly of eukaryotic ribosomes in vivo. Annu Rev Biochem . 2015;84:93-129.
- Does functional specialization of ribosomes really exist? RNA . 2019 May;25(5):521-538.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Golgi Apparatus: Function, Definition, Structure, and Formation
Continue ReadingWhat are Golgi Apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus (GA), additionally called Golgi body or complex is seen generally in both plant and creature cells.
It is regularly involved a progression of five to eight cup-molded, film covered sacs called cisternae that look something like a pile of emptied inflatables.
In some unicellular lashes, in any case, upwards of 60 cisternae may join to make up the Golgi apparatus.
Essentially, the quantity of Golgi bodies in a cell fluctuates as per its capacity. Creature cells for the most part contain somewhere in the range of ten and twenty Golgi stacks for every cell, which are connected into a solitary complex by rounded associations between cisternae.
This complex is typically found near the cell nucleus.It is alluded to as the assembling and the delivery focus of the cell.
Golgi is engaged with the bundling of the protein atoms before they are shipped off their objective. These organelles help in preparing and bundling the macromolecules like proteins and lipids that are orchestrated by the cell and consequently go about as the ‘mailing station’ of the cell.
Golgi apparatus was found in the year 1898 by an Italian scientist Camillo Golgi.
Structure of Golgi Apparatus
Under the electron magnifying instrument, the Golgi apparatus apparently is made out of heaps of smoothed constructions that contain various vesicles containing secretory granules.
The Golgi apparatus is morphologically basically the same in both plant and creature cells.
Notwithstanding, it is amazingly pleomorphic: in some cell types it seems reduced and restricted, in others spread out and reticular (net-like).
Commonly, be that as it may, Golgi apparatus shows up as an unpredictable exhibit of interconnecting tubules, vesicles, and cisternae.
A. Golgi Apparatus: Cisternae
It is the easiest unit of the Golgi apparatus is the cisterna. Cisternae (around 1 μm in measurement) are focal, straightened, plate-like or saucer-like shut compartments that are held in equal packages or stacks one over the other.
In each stack, cisternae are isolated by a space of 20 to 30 nm which may contain pole like components or strands.
Each heap of cisternae structures a dictyosome which may contain 5 to 6 Golgi cisternae in creature cells or at least 20 cisternae in plant cells.
Every cisterna is limited by a smooth unit film (7.5 nm thick), having a lumen shifting in width from around 500 to 1000 nm.
The edges of every cisterna are tenderly bended so the whole dictyosome of the Golgi apparatus takes on a bow-like appearance.
The cisternae at the raised finish of the dictyosome include proximal, framing or cis-face and cisternae at the curved finish of the dictyosome involve the distal, developing or trans-face.
B. Golgi Apparatus: Tubules
An unpredictable exhibit of related vesicles and anastomosing tubules (30 to 50 nm width) encompass the dictyosome and emanate from it. Indeed, the fringe space of the dictyosome is fenestrated (trim like) in structure.
C. Golgi Apparatus: Vesicles
The vesicles (60 nm in breadth) are of three sorts:
(I) Transitional vesicles are little film restricted vesicles which are thought to shape as blebs from the temporary ER to move and unite to cis face of Golgi, where they blend to frame new cisternae.
(ii) Secretory vesicles are shifted estimated layer restricted vesicles that release from edges of cisternae of Golgi. They, frequently, happen between the developing essence of Golgi and the plasma film.
(iii) Clathrin-covered vesicles are round projections, around 50 μm in width and with a harsh surface. They are found at the outskirts of the organelle, for the most part at the finishes of single tubules, and are morphologically very particular from the secretory vesicles.
The clathrin-covered vesicles are known to assume a part in intracellular rush hour gridlock of layers and of secretory items, i.e., among ER and Golgi, just as, between the GELR locale and the endosomal and lysosomal compartments.
Function of Golgi Apparatus
1. Golgi vesicles are regularly, alluded to as the “traffic police” of the cell. They assume a critical part in arranging a considerable lot of the cell’s proteins and layer constituents, and in guiding them to their legitimate objections.
To play out this capacity, the Golgi vesicles contain various arrangements of catalysts in various sorts of vesicles—cis, center and trans cisternae—that respond with and change secretory proteins going through the Golgi lumen or film proteins and glycoproteins that are momentarily in the Golgi layers as they are in transit to their last objections.
