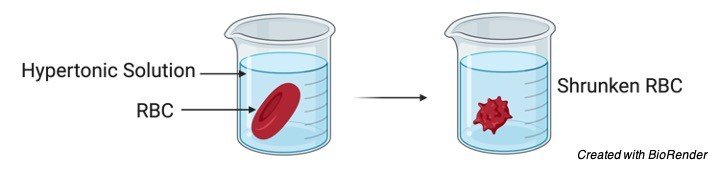
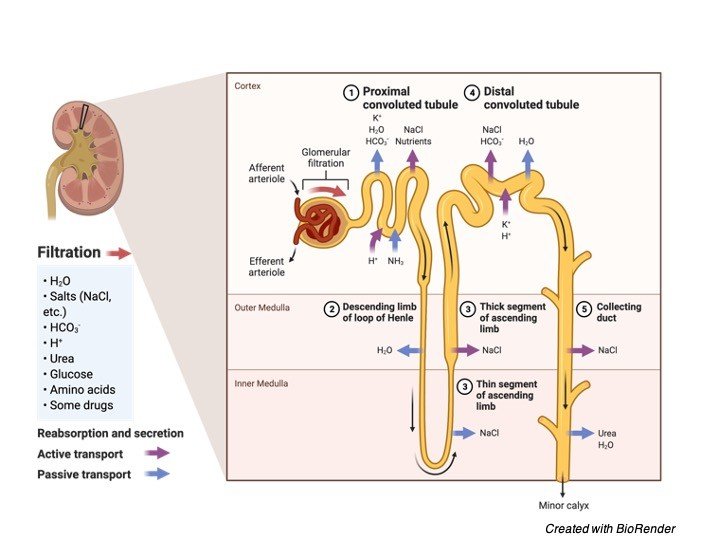
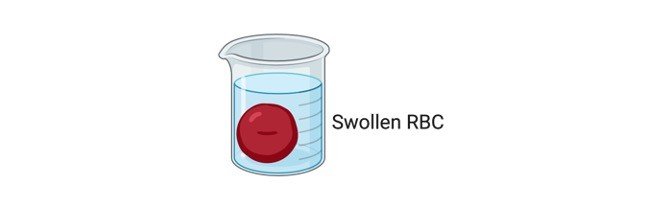
A. Animal Cells: If the concentration of water is higher outside on comparing inside of the cell, as a result in movement of water from outside into the cell and as a results cell gains water and swells.
On swelling the internal pressure of the cell increases and it leads to rupturing of a cell or hemolysis.
B. Plant Cells: In case of plant cells the cell swells by increasing its volume and pushes the cell against the cell wall and causes turgidity but not lysis because the cell wall protects it from becoming lysed and these cells also do not stay turbid for a longer period.
Animal cell don’t have the capacity to stay turbid as it lacks cell wall.
C. Protists: Tonicity is essential for regulating the life of almost every organisms. Considering the protists such as paramecia and amoebae which are able to retain their structure due to tonicity regulation though they do not have a cell wall or a cytoskeleton.
As these organisms live in a hypotonic environment where continuous water influx occurs which helps the cell to maintain a definite structure and prevent it from cell lysis.
These organisms contain contractile vacuoles which in the sense acts as a specialized organ to retain excess of water from the cell.
D. Mangroves and Marshy Areas: Considering the areas of mangroves and marshy, they have a high hypertonic environment due to high salt content.
A normal plant will not survive in such extreme conditions. However, those plants which exist in marshy areas or mangroves adapted themselves to create a hypertonic condition in their root cells.
As a result, hypotonic condition around the roots in their external environment helps these plants to absorb water from the surroundings.
E. Freshwater Fishes: Aquatic animals living in freshwater or near seawater adapt a condition to regulate osmoregulation.
Due to this condition, salt content in the water is critical for the aquatic life in any water body.
Sea turtles have adapted themselves to a hypertonic environment with the help of their salt glands.
Thus, these adaptations help the aquatic or freshwater or marine animals to survive in critical hypotonic conditions.
F. Humans: When human body loses excess sodium comparing to that of water loss it results in reduced serum osmolarity. Which is relatively known as hypotonic dehydration.
This condition results in influx of water from extracellular to intracellular space which leads to swelling of the cells.
Thus, the imbalance of sodium in the cells leads to many neurological effects such as nausea or vomiting, confusion, edema etc.
Sometimes in most extreme cases it may also lead to unconsciousness, coma or death.
Considering all these cases it is important to understand that hypotonic dehydration which leads to cell swelling and edema are all due to excessive water retention.
This condition occurs if there is an excessive loss of fluid due vomiting, diarrhea or through burns and wounds.
Sometimes it is also due to Addison’s disease, renal tubular acidosis or because of chronic use of diuretics or over use of intravenous hypotonic fluids or regular saline in patients or hypotonia.
The normal range of blood sodium level in our body ranges from 135-145mEq/ L.
Hypotonia is a condition where sodium in our body falls below 135mEq/L.
This condition results in various heart disease, kidney failure etc. Drinking too much of water and decreased intake of salts may lead to this condition.