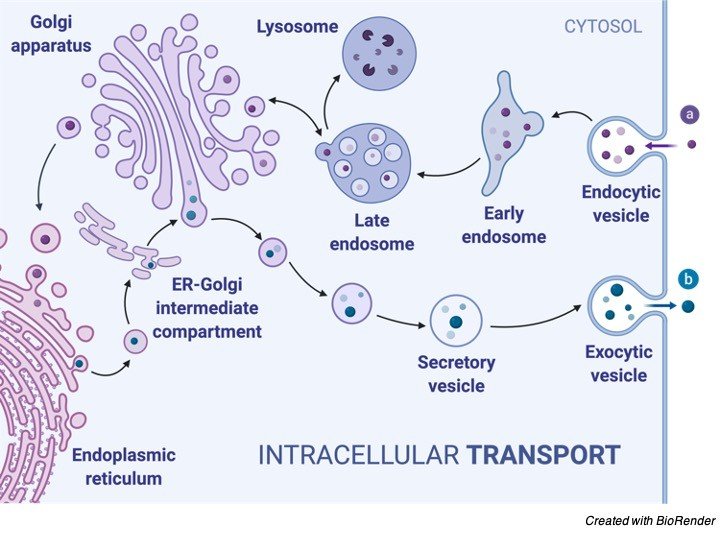
The Golgi apparatus subsequently goes about as the get together plant of the cell where the crude materials are coordinated to the Golgi apparatus prior to being dropped from the cell.
2. In creatures, the Golgi apparatus is associated with the bundling and exocytosis of the accompanying materials : Zymogen of exocrine pancreatic cells; Bodily fluid (=a glycoprotein) emission by cup cells of the digestive system ; Lactoprotein (casein) discharge by mammary organ cells (Merocrine emission) ; Discharge of mixtures (thyroglobulins) of thyroxine chemical by thyroid cells; Discharge of tropocollagen and collagen ; Development of melanin granules and different colors; and Development of yolk and vitelline layer of developing essential oocytes.
3. It is likewise associated with the development of certain cellular organelles like plasma layer, lysosomes, acrosome of spermatozoa and cortical granules of an assortment of oocytes.
4. They are likewise engaged with the vehicle of lipid particles around the cell.
5. The Golgi complex likewise assumes a significant part in the creation of proteoglycans. The proteoglycans are atoms that are available in the extracellular lattice of the creature cells.
6. It is likewise a significant site of combination of starches. These carbohydratres incorporate the union of glycosaminoglycans, Golgi connects to these polysaccharides which then, at that point appends to a protein created in the endoplasmic reticulum to shape proteoglycans.
7. The Golgi includes in the sulfation cycle of specific atoms.
8. The interaction of phosphorylation of atoms by the Golgi requires the import of ATP into the lumen of the Golgi.
9. In plants, Golgi apparatus is primarily engaged with the discharge of materials of essential and optional cell dividers (e.g., development and fare of glycoproteins, lipids, gelatins and monomers for hemicellulose, cellulose, lignin, and so on).
Golgi Apparatus Citations
- Specific organization of Golgi apparatus in plant cells. Biochemistry (Mosc) . 2014 Sep;79(9):894-906.
- Golgi apparatus analyzed by cryo-electron microscopy. Histochem Cell Biol . 2013 Oct;140(4):369-81.
- The yeast Golgi apparatus. Traffic . 2012 Apr;13(4):505-10.
- The Golgi apparatus. Curr Biol . 2000 Aug 24;10(16):R583-5.
- The Golgi apparatus: insights from filamentous fungi. Mycologia . May-Jun 2016;108(3):603-22.
- Mechanical model of Golgi apparatus. Phys Biol . 2019 Sep 5;16(6):066003.
Share
Similar Post:
-

Lysosome: Definition, Structure, Function, and Formation
Continue ReadingWhat are Lysosome?
A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle that possess digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are engaged with different cell processes.
They breakdown excess or destroyed cell parts. They might be utilized to destroy attacking viruses and microscopic organisms.

In the event that the cell is harmed beyond repair, they can digest these natural materials since they have solid stomach related enzymes that can separate natural mixtures.
Thereby helping cells to self-destruct and the interaction is known as programmed cell demise, or apoptosis.
In this manner, lysosome is otherwise called a suicide sac.
Features of Lysosome
Lysosomes contain a variety of enzymes fit for separating a wide range of biological polymers—proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Lysosomes work as the digestive system of the cell, serving both to debase material taken up from outside the cell and to process outdated parts of the actual cell.
In their most straightforward structure under electron microscope, lysosomes are imagined as thick round vacuoles, yet they can show impressive variety fit as a fiddle because of contrasts in the materials that have been taken up for processing.
Lysosomes accordingly address morphologically different organelles characterized by the common function of degrading intracellular material.
It initiate budding from the membrane of the trans-golgi organization, a locale of the Golgi complex responsible for structuring recently assimilated protiens, might be assigned for use in lysosomes, endosomes, or the plasma film.
Lysosome Acid Hydrolases
Lysosomes contain around 50 distinct degradative enzymes that can hydrolyze proteins, DNA, RNA, polysaccharides, and lipids.
Mutation in the genes that encrypt these enzymes are liable for in excess of 30 unique human hereditary sicknesses, which are called lysosomal storage diseases on the grounds that undegraded material gathers inside the lysosomes of affected individual.
The vast majority of these diseases result from insufficiencies in single lysosomal enzymes.
For instance, Gaucher’s illness (the most well-known of these problems) results from a mutation in the gene that encodes a lysosomal compound needed for the breakdown of glycolipids.
A fascinating exemption is I-cell disease, which is brought about by a lack in the protein that catalyzes the initial phase in the labeling of lysosomal enzymes with mannose-6-phosphate in the Golgi apparatus.
The outcome is a general failure of lysosomal enzymes to be consolidated into lysosomes.
The entirety of the lysosomal enzymes are acid hydrolases, which are dynamic at the acidic pH (around 5) that is kept up with inside lysosomes yet not at the nonpartisan pH (about 7.2) normal for the remainder of the cytoplasm.
The necessity of these lysosomal hydrolases for acidic pH gives twofold protection against uncontrolled processing of the substance of the cytosol; regardless of whether the lysosomal membrane was to break down, the delivered acid hydrolases would be idle at the unbiased pH of the cytosol.
To keep up with their acidic interior pH, lysosomes should effectively focus H+ particles (protons).
This is refined by a proton pump in the lysosomal membrane, which effectively transport protons into the lysosome from the cytosol.
This pumping requires use of energy as ATP hydrolysis, since it keeps up with roughly a hundredfold higher H+ concentration inside the lysosome.
Numerous researchers accept that lysosomes are absent in plant cells and their capacity of lysosomes in plants is performed by vacuole.
Endocytosis and Lysosome Formation
One of the significant elements of lysosomes is the digestion of material taken up from outside the cell by endocytosis.
Nonetheless, the part of lysosomes in the absorption of material taken up by endocytosis relates not exclusively the functional capacity of lysosomes but also to their formation.
Specifically, lysosomes are formed by the combination of transport vesicles matured from the trans Golgi network with endosomes, which contain molecules taken up by endocytosis at the plasma layer.
The arrangement of lysosomes hence addresses a crossing point between the secretory pathway, through which lysosomal proteins are handled, and the endocytic pathway, through which extracellular molecules are taken up at the cell surface.
Material from outside the cell is taken up in clathrin-covered endocytic vesicles, which bud from the plasma matrix and afterward intertwine with early endosomes.
Membrane components are then reused to the plasma layer and the early endosomes progressively develop into late endosomes, which are the antecedents to lysosomes.
One of the significant changes during endosome development is the bringing of the inner pH down to about 5.5, which assumes a vital part in the conveyance of lysosomal acid hydrolases from the trans Golgi organization.
Acid hydrolases are designated to lysosomes by mannose-6-phosphate deposits, which are perceived by mannose-6-phosphate receptors in the trans Golgi network and packaged into clathrin-covered vesicles. Following expulsion of the clathrin coat, these transport vesicles meld with late endosomes, and the acidic inner pH causes the hydrolases to separate from the mannose-6-phosphate receptor.
The hydrolases are hence delivered into the lumen of the endosome, while the receptors stay in the membrane and are at last reused to the Golgi.
Late endosomes then mature into lysosomes as they procure a full supplement of acid hydrolases, which digest the molecules initially taken up by endocytosis.
Phagocytosis, Autophagy, and Lysosome
Degrading molecules taken up by endocytosis, lysosomes digest material got from two different courses:
1. Phagocytosis
2. Autophagy
In phagocytosis, specific cells, like macrophages, take up and degrade huge particles, including microorganisms, cell trash, and matured cells that should be wiped out from the body.
Such enormous particles are taken up in phagocytic vacuoles (phagosomes), which then, at that point combine with lysosomes, bringing about digestion of their substance.

The lysosomes formed thusly (phagolysosomes) can be very enormous and heterogeneous, since their size and shape is determined by the substance of material that is being digested.
Lysosomes are additionally liable for autophagy, the progressive turnover of the cell’s own segments.
The initial step of autophagy seems, by all accounts, to be the enclosure of an organelle (e.g., a mitochondrion) in layer got from the ER.
The subsequent vesicle (an autophagosome) then joins with a lysosome, and its substance are digested.
Autophagy is liable for the slow turnover of cytoplasmic organelles.
Lysosome and Disease
Lysosomal storage diseases are hereditary issues in which a genetic mutation influences the activity of at least one of the acid hydrolases.
In such sicknesses, the normal metabolism of explicit macromolecules is obstructed and the macromolecules aggregate inside the lysosomes, causing extreme physiological harm or disfigurement.
Hurler syndrome, which includes a deformity in the metabolism of mucopolysaccharides, is a lysosomal storage disease.
Lysosome Citations
Share
Similar Post